India is the land of geographical diversity. If you are aspiring to study the Indian Physical Geography then Mountain Ranges in India Map will help in your study. Important mountain ranges in India are: the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and the Eastern Ghats.
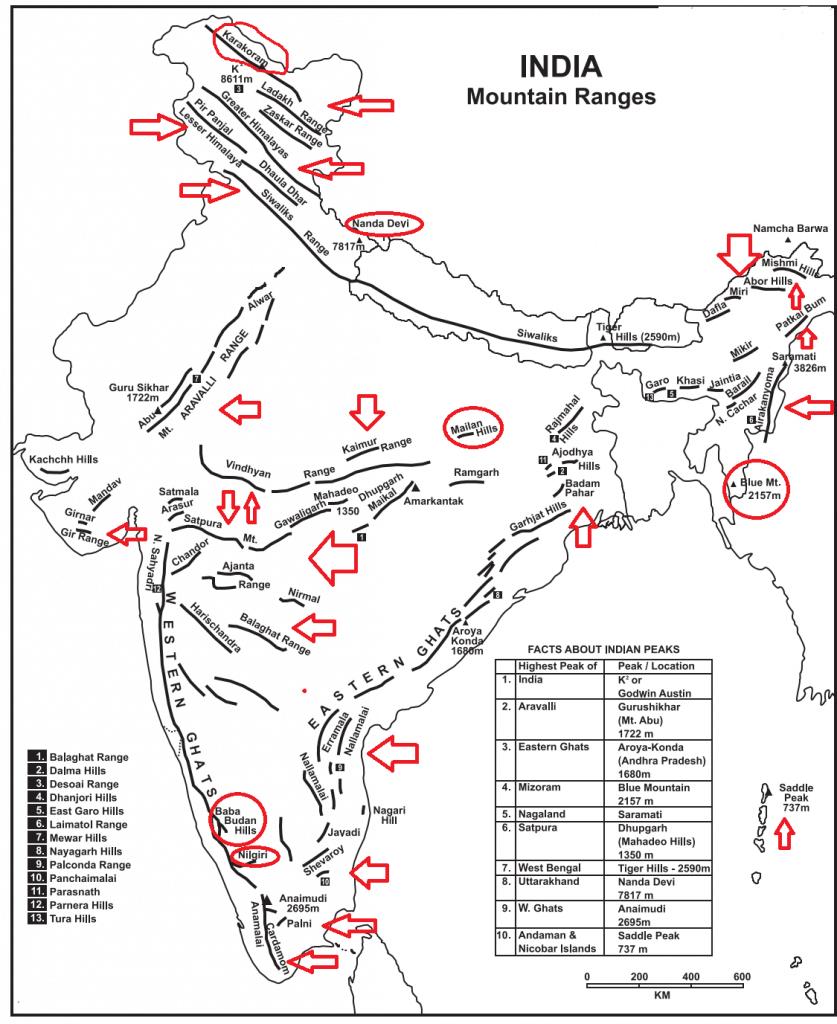
Table of Contents
The Himalayas
The Himalayan mountain range is the highest in the world and spread across the northern and north-eastern regions of India. It has some of the world’s highest peaks, such as Mount Everest (Nepal), K2 (India), and Kangchenjunga (India). It acts the natural barrier to the South Western monsoon winds and causes significant rainfall in India.
Himalaya
| Countries | Highest Peak | Rivers |
|---|---|---|
| India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Pakistan, and Afghanistan | Mount Everest (8,848 m/29,029 ft) | Ganga, Yamuna, Indus, Brahmaputra etc. |
Origin of the Himalayas
The Himalayas originated as a result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Around 50 million years ago, the Indian Plate began moving northward and collided with the Eurasian Plate. This immense tectonic pressure caused the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, leading to the uplift of sedimentary rocks from the Tethys Sea, forming the Himalayan mountain range.
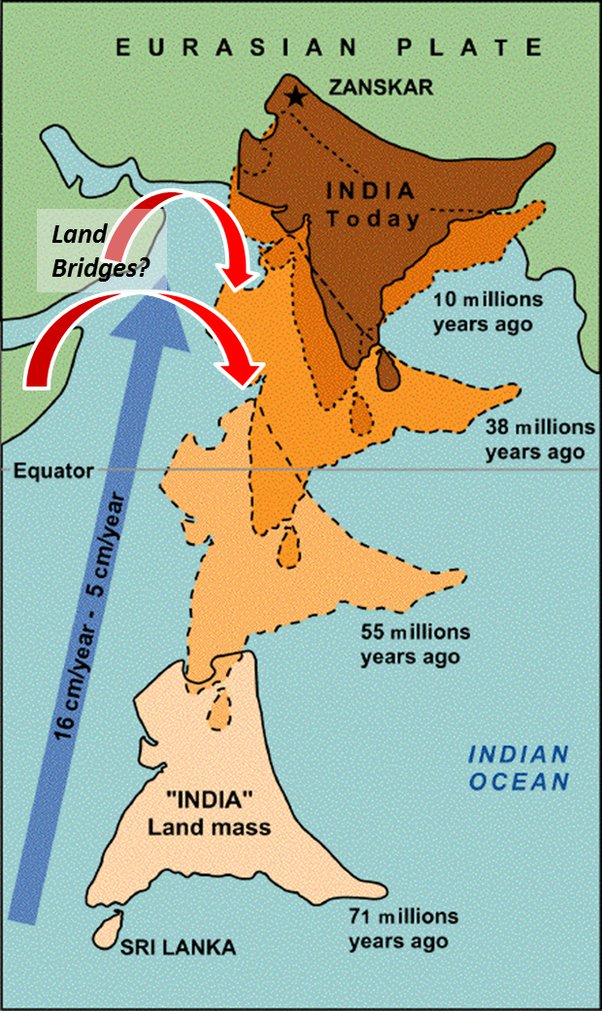
This process is known as convergent plate tectonics, where two continental plates collide. The Himalayas continue to rise even today, making them one of the youngest and most dynamic mountain ranges in the world. Earthquakes and geological activity in the region are direct results of this ongoing tectonic movement.
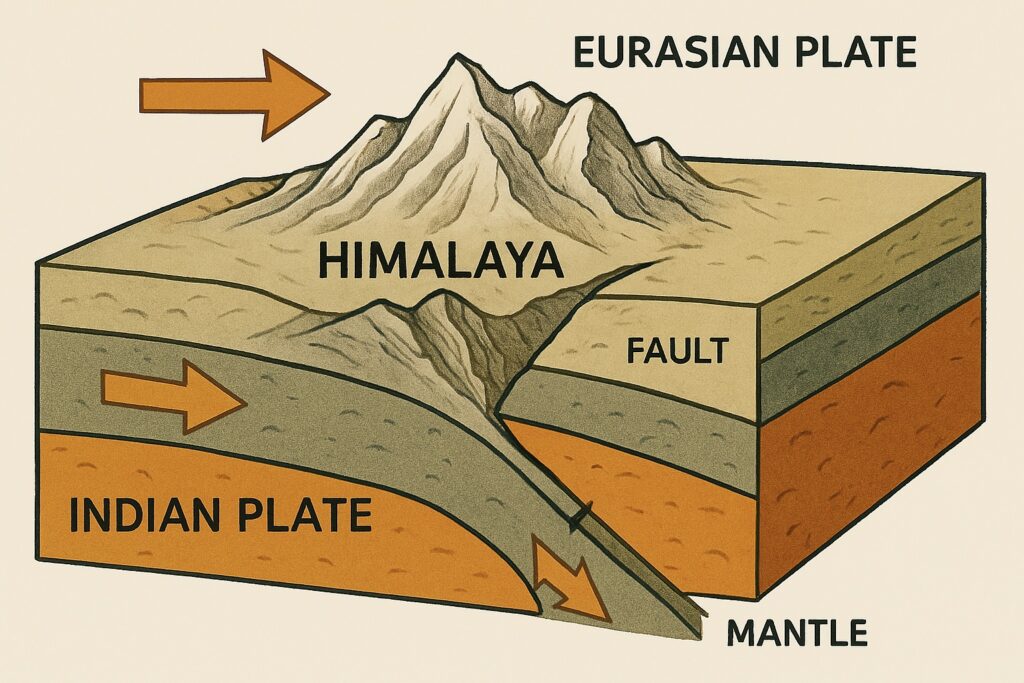
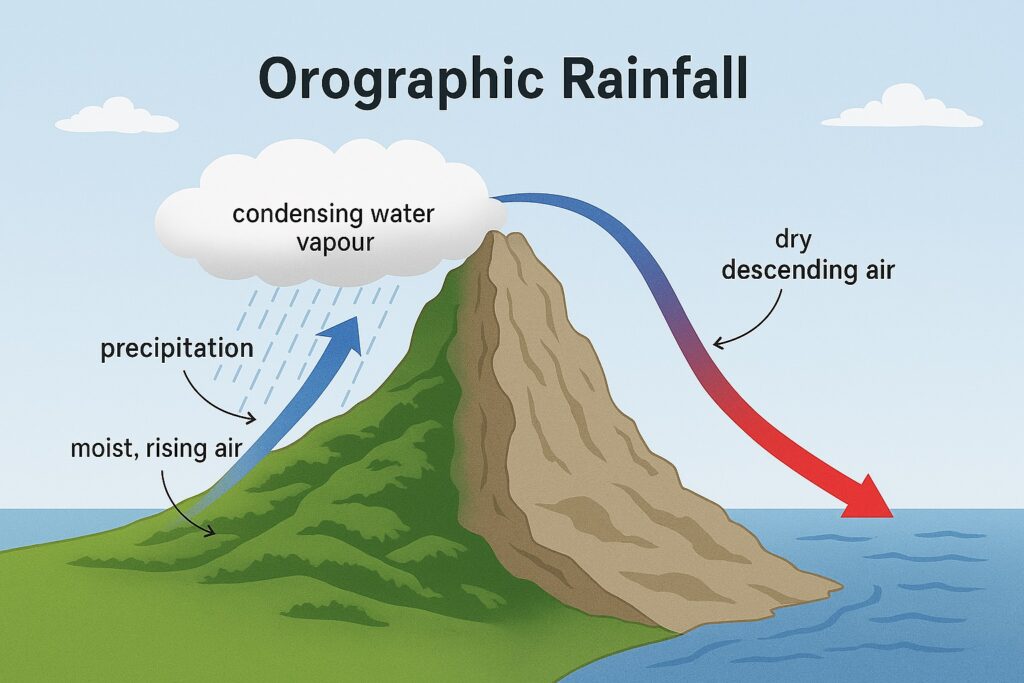
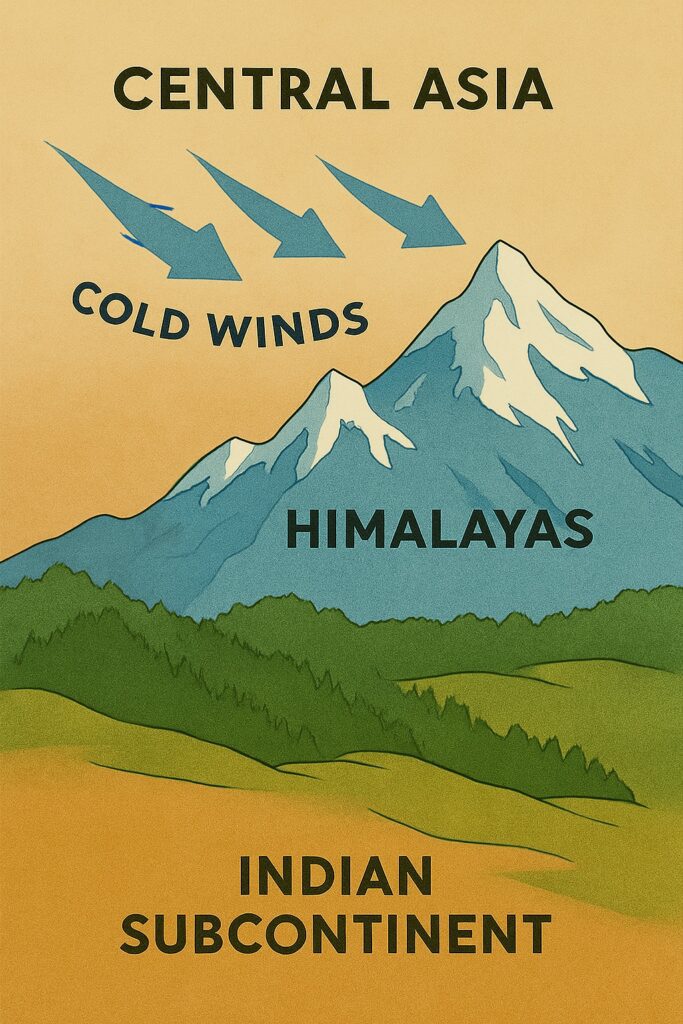
The Himalayas serve as a natural barrier between India and China, and are important for the region’s ecology, culture, and economy. They act as a barrier to the cold, dry winds from Central Asia. The mountain range acts as the barrier to the South-West Monsoon Winds causing significant increase in the rainfall in the region.

