The Keynesian theory, developed by British economist John Maynard Keynes, revolutionized modern economics during the Great Depression of the 1930s. His groundbreaking ideas were published in his influential book, “The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money” (1936). Keynes challenged the classical view that markets are always self-correcting and instead argued that active government intervention is essential to maintain economic stability and full employment.
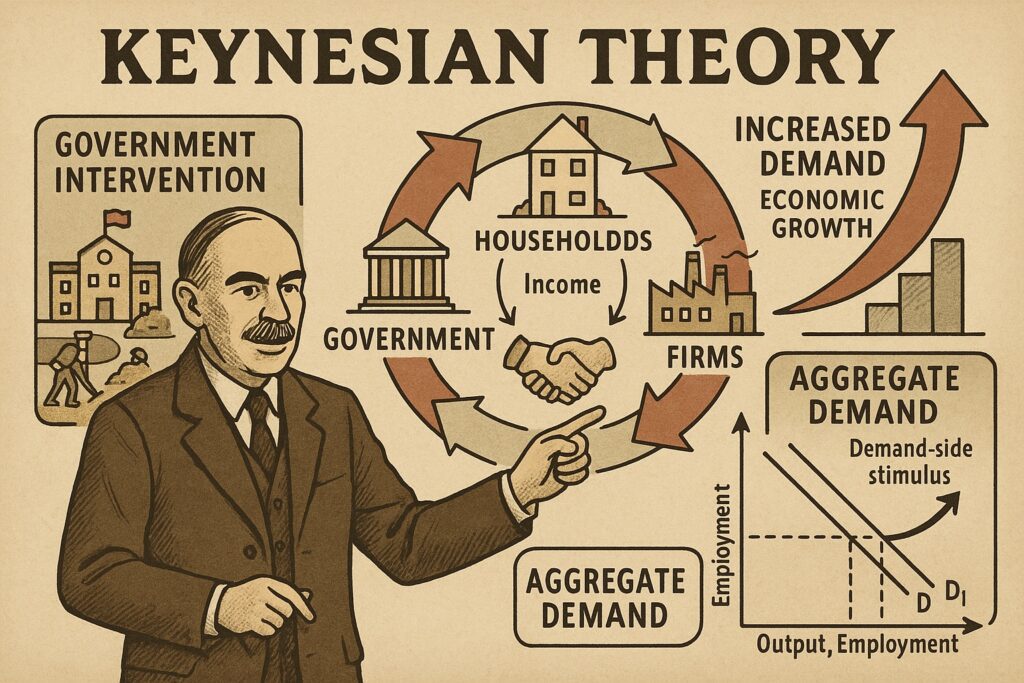
Table of Contents
What is Keynesian Theory?
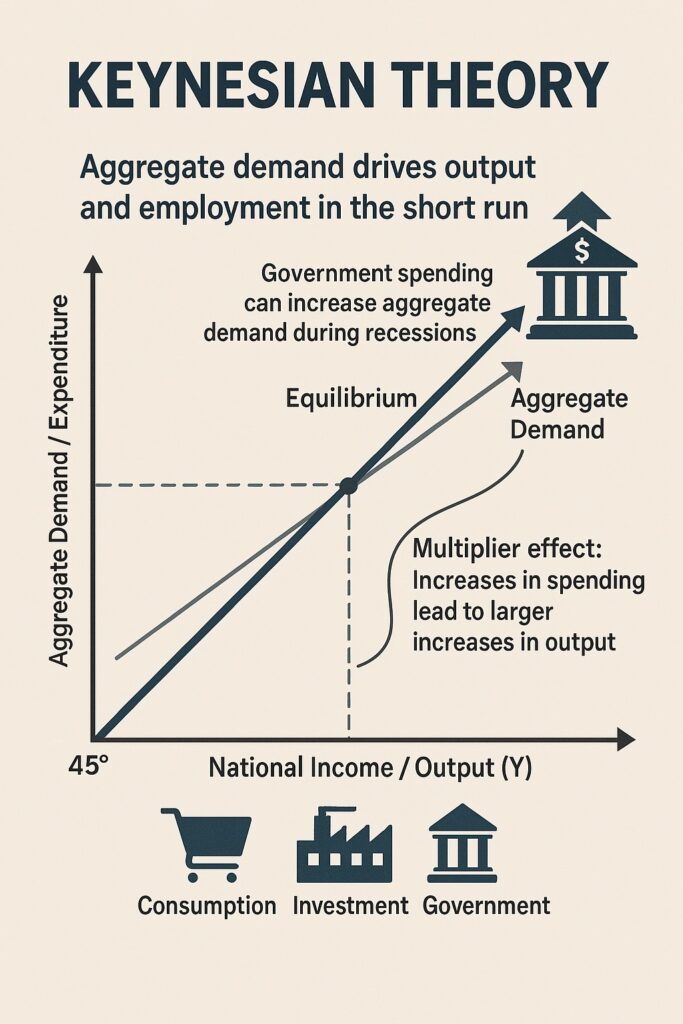
Keynesian theory is an economic theory that emphasizes the total spending in the economy (aggregate demand) and its effects on output and inflation. According to Keynes, fluctuations in demand—not supply—are the primary cause of economic downturns like recessions or depressions.
Core Concepts of Keynesian Theory
- Aggregate Demand (AD): Total spending by households, businesses, and the government in an economy.
- Government Intervention: Keynes believed the government should use fiscal policy (changes in government spending and taxation) to boost demand during downturns.
- Multiplier Effect: An increase in spending (especially by the government) leads to an even greater increase in national income.
- Underemployment Equilibrium: The economy can settle at an equilibrium where resources are not fully used, especially labor.
- Liquidity Preference Theory: Explains how interest rates are determined by the supply and demand for money.
- Consumption Function: People consume more as their income rises, but not all income is spent; some is saved.
Key Tools in Keynesian Policy
- Fiscal Policy:
- Expansionary Policy (during a recession): Increase government spending, cut taxes.
- Contractionary Policy (during inflation): Reduce spending, increase taxes.
- Public Investment: Government should invest in infrastructure, education, and healthcare to stimulate the economy.
- Deficit Spending: Borrowing by the government is acceptable during downturns to support demand and reduce unemployment.
Importance of Keynesian Theory
- Changed how governments and economists approached economic crises.
- Laid the foundation for modern macroeconomics.
- Influenced post-WWII policies that led to decades of economic growth and low unemployment.
- Justified large-scale public spending during recessions (e.g., U.S. New Deal programs, COVID-19 stimulus packages).
Criticisms of Keynesian Theory
- Too much government intervention may lead to budget deficits and national debt.
- Critics argue it may cause inflation in the long run.
- Supply-side economists believe that lowering taxes and reducing regulation is more effective than government spending.
- Assumes that all spending is equally productive, which may not always be true.
Conclusion
Keynesian economics marked a turning point in economic thinking. By emphasizing the importance of aggregate demand and supporting government action during economic downturns, Keynesian theory offered practical tools to combat unemployment and promote growth. Though it has evolved and faced criticism over the decades, Keynesian principles still play a central role in economic policymaking around the world.
Read: Economy Notes