River capture is a geological phenomenon that occurs when one river diverts the flow of another river. In this article, we will explore what river capture is, how it happens, and its impacts on the surrounding environment.
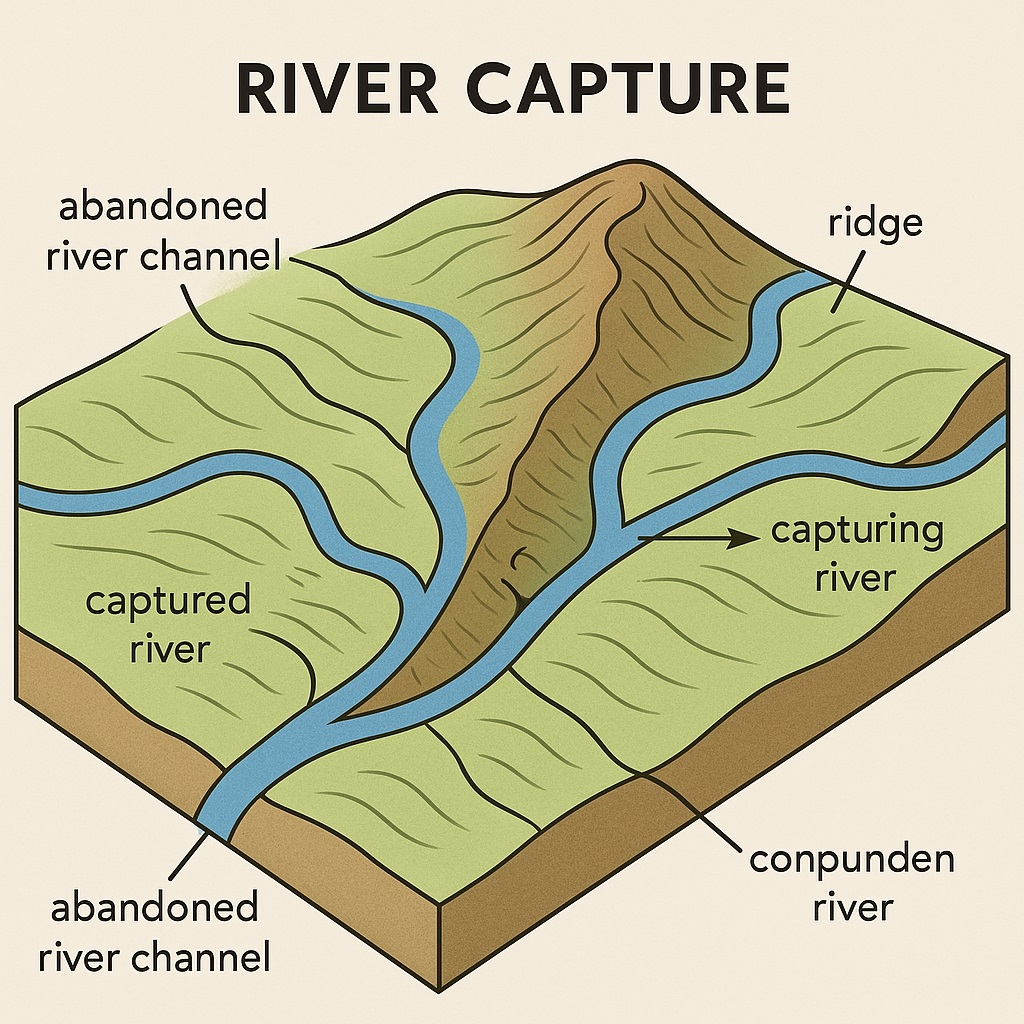
Table of Contents
What is River Capture?
It occurs when one river captures the flow of another river. This can happen when a river erodes its way through a divide, which is a high point of land that separates two drainage basins. As the river erodes through the divide, it can capture the flow of another river and divert it into its own drainage basin. River capture, also known as stream piracy. This phenomenon occurs when a more vigorous river, often with a steeper gradient and greater erosive power, breaches a divide and captures the flow of a neighboring river, redirecting its waters into its own channel.