The countries that are encompassed within the Himalayan range are: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. The highest peak in the world, Mount Everest, is situated within the Himalayas, at an elevation of 8,848 meters (29,029 feet) above sea level.
"Mount Everest, the highest peak in the world, is part of the Himalaya mountain range."

Himalayan range is source of rivers, like the Ganga, Yamuna, Indus, and Brahmaputra, among others. The Himalayas are relatively young mountains, formed around 50 million years ago when the Indian tectonic plate collided with the Eurasian plate.
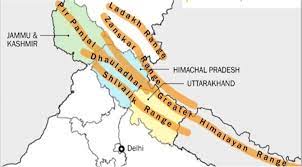
Latitudinal Division of Himalaya
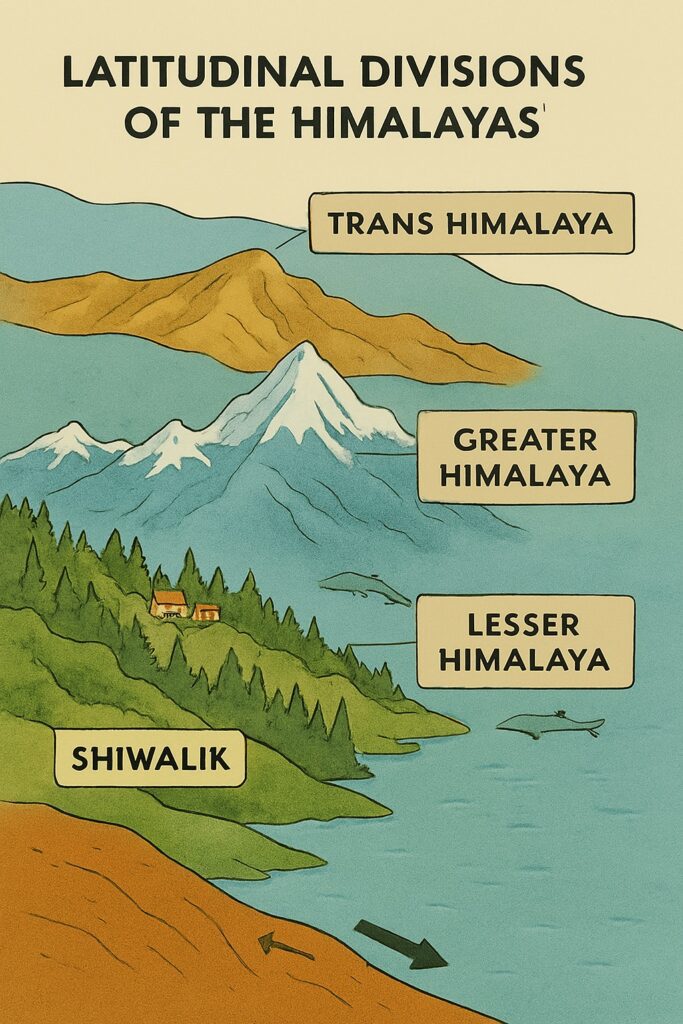
Following is the latitudinal division of Himalaya.
- Trans Himalaya
- Greater Himalaya
- Lesser Himalaya
- Shiwalik
Trans Himalaya
The Trans Himalaya is known as the Tibetan Himalaya. It is a located in the most-northern part of the Himalaya range. It is the extension of the Himalayan mountain range that stretches across Tibet, Bhutan, Nepal, and India.
The Trans Himalaya has high-altitude plateaus, deep canyons, and towering peaks. The region is home to several major rivers, including the Indus, the Brahmaputra, and the Sutlej.
The range is mostly composed of volcanic and granite rocks. The vegetation in the region is sparse, with mainly grasslands and shrubs found at lower elevations, and no trees or vegetation above a certain altitude.
Trans-Himalaya is characterized by broad plateaus, high-altitude deserts, and rugged mountains.
Karakoram Range
The Karakoram Range is a mountain range located in the northernmost part of the Indian subcontinent, spanning the borders of Pakistan, India, and China. It is one of the highest and most rugged mountain ranges in the world, with several peaks rising above 8,000 meters, including K2, the second-highest mountain in the world.
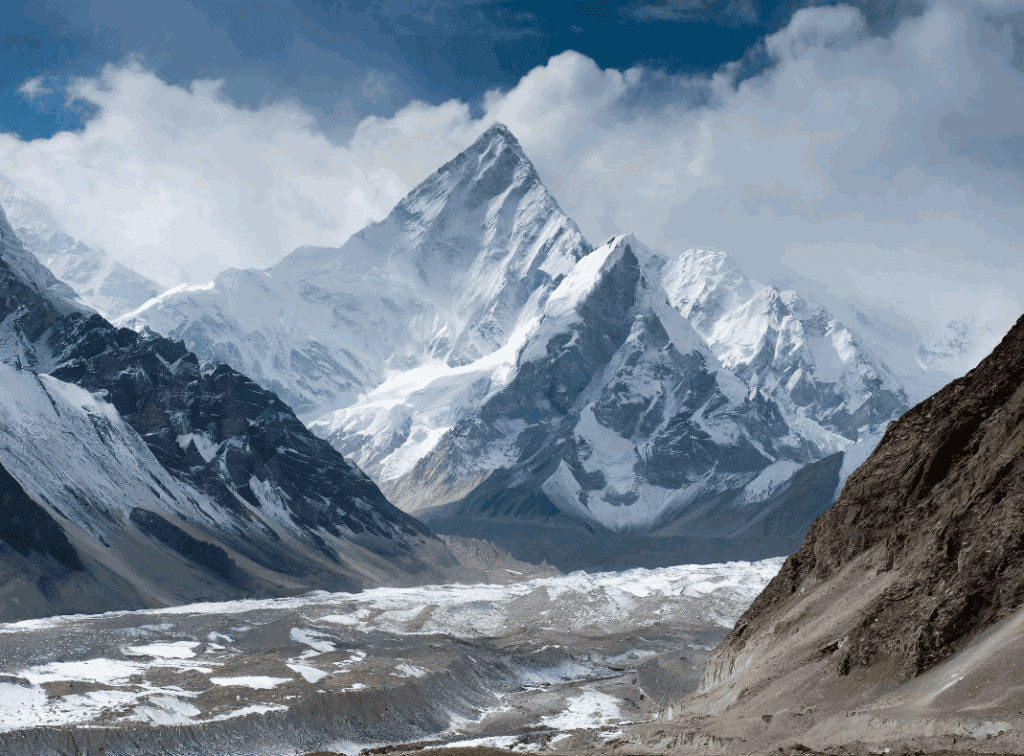

The Karakoram Range is characterized by sharp, jagged peaks, deep valleys, and glaciers. It is home to some of the world’s largest glaciers outside of the polar regions, including the Siachen Glacier, which is the longest glacier in the world outside of the polar regions. The region is also home to several important rivers, including the Indus, the Shyok, and the Nubra, which are a major source of water for the region.
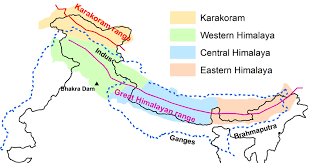
The Karakoram Range is located at the intersection of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, and is therefore prone to earthquakes and landslides. The region is also characterized by extreme weather conditions, with temperatures dropping below -50°C in the winter and high winds and snowfall in the summer.
The Karakoram Range is an important cultural and historical region, with several ancient trade routes passing through it, connecting India and Central Asia. The region is home to several ethnic groups, including the Baltis, the Burushos, and the Wakhi people. The region is also home to several important religious sites, including the famous Silk Road-era Karakoram Highway.
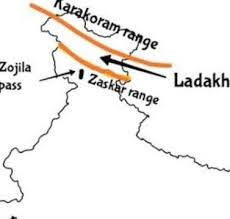
Ladakh Range
Ladakh is a region located in the northernmost part of India, in the state of Jammu and Kashmir. It is a high-altitude desert.
Ladakh has a rich cultural and historical heritage, and is home to several ancient Buddhist monasteries and other religious sites. The region is also known for its unique cuisine, traditional handicrafts, and stunning natural landscapes, including vast expanses of rugged mountains, pristine lakes, and frozen rivers.

Tourism is one of the main industries in Ladakh, and visitors come from all over the world to experience its beauty and culture. However, the region also faces several challenges, including environmental degradation, cultural preservation, and political instability due to the ongoing conflict between India and Pakistan over the territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
Zanskar Range
The Zanskar Range is located in the union territory of Ladakh, in the northern part of India. It is situated in the eastern part of the Union Territory of Ladakh, between the Great Himalayas to the south and the Ladakh Range to the north. The range runs approximately in a northwest-southeast direction and is characterized by a series of high mountain passes.
The Zanskar Range is home to several peaks that soar above 6,000 meters in height. Some of the notable peaks in the range include Stok Kangri (6,153 meters), Nun Kun (7,135 meters), and Saltoro Kangri (7,742 meters).
Pir Panjal Range
The Pir Panjal Range is a significant mountain range situated in the northern part of India, primarily in the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. This range forms a part of the larger Himalayan mountain system and extends across the region, separating the Kashmir Valley from the plains of Jammu. The Pir Panjal Range spans approximately 600 kilometers and runs parallel to the Himalayas, lying to the southwest of the main Great Himalayan range. It serves as a natural boundary between the Kashmir Valley and the Jammu region, extending into the Poonch and Rajouri districts.
Kailash range
The Kailash Range is a mountain range located in the western part of the Himalayas, primarily in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, but also extending into India and Nepal. The range is named after Mount Kailash, which is considered a sacred peak by several religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.

The Kailash Range is known for its stunning natural beauty and rugged terrain, with peaks rising to heights of over 6,000 meters. In addition to Mount Kailash, some of the other notable peaks in the range include Gurla Mandhata, Mount Api, and Mount Nampa.
The Kailash Range is also home to several important rivers, including the Indus, Sutlej and Brahmaputra. These rivers are an important source of water for millions of people in the region and are vital for agriculture, hydropower, and other economic activities.
The Greater Himalaya
The Greater Himalaya region is characterized by high peaks, glaciers, and snowfields and is also known by several other names as Himadri or central Himalaya. It is mainly formed by Granites and other sedimentary rocks. The range has been formed by asymmetrical folding, having steep southern slope and gentle north slope.
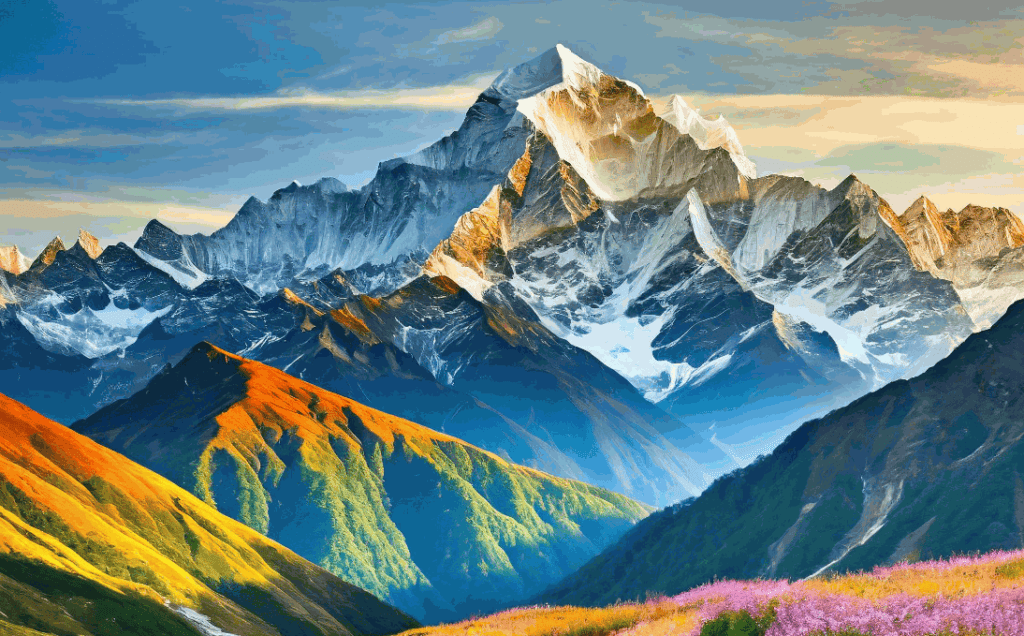

