Q1. Solar eclipse occurs when
(a) Earth comes between sun and moon
(b) Moon is at right angle to the earth
(c) Moon comes between sun and earth
(d) Sun comes between moon and earth
Answer: (c) Moon comes between sun and earth
Explanation:
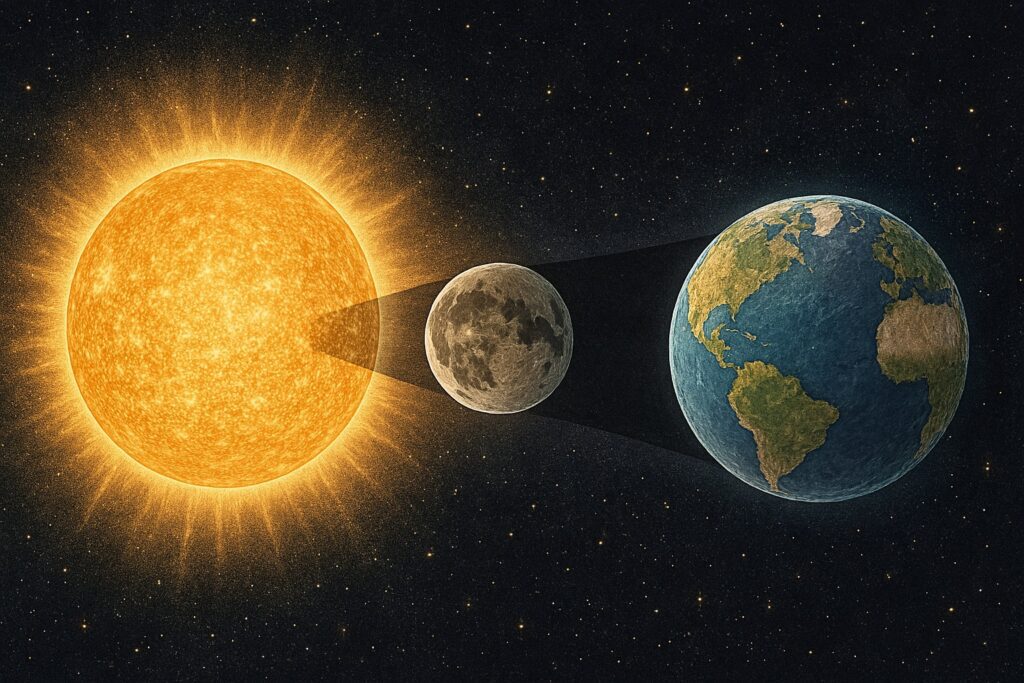
A solar eclipse takes place when the Moon moves directly between the Sun and the Earth, causing the Sun’s light to be blocked either partially or completely. This alignment leads to the Moon casting a shadow on Earth, and the eclipse is visible only from specific regions where this shadow falls. The Moon must be in its new moon phase for this phenomenon to occur.
Q2. When a man circles round the earth in a satellite, then
(a) His mass becomes zero but weight remains constant
(b) Mass remains constant but weight becomes zero
(c) Both mass and weight remain constant
(d) Both mass and weight remain zero
Answer: (b) Mass remains constant but weight becomes zero
Explanation:
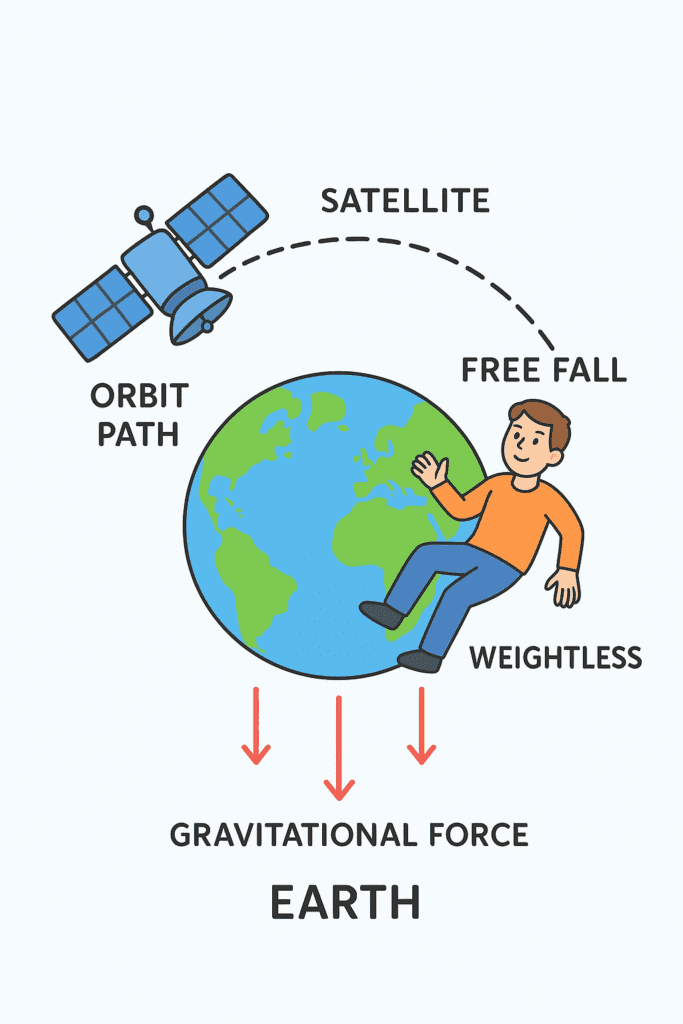
In a satellite orbiting Earth, a person experiences weightlessness due to the free-fall condition of orbit. While mass is an intrinsic property and remains unchanged, weight depends on gravitational force. In orbit, the person is in continuous free fall, which results in zero apparent weight, even though gravity is still acting.
Q3. The weight of an object at the poles is greater than at the equator. This is because
(a) Of the shape of the earth
(b) The attraction of the moon is maximum at the earth’s surface
(c) The attraction of the sun is maximum at the earth’s surface
(d) Gravitational pull is more at the poles
Answer: (d) Gravitational pull is more at the poles
Explanation:
The Earth is not a perfect sphere; it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This shape causes the distance from the center of the Earth to the poles to be less than to the equator. As a result, the gravitational force is stronger at the poles, making the weight of objects greater there.
Q4. The first metal used by the man was
(a) Iron
(b) Copper
(c) Aluminium
(d) Gold
Answer: (b) Copper
Explanation:
