The Pole Star is one of the most famous and significant stars in the night sky. It is called the “Pole Star” because it appears very close to the north celestial pole, the point in the sky directly above the Earth’s North Pole.
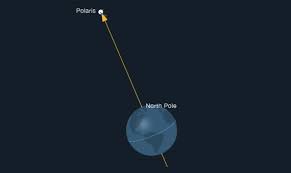
Due to its alignment with the Earth’s axis of rotation, the Pole Star appears almost stationary in the night sky, while other stars appear to rotate around it as the Earth spins on its axis. This unique characteristic makes it a valuable navigational tool for astronomers, sailors, and travelers since ancient times.
For observers in the Northern Hemisphere, locating the Pole Star helps find the direction of the true north, making it useful for navigation and orientation, especially during clear nights when other landmarks may not be visible.
It is located in the constellation Ursa Minor (the Little Dipper), and it is the brightest star in that constellation. While it may not be the brightest star in the sky, its strategic location and steady position have made it an essential guide for travelers and stargazers alike, earning its reputation as a symbol of stability and guidance in the vastness of the night sky.
Important Links