The highest peak in the world the Mount Everest is located on this range.
The Lesser Himalaya
The Lesser Himalaya is a region of the Himalayan mountain range that lies to the south of the Great Himalayas and to the north of the Siwalik Hills. It extends for about 2,400 km from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east, and has an average width of about 100 km.
The Lesser Himalaya is characterized by a series of parallel ranges and valleys, with elevations ranging from about 1,000 to 4,000 meters above sea level. The region is known for its rugged terrain, deep valleys, and steep slopes, and is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna.
Shiwalik
The Siwalik Hills, also known as the Outer Himalayas, is a mountain range in South Asia that runs parallel to the Himalayas, separating the Indo-Gangetic Plain from the foothills of the Himalayas. The range extends over 2,400 km from the Jammu region in the west to the Brahmaputra Valley in the east, and is approximately 10-50 km wide.
The Siwalik Hills are composed of sedimentary rocks and are characterized by a series of low hills and valleys with elevations ranging from about 600 to 1,500 meters above sea level.
The Siwalik Hills are also known for their rich biodiversity and are home to a diverse array of flora and fauna. The region is known for its tropical forests, grasslands, and wetlands, and is home to a number of endangered species, including the Indian rhinoceros, Bengal tiger, and Asian elephant.
The Siwalik Hills have been inhabited by humans for thousands of years and are home to many small communities that rely on the natural resources of the region for their livelihoods. The region is also an important area for agriculture and forestry, and is home to many important wildlife reserves and national parks.
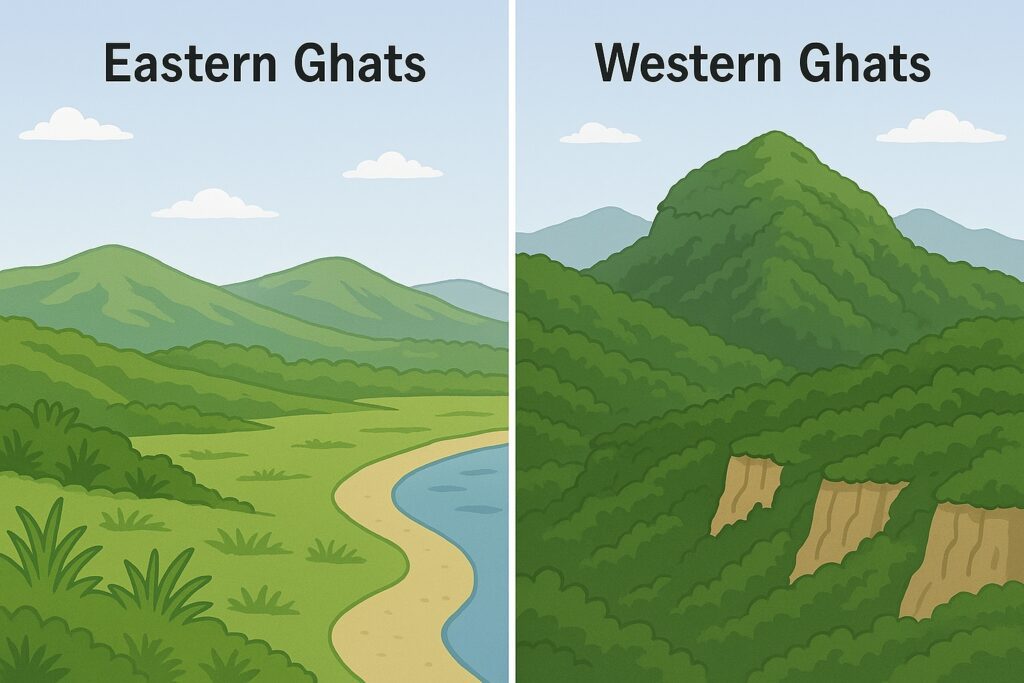
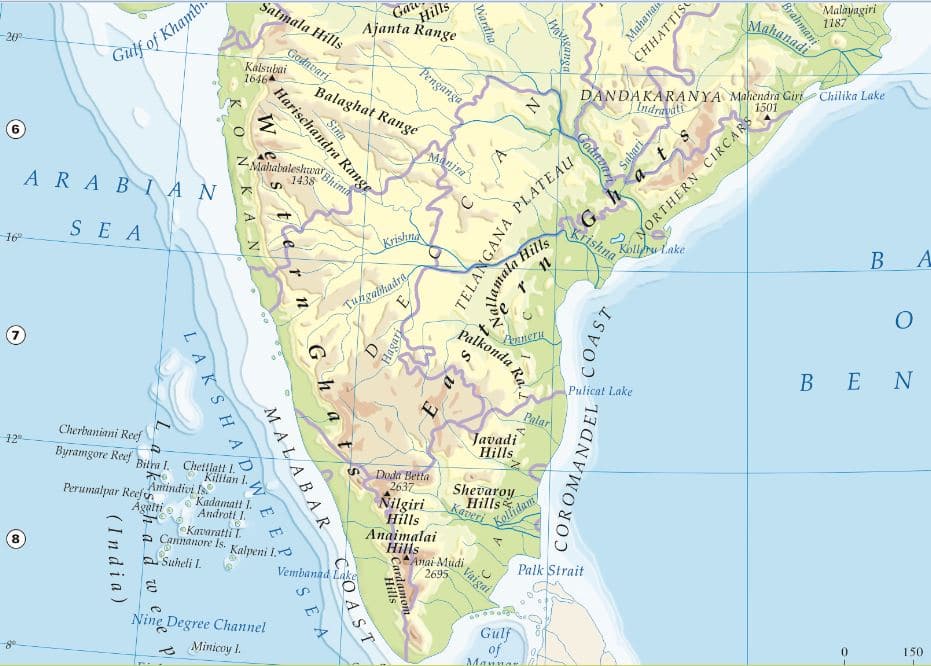
The Western Ghats
