The lapse rate is an important concept in atmospheric science and meteorology. It refers to the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude in the atmosphere. The lapse rate has significant implications for weather forecasting, aviation, and climate science. In this article, we will discuss the different types of lapse rates, their causes, and their importance in atmospheric science.
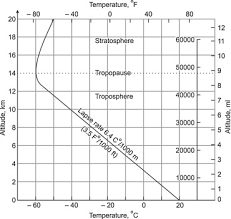
Table of Contents
Types of Lapse Rates
There are three types of lapse rates: environmental lapse rate, adiabatic lapse rate, and saturated adiabatic lapse rate.
Environmental Lapse Rate
The environmental lapse rate (ELR) refers to the actual change in temperature with altitude in the atmosphere. The ELR varies depending on the time of day, season, and location. On average, the ELR is around 6.5 degrees Celsius per 1000 meters (3.5 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 feet). However, the actual ELR can vary significantly from this average value. The ELR is typically measured using radiosondes, which are weather balloons equipped with temperature and humidity sensors.
Adiabatic Lapse Rate
The adiabatic lapse rate (ALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude in a parcel of air that is not exchanging heat with its surroundings. The ALR depends on the type of adiabatic process that the air parcel undergoes. The two types of adiabatic processes are the dry adiabatic process and the moist adiabatic process.
Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate
The dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude in a parcel of dry air that is not exchanging heat with its surroundings. The DALR is approximately 9.8 degrees Celsius per 1000 meters (5.4 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 feet). This value is constant and is not affected by the moisture content of the air.
Moist Adiabatic Lapse Rate
The moist adiabatic lapse rate (MALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude in a parcel of moist air that is not exchanging heat with its surroundings. The MALR is lower than the DALR because the presence of water vapor in the air affects the rate at which the air parcel cools as it rises. The MALR varies depending on the moisture content of the air and can range from 5 to 9 degrees Celsius per 1000 meters (2.7 to 4.9 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 feet).
Saturated Adiabatic Lapse Rate
The saturated adiabatic lapse rate (SALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude in a parcel of air that is saturated with water vapor. The SALR is lower than the MALR because the presence of water vapor in the air affects the rate at which the air parcel cools as it rises. The SALR varies depending on the temperature and pressure of the air and can range from 1 to 3 degrees Celsius per 1000 meters (0.5 to 1.6 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 feet).
Causes of Lapse Rates
The different types of lapse rates are caused by different factors. The ELR is influenced by many factors, including the heating and cooling of the Earth’s surface, the amount of moisture in the air, and the circulation of the atmosphere. The DALR and the MALR are caused by the expansion and compression of air as it rises and falls in the atmosphere. The SALR is caused by the condensation of water vapor in the air as it rises and cools.
Importance of Lapse Rates
- Weather Forecasting: The lapse rate is an important factor in determining the stability of the atmosphere. A steep lapse rate indicates that the temperature is decreasing rapidly with altitude, which can lead to unstable atmospheric conditions and the potential for severe weather such as thunderstorms. A shallow lapse rate indicates that the temperature is changing slowly with altitude, which can lead to stable atmospheric conditions and less severe weather.
- Aviation: The lapse rate is also important for aviation because it affects the performance of aircraft. A steep lapse rate can cause turbulence, which can be hazardous for airplanes. Pilots need to be aware of the lapse rate and other atmospheric conditions when planning and executing flights.
- Climate Science: The lapse rate plays a role in climate science because it affects the way that heat is distributed in the atmosphere. The rate at which the temperature changes with altitude affects the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing infrared radiation, which can have implications for global climate patterns.
- Environmental Monitoring: The lapse rate can also be used to monitor changes in the atmosphere over time. By measuring the lapse rate at different locations and times, scientists can track changes in the atmosphere such as temperature trends and changes in the amount of moisture in the air.
- Atmospheric Physics: The study of the lapse rate is also important for understanding the fundamental physics of the atmosphere. By studying the way that air behaves as it rises and falls, scientists can gain insights into the processes that drive weather patterns and global climate trends.
Important Links