Causes of River Capture
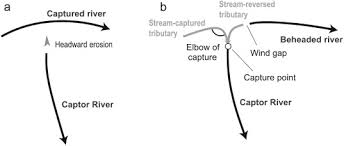
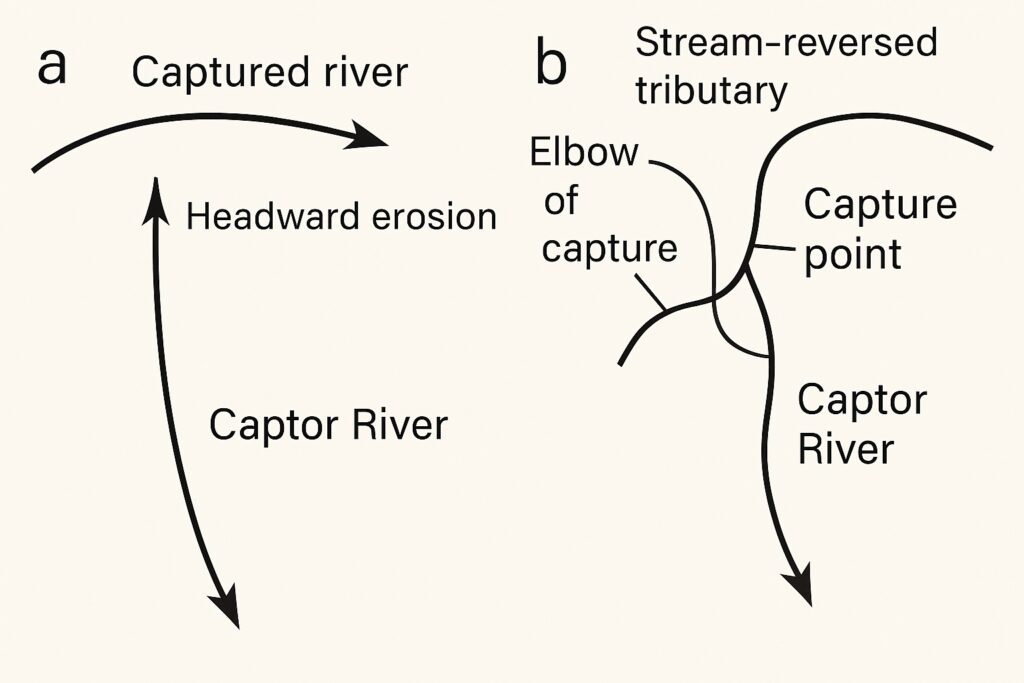
- Headward Erosion – The capturing river extends its course upstream through erosion, eventually intersecting the flow of a neighboring river.
- Tectonic Movements – Changes in the earth’s crust, such as uplift or faulting, may alter drainage patterns, forcing a river to change its course.
- Differential Erosion – Rivers with greater erosive potential wear down barriers more quickly, allowing them to capture weaker neighboring streams.
- Climate Change & Glaciation – Historical climate shifts have influenced river behaviour, with glaciers altering watersheds and contributing to stream piracy.
How Does River Capture Happen?
It can happen through a variety of geological processes. One of the most common ways it occurs is through headward erosion. Headward erosion happens when a river erodes its way upstream, gradually lengthening its course and capturing the flow of smaller streams and rivers in the process.
Another way that it can occur is through tectonic activity. When the earth’s crust shifts and changes, it can alter the drainage patterns of rivers and cause one river to capture the flow of another.
Effects of River Capture
- Abandoned River Channels (Misfit Streams) – The captured river may leave behind a dry or underfit stream in its former course.
- Changes in Drainage Patterns – The redirection of water can create new valleys, lakes, or floodplains.
- Disruption of Ecosystems – Flora and fauna dependent on the original river system may be affected by the shift in water flow.
- Human Impact – Altered river courses can affect agriculture, settlements, and water availability for communities.
Impacts
It can have significant impacts on the surrounding environment. For example, it can alter the flow of water and sediment through a landscape, which can impact erosion and the formation of landforms. It can also lead to changes in the distribution of aquatic species and affect the overall health of a river ecosystem.
Example of River Capture (India)
One example is the case of the Chambal and Yamuna Rivers. The Chambal River used to flow into the Bay of Bengal, while the Yamuna River flowed into the Arabian Sea. However, around 4 million years ago, the river Chambal captured the flow of the Yamuna River through headward erosion, gradually extending its course upstream and diverting the flow of the Yamuna into its own drainage basin.
Kaveri River basin has seen evidence of stream piracy over geological timescales.
Examples of River Capture (World)
One well-known example is the River Thames, which is believed to have undergone capture in prehistoric times due to tectonic shifts.
River capture is an integral part of landscape evolution, shaping valleys, altering ecosystems, and influencing human geography. Understanding this process is key to studying geomorphology and its implications for environmental and hydrological changes.
"Another famous example is the case of the River Thames and the River Medway in England. The River Thames captured the flow of the River Medway around 2 million years ago through headward erosion, which dramatically altered the landscape and drainage patterns of the region."
Significance
This had significant impacts on the surrounding environment. It changed the drainage patterns of the region, leading to the formation of new landforms and altering the distribution of aquatic species. It also played a role in the development of human civilization in the region, as communities adapted to the new river system created by the capture event.
It has shaped the landscapes and ecosystems of our planet for millions of years. Its study will remain an important area of research, providing valuable insights into the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our planet.
Read: Geography