The Western Ghats are a range of mountains that run parallel to the western coast of India, from the state of Gujarat in the north to Tamil Nadu in the south. The range includes several important wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, such as the Periyar Wildlife Sanctuary and the Silent Valley National Park.
The highest peak is Anamudi (2,695 m/8,842 ft).
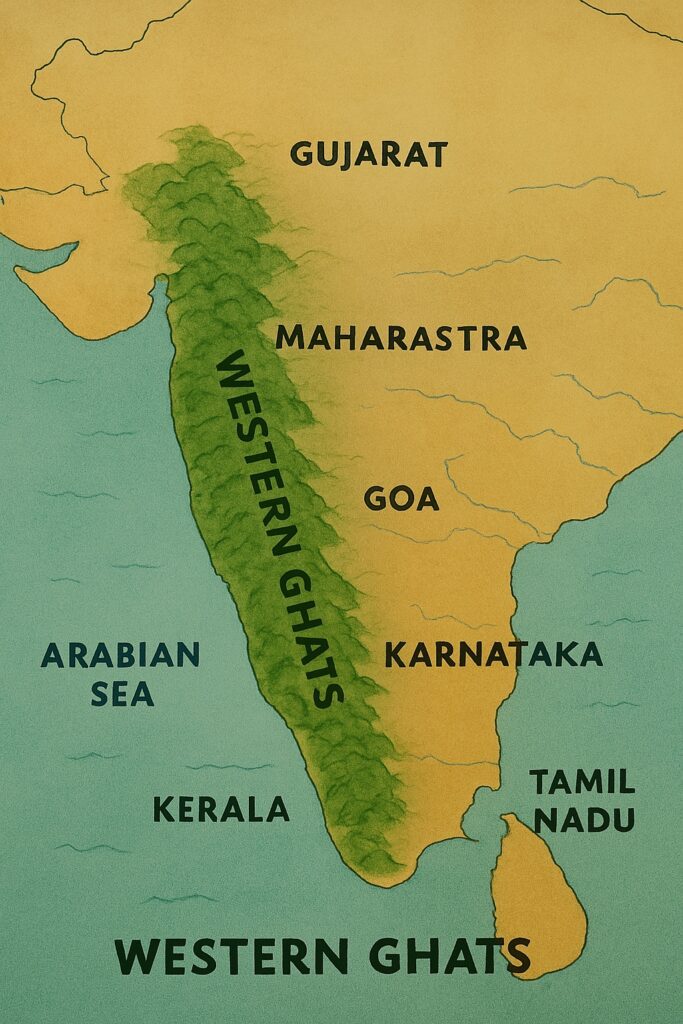
The Western Ghats are recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots due to their rich and diverse flora and fauna. They are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region, meaning they are found nowhere else on Earth.
The Western Ghats play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of the Indian subcontinent. They act as a barrier to the moisture-laden winds coming from the Arabian Sea, causing heavy rainfall along the western slopes and creating a distinct rain shadow effect on the eastern side.
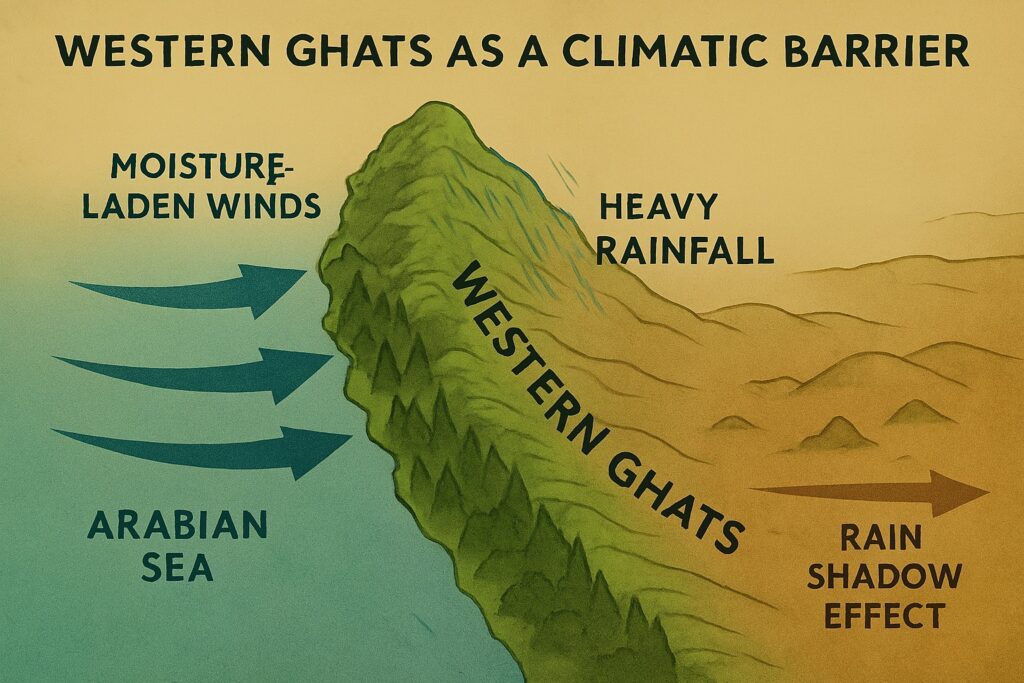
The Western Ghats are the source of many important rivers in peninsular India like the Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, and Tungabhadra rivers.
Formation of Western Ghat
Unlike the Himalayas (which are young fold mountains), the Western Ghats are block mountains formed by the vertical uplift of land. In fact, the Western Ghats are an uplifted edge of the Deccan Plateau, which was formed by volcanic activity around 60 to 68 million years ago during the Cretaceous period. Massive volcanic eruptions in the region led to the outpouring of basaltic lava, which solidified to form the Deccan Traps.
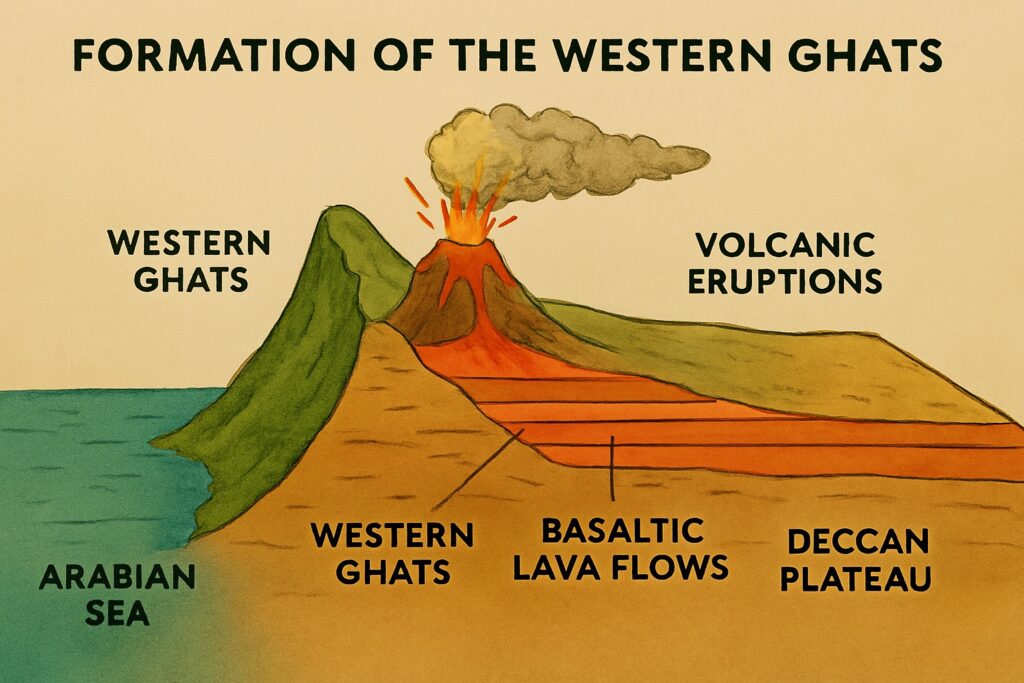
As the Indian plate drifted northwards after separating from the ancient Gondwana supercontinent, tectonic forces caused the western edge of the plateau to rise. This uplift formed a steep escarpment facing the Arabian Sea, resulting in the Western Ghats.
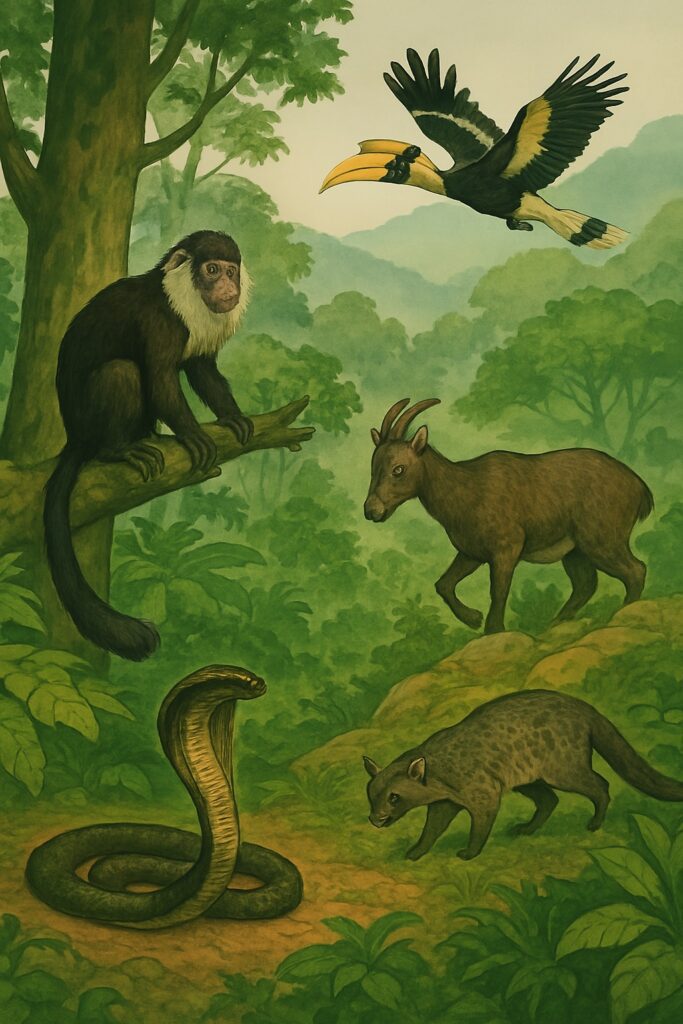
Flora and Fauna of Western Ghats
The Western Ghats are one of the world’s most significant biodiversity hotspots, rich in endemic species and unique ecosystems. It is home to iconic species like the Lion-tailed macaque, Nilgiri tahr, Malabar civet, King cobra, and Great Indian hornbill.

The Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a range of mountains that run parallel to the eastern coast of India, from the state of Odisha in the north to Tamil Nadu in the south. The range is relatively lower in elevation compared to the Western Ghats, but is still an important ecological and economic region. The Eastern Ghats are also home to several important rivers, like the Mahanadi, Godavari, and Krishna.
The highest peak of eastern Ghat is Mahendragiri (1,501 m/4,922 ft).
"Red Sandlewood is endemic to the Eastern Ghat"
Unlike the Western Ghats, which have higher peaks and are continuous, the Eastern Ghats are more fragmented and less prominent in terms of elevation.

The Eastern Ghats are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. The region’s vegetation varies from dry deciduous forests and scrublands to tropical moist forests and grasslands.
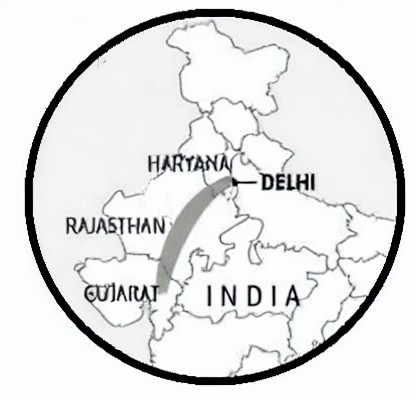
The Aravalli Range
The Aravali Range is one of the oldest mountain ranges in the world, believed to have originated during the Precambrian era, over 2 billion years ago. It stretches from Gujarat to Delhi, passing through Rajasthan and Haryana, covering approximately 692 km. It starts near Delhi and ends in Gujarat in Ahmadabad. The range is relatively old and has been weathered by erosion over millions of years, resulting in unique rock formations and landscapes. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar (1,722 m/5,650 ft).

The Aravalli Range is an important region for mining and has significant mineral deposits of zinc, lead, and copper etc.
"Aravali Range is an important source of White Marble in India"
The unchecked mining activities have led to environmental degradation, deforestation, and habitat loss, posing significant challenges to the Aravali ecological balance. Several rivers originate here, including Banas, Sabarmati, and Luni. Today, the Aravalis are crucial for ecological balance, acting as a natural defense against desert expansion.
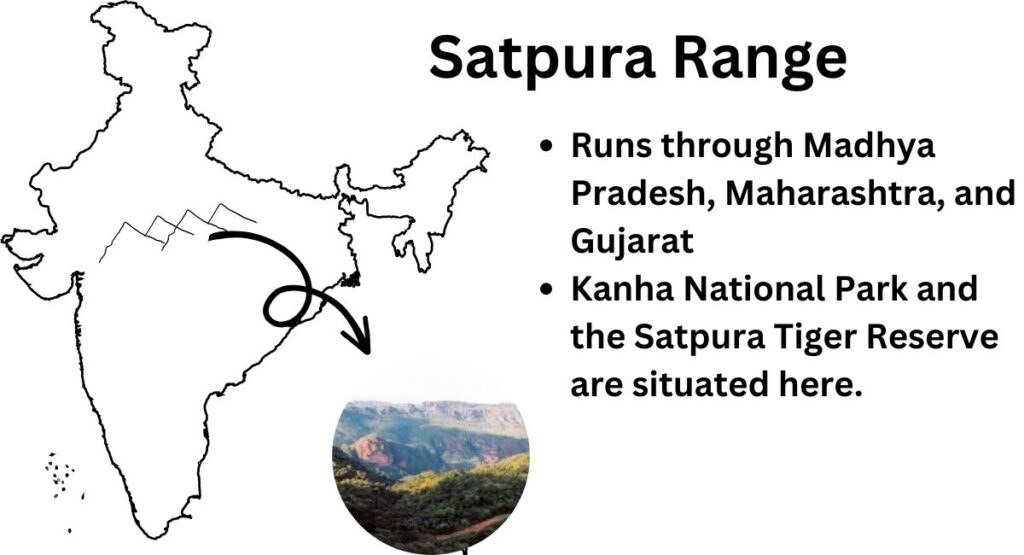
The Satpura Range
The Satpura Range is a range of mountains that runs through the central Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
The highest peak is Dhupgarh (1,350 m/4,429 ft).
Satpura Range
| Length | Highest Peak | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 900 km | Dhupgarh (1,350 m/4,429 ft) | Kanha National Park and the Satpura Tiger Reserve |
The range is relatively low in elevation but is an important ecological region and is home to several important wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, such as the Kanha National Park and the Satpura Tiger Reserve.
The Vindhya Range
The Vindhya Range is one of the major mountain ranges in central India. It is a significant geographical feature that separates the northern Indian subcontinent from the southern Deccan Plateau. The Narmada River flows between Satpura and Vindhya Range.
The highest peak of Vindhya range is Amarkantak (1,048 m/3,438 ft).
"Narmada River flows between the Satpura and Vindhya Range"
The Vindhya Range stretches across Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and parts of Maharashtra and Rajasthan. It runs roughly parallel to the Narmada River.
Dhauladhar Range
The Dhauladhar Range is a mountain range located in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It runs roughly from the Kangra Valley in the west to the Chamba Valley in the east, covering a distance of about 60 kilometers. The range is part of the larger Himalayan mountain system and lies in close proximity to Dharamshala.
Patkai Range
The Patkai Range is also known as the Purvanchal Hills. It is a mountain range located in northeastern India and northwestern Myanmar.
It is a part of the larger Himalayan mountain system and runs parallel to the eastern edge of the Himalayas. The Patkai Range extends for about 800 kilometers from the Diphu Pass in Assam to the Hukawng Valley in Myanmar.
The Patkai Range is primarily composed of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, with some volcanic rocks present in certain areas. The range was formed as a result of the tectonic collision between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate, which began around 50 million years ago during the Eocene epoch. The ongoing Indian plate’s movement towards the north continues to push against the Eurasian plate, leading to the formation of fold mountains, including the Patkai Range.
Javadi Hills
The Javadi Hills is a range of low mountains situated in the northeastern part of Tamil Nadu. These hills are a extension of Eastern Ghats mountain range, which runs along the eastern coast of India. The Javadi Hills are spread across the districts of Tiruvannamalai and Vellore in Tamil Nadu.
Anamalai Hills
The Anamalai Hills are a mountain range located in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Hills exhibit natural beauty and rich biodiversity.
The region is famous for tea and coffee plantations. At the heart of the Anamalai Hills lies the Anamudi Peak, the highest peak in South India.
The Anaimalai Hills stretch from the Palakkad Gap in Kerala to the Valparai plateau in Tamil Nadu. The Indira Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park is located in the Anamalai Hills.
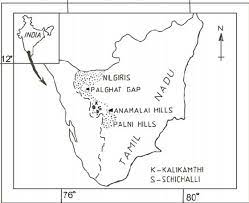
Nilgiri Hills
The Nilgiri Hills is referred as “Blue Mountains”. They are a mountain range located in the southern part of India, spanning across the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala. These hills are part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its rich biodiversity and natural beauty. The Nilgiri Hills extend for about 150 kilometers in a north-south direction.
Cardamom Hill
The Cardamom Hills stretch across the southern Indian states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
They extend from the Palar River in the north to the southern tip of India, near Kanyakumari.
Nallamala Hills
Nallamala Hills is a mountain range situated in southern India, primarily in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. It is part of the larger Eastern Ghats mountain range that runs parallel to the southeastern coast of India.
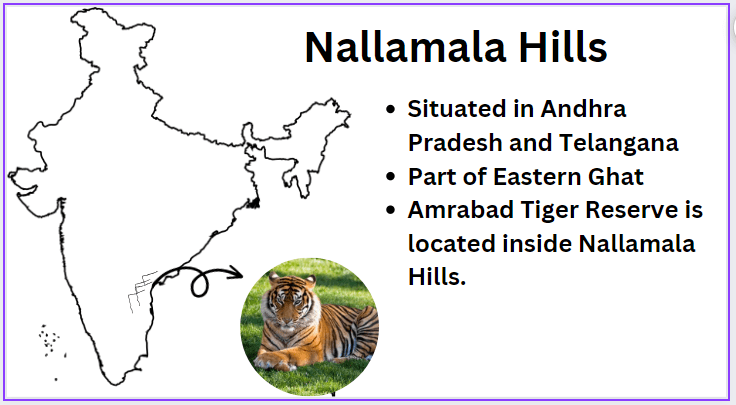
The Nallamala Hills stretch over an area of approximately 15,000 square kilometers and are characterized by dense forests, valleys, plateaus, and numerous rivers and streams. The region is known for its rich biodiversity. The Amrabad Tiger reserve lies inside Nallamala hills.
Garo Hills
The Garo Hills are situated in the western part of Meghalaya. Inhabitants: Hills are predominantly inhabited by the Garo people, an indigenous community with a rich cultural heritage. The economy of the region is mainly agrarian, with agriculture and horticulture being the primary sources of livelihood. The Garo Hills are also known for their traditional handicrafts and handloom products.

