Q1: Drift speed of electrons, when 1.5 A of current flows in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 5 mm2 is v. If the electron density of copper is 9 × 1028/m3 the value of v in mm/s is close to (Take charge of electron to be = 1.6 × 10–19 C)
(a) 3
(b) 0.2
(c) 2
(d) 0.02
Ans: (d) 0.02
Solution:
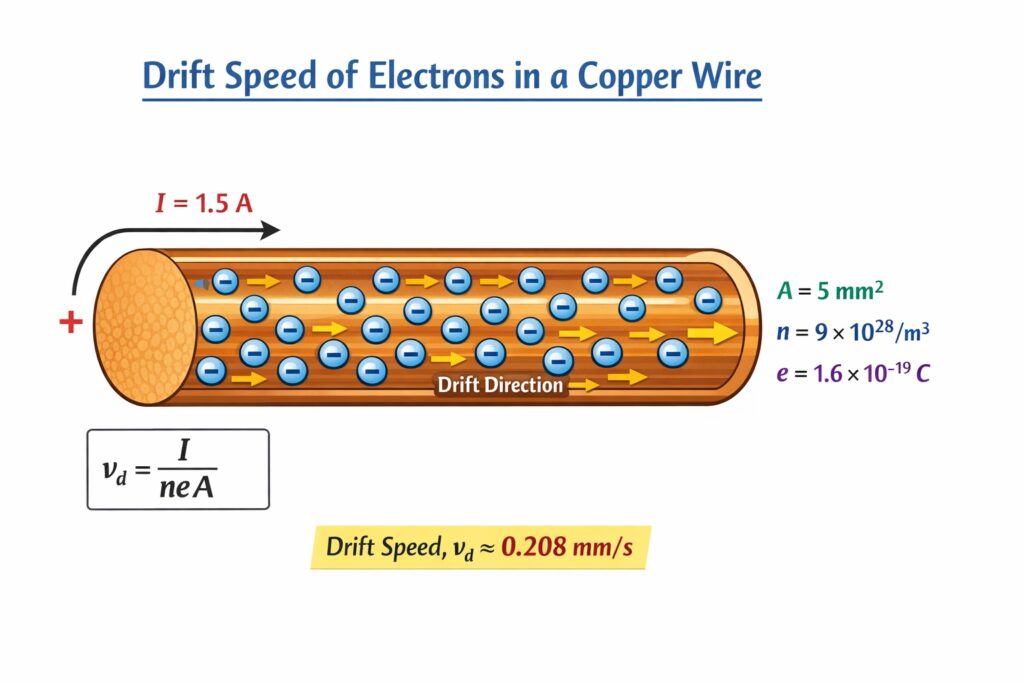
Step 1: Formula for drift speed
The current in a conductor is given by:
\( I = n e v_d A \)
where:
I = current
n = number density of electrons
e = charge of electron
v_d = drift speed
A = cross-sectional area
Rearranging for drift speed:
\( v_d = \frac{I}{n e A} \)
Step 2: Convert units to SI system
Given:
I = 1.5 A
A = 5 mm² = 5 × 10⁻⁶ m²
n = 9 × 10²⁸ m⁻³
e = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
Step 3: Substitute values
\( v_d = \frac{1.5}{(9 \times 10^{28}) \times (1.6 \times 10^{-19}) \times (5 \times 10^{-6})} \)
First calculate denominator:
\( 9 \times 10^{28} \times 1.6 \times 10^{-19} = 1.44 \times 10^{10} \)
\( 1.44 \times 10^{10} \times 5 \times 10^{-6} = 7.2 \times 10^{4} \)
So:
\( v_d = \frac{1.5}{7.2 \times 10^{4}} = 2.083 \times 10^{-5} \, \mathrm{m/s} \)
Step 4: Convert to mm/s
\( 1 \, \mathrm{m/s} = 1000 \, \mathrm{mm/s} \)
\( v_d = 2.083 \times 10^{-5} \times 1000 = 0.02083 \, \mathrm{mm/s} \approx 0.021 \, \mathrm{mm/s} \)
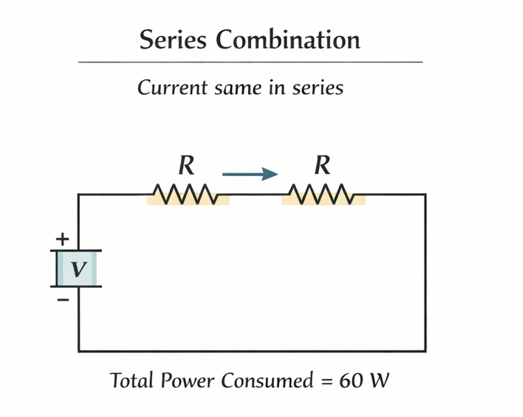
Q2. Two equal resistances when connected in series to a battery consume electric power of 60 W. If these resistances are now connected in parallel combination to the same battery, the electric power consumed will be
Solution: Let each resistance = R
Battery voltage = V (remains constant)
Equivalent resistance = R + R = 2R
Power consumed =
\( P_s = \frac{V^2}{2R} = 60 \, \mathrm{W} \)
Equivalent resistance =
\( R_\parallel = \frac{R}{2} \)
Power consumed =
\( P_p = \frac{V^2}{R/2} = \frac{2V^2}{R} \)
\( \frac{V^2}{2R} = 60 \)
\( \Rightarrow \frac{V^2}{R} = 120 \)
\( P_p = 2 \times 120 = 240 \, \mathrm{W} \)
For two equal resistances, changing from series to parallel (same battery):
Equivalent resistance becomes 1/4th
Power ∝ 1/R_eq → Power becomes 4 times
60 W × 4 = 240 W
Q3: A current of 2 mA was passed through an unknown resistor which dissipated a power of 4.4 W. Dissipated power when an ideal power supply of 11 V is connected across it is
(a) 11 × 10–4 W
(b) 11 × 10–5 W
(c) 11 × 105 W
(d) 11 × 10–3 W
Ans: (b) 11 × 10–5 W
Solution: Current I = 2 mA = 0.002 A
Power dissipated P = 4.4 W
We know,
P = I²R
⇒ R = P / I²
= 4.4 / (0.002)²
= 4.4 / 0.000004
= 1,100,000 Ω (or 1.1 MΩ)
When 11 V is connected across the same resistor:
New power = V² / R
= (11)² / 1,100,000
= 121 / 1,100,000
= 0.00011 W
= 1.1 × 10–4 W
= 11 × 10–5 W