Son River is a major river in central India. It flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar, and is one of the largest tributaries of the Ganges. The river is an important source of water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation, and it also holds significant cultural and religious importance for the people of the region.
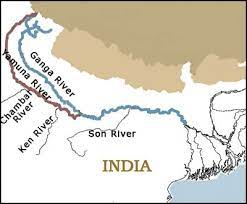
Table of Contents
Geography and Importance of Son Rover
The Son River originates in the Maikal Hills of Madhya Pradesh and flows for a distance of around 780 kilometers before joining the Ganges River near Patna in Bihar.
The Son River is a major source of water for irrigation in the region, and it plays a vital role in the agriculture and economy of the region. The river also has several dams and reservoirs constructed on it, including the Rihand Dam, Bansagar Dam, and Sone Barrage. These dams not only provide water for irrigation but also generate hydroelectric power for the region.
Apart from its economic importance, the Son River is also significant culturally and religiously. The river is considered sacred by the people of the region, and many important temples and religious sites are situated on its banks. The most famous among them is the Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Varanasi, which is visited by millions of devotees every year.
Flora and Fauna in Son River
The Son River basin is home to a rich variety of flora and fauna. The river supports a diverse range of fish species, including catfish, murrel, and mahseer. The river is also home to several species of freshwater turtles and crocodiles. The surrounding forests are home to several species of wild animals, including tigers, leopards, and deer.
Conservation Efforts in Son River
Despite its importance, the Son River faces several challenges, including pollution, deforestation, and unsustainable fishing practices. The river has become increasingly polluted due to industrial and domestic waste, and the construction of dams and barrages has also affected the river’s flow and ecology.
To address these challenges, several conservation efforts have been initiated by the government and non-governmental organizations. These include the conservation of forests and wetlands, the promotion of sustainable fishing practices, and the installation of sewage treatment plants.
Conclusion
It is an important river in central India, with significant economic, cultural, and religious importance. It supports a rich variety of flora and fauna and plays a vital role in the ecology and economy of the region. However, the river faces several challenges, and conservation efforts are necessary to ensure its sustainability and well-being for future generations.
Important Links