Khasi Hills
The Khasi Hills are located in the central part of Meghalaya, sharing borders with Bangladesh to the south. The Khasi Hills are predominantly inhabited by the Khasi people, another indigenous community of Meghalaya. The Khasi Hills are also known for their unique matrilineal system, where “property and family names are passed down through the female line”.

Jaintia Hills
The Jaintia Hills are situated in the eastern part of Meghalaya, sharing borders with Bangladesh. The Jaintia Hills are predominantly inhabited by the Jaintia people, who are one of the indigenous communities of Meghalaya. The Jaintia Hills are also known for their rich mineral resources, particularly coal, which has been a source of both livelihood and environmental challenges.
Maikal Range
Maikala Range or Maikala Hills is a prominent hill range located in central India. The hills are part of the larger Satpura Range, which is one of the major mountain ranges in India.
The Maikal Hills are primarily located in the state of Chhattisgarh, but they also extend into the eastern parts of Madhya Pradesh. The hills cover a considerable area and are characterized by dense forests and rugged terrain.




Mikir Hills
The Mikir Hills are located in the northeastern state of Assam. These hills are characterized by green forests, and diverse wildlife. The region is primarily inhabited by the Karbi tribe, known for their distinct culture and traditions.
Economically, the Mikir Hills are significant for tea cultivation and coal mining. The area’s geographical isolation has contributed to the preservation of its unique biodiversity, making it an ecologically important zone.



Mizo Hills
The Mizo Hills are located in the northeastern state of Mizoram. Home to the Mizo people, the hills are characterized by terraced slopes, dense forests, and cascading waterfalls. The region’s pleasant climate and fertile land make it suitable for agriculture, with rice being the staple crop.



Rajmahal Hills
Rajmahal Hills are the region located in the eastern Indian state of Jharkhand. It derives its name from the historical Rajmahal Fort. The Rajmahal Hills are part of the Chota Nagpur Plateau and are known for their dense forests, and fertile agricultural lands. The region has significant historical importance, having been a significant center during the Mughal and British colonial eras.


Kaimur Range
The Kaimur Range is a vast and rugged mountain range located in the central part of India. It stretches across the states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh. The Kaimur Range is a part of the larger Vindhya Mountain Range and forms the southern edge of the Vindhya region.
The range is characterized by its rocky and forested terrain, with numerous hills and valleys. The Son River, a major tributary of the Ganges, flows through the Kaimur Range, shaping the landscape and providing valuable water resources for the surrounding regions. The Kaimur Hills are home to various indigenous tribes and support a variety of flora and fauna. These hills have historical significance and have witnessed various cultural and historical events over the centuries.




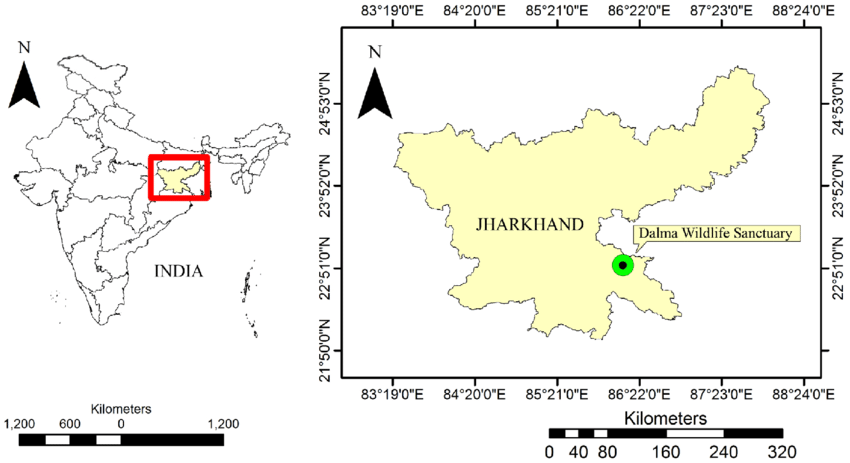
Dalma Hills
The Dalma Hills are a picturesque hill range situated in the Indian state of Jharkhand. These hills are part of the Eastern Ghats mountain system and are located in the eastern part of the state, near the city of Jamshedpur. The Dalma Hills are characterized by dense forests, verdant landscapes, and diverse wildlife, making it an important ecological hotspot in the region. The hills are home to the Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary.

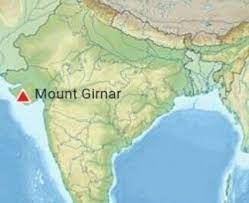
Girnar Hills
Girnar Hills are situated in the Junagadh district of Gujarat. The rugged terrain encompasses a series of hills and valleys, housing important pilgrimage sites for both Hindus and Jains. The Girnar Jain Temples, dedicated to various Tirthankaras, attract Jain devotees, while the Amba Mata Temple and Dattatreya Temple hold significance for Hindus.

