Table of Contents
What causes the Kuroshio Current?
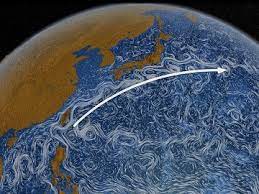
The Current is primarily driven by the combination of the North Equatorial Current, the South China Sea Current, and the Kuroshio Extension. The North Equatorial Current originates in the western Pacific and flows towards the west, while the South China Sea Current flows from the South China Sea towards the northeast. These two currents merge near the coast of Taiwan, forming the Kuroshio Current. The Kuroshio Extension, on the other hand, is an extension of the Kuroshio Current that flows towards the east of Japan.
Impact of the Kuroshio Current
The Current plays an important role in the climate of the Pacific region. It transports warm water from the tropics to the north, contributing to the mild climate of Japan and the Korean Peninsula. The warm waters of the Kuroshio Current also provide a suitable habitat for a diverse range of marine species, including tuna, whales, and sea turtles.
However, the Current can also have a destructive impact. When it encounters cold water from the north, it can cause heavy rainfall, floods, and landslides in Japan. In addition, the Kuroshio Current can transport debris and pollutants across the ocean, affecting the marine ecosystem in other regions.
Conclusion
The Current is a powerful and complex ocean current that has both positive and negative impacts on the Pacific region. While it provides warmth and sustenance to a diverse range of marine life, it can also cause severe weather conditions and transport pollutants. Understanding the dynamics of the Kuroshio Current is important for mitigating its negative impacts and preserving the health of the Pacific Ocean.
Summary
- The Current, also known as the Japan Current, is a strong ocean current that flows through the Pacific Ocean.
- It begins in the Philippines and flows northeastward along the eastern coast of Taiwan, Japan, and the Kamchatka Peninsula.
- The Current is primarily driven by the combination of the North Equatorial Current, the South China Sea Current, and the Kuroshio Extension.
- The current transports warm water from the tropics to the north, contributing to the mild climate of Japan and the Korean Peninsula.
- The Current is a suitable habitat for marine species such as tuna, whales, and sea turtles.
- It can cause heavy rainfall, floods, and landslides in Japan when it encounters cold water from the north.
- The Current can transport debris and pollutants across the ocean, affecting the marine ecosystem in other regions.
- Understanding the dynamics of the Current is important for mitigating its negative impacts and preserving the health of the Pacific Ocean.
MCQ
Q. What is another name for the Kuroshio Current?
a. Japan River
b. China Current
c. Taiwan Stream
d. Japan Current
Answer: d. Japan Current. The Kuroshio Current is also commonly referred to as the Japan Current.
Q. Where does the Kuroshio Current begin?
a. Indian Ocean
b. South China Sea
c. Philippines
d. Japan
Answer: c. Philippines. The Kuroshio Current begins in the Philippines and flows northeastward along the eastern coast of Taiwan, Japan, and the Kamchatka Peninsula.
Q. What is the speed of the Kuroshio Current?
a. Up to 1 meter per second
b. Up to 2 meters per second
c. Up to 3 meters per second
d. Up to 4 meters per second
Answer: d. Up to 4 meters per second. The Kuroshio Current is one of the strongest ocean currents in the world, with speeds that can reach up to 4 meters per second.
Q. What role does the Kuroshio Current play in the climate of the Pacific region?
a. It causes severe weather conditions
b. It transports cold water from the north to the tropics
c. It transports warm water from the tropics to the north
d. It has no impact on the climate of the Pacific region
Answer: c. It transports warm water from the tropics to the north. The warm waters of the Kuroshio Current contribute to the mild climate of Japan and the Korean Peninsula.
Q. What negative impact can the Kuroshio Current have?
a. Heavy rainfall and landslides in Japan
b. Droughts in the Pacific region
c. Harmful algal blooms in the Philippines
d. Increased fish population in the South China Sea
Answer: a. Heavy rainfall and landslides in Japan. When the Kuroshio Current encounters cold water from the north, it can cause heavy rainfall, floods, and landslides in Japan.
Important Links