Baba Budan Giri Hills
Baba Budan Giri Hills are located in the Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, are a sacred mountain range with historical and religious significance. Named after the revered Muslim saint Baba Budan, who introduced coffee cultivation to India, the hills are home to two important shrines, one dedicated to Baba Budan and the other to Guru Dattatreya, a Hindu deity.

This unique blend of Hindu and Muslim religious sites makes it a symbol of communal harmony. Additionally, the region is renowned for its lush greenery, coffee plantations, and serene landscapes.
Balaghat range
The Balaghat Range is a mountainous region located in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is a part of the larger Satpura Range, which stretches across central India. The Balaghat Range is characterized by its rugged terrain, dense forests, and rich biodiversity. The region is known for its picturesque landscapes, with numerous hills and valleys. It is home to various wildlife species, including tigers, leopards, and various species of deer, making it an important wildlife habitat. The range is also known for its mineral resources, particularly significant deposits of manganese ore, contributing to the region’s economic importance.

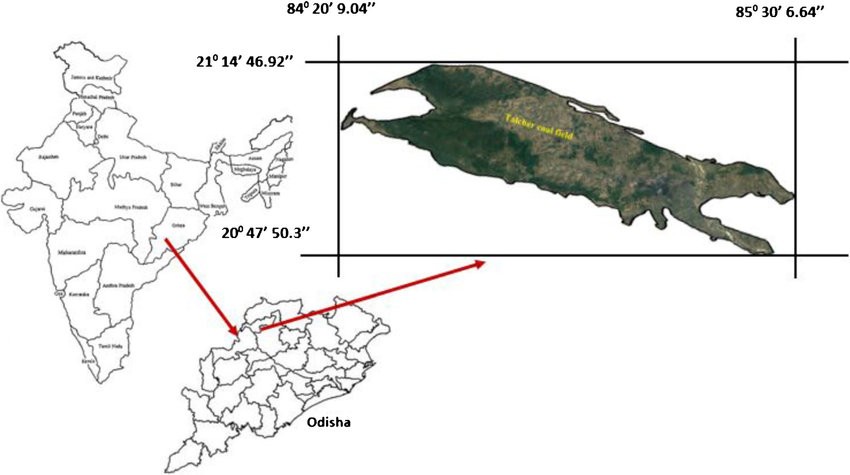
Talcher Series
The Talcher Series is a geological formation located in the Talcher region of the Indian state of Odisha. It comprises a sequence of sedimentary rocks that have accumulated over millions of years, dating back to the Gondwana period. The Talcher Series is of significant economic importance as it contains vast reserves of coal, making it one of the major coal-bearing regions in India. The coal extracted from the Talcher mines is essential for power generation, industrial processes, and other economic activities. Additionally, the sedimentary rocks in the Talcher Series provide valuable insights into the Earth’s geological history and contribute to the understanding of past environmental conditions and ancient ecosystems.

Palani Hills
The Palani Hills are a scenic mountain range situated in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. Located near the town of Palani, the hills are a part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its rich biodiversity. The Palani Hills are characterized by lush forests, rolling hills, and numerous streams and waterfalls, creating a picturesque landscape. At the highest point of the range stands Palani Hill, which is a popular pilgrimage site housing the Palani Murugan Temple dedicated to Lord Murugan, a prominent deity in Hindu mythology.
Pachamalai Hills
The Pachamalai Hills are located in the state of Tamil Nadu. I is a part of the Eastern Ghats. Known for their lush greenery and scenic landscapes, these hills offer a serene and tranquil environment. The region is rich in biodiversity, housing various plant and animal species endemic to the area. The hills are also home to tribal communities, adding to the cultural significance of the region.
Shevaroy Hill
Shevaroy Hill is a prominent hill range located in the Eastern Ghats of Tamil Nadu, South India. It is part of the Yercaud Hills. The hill range is named after the local deity, Shevaroyan, who is worshipped by the local tribes.


Elevation: The highest point in the Shevaroy Hills is Servarayan Temple, which stands at an elevation of about 1,623 meters (5,325 feet) above sea level.
Badam Pahar
The mountain is situated in the Singhbhum district of Jharkhand. It is famous from Iron ore, Hematite.
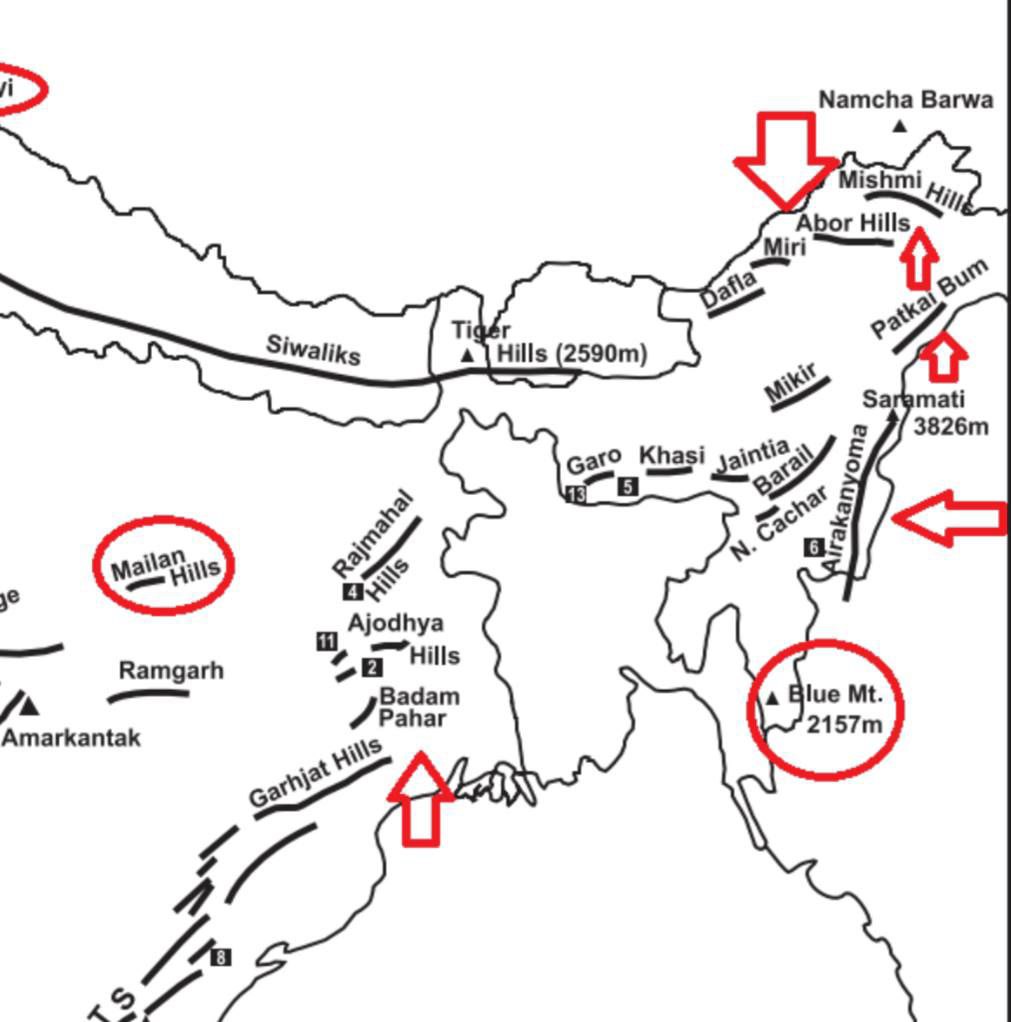

Dafla Hill
Dafla Hills is situated on the border of western Arunachal and Assam. It is occupied by the tribe called Dafla. It bounded on west by the Aka Hills and on east by the Abor Hill.
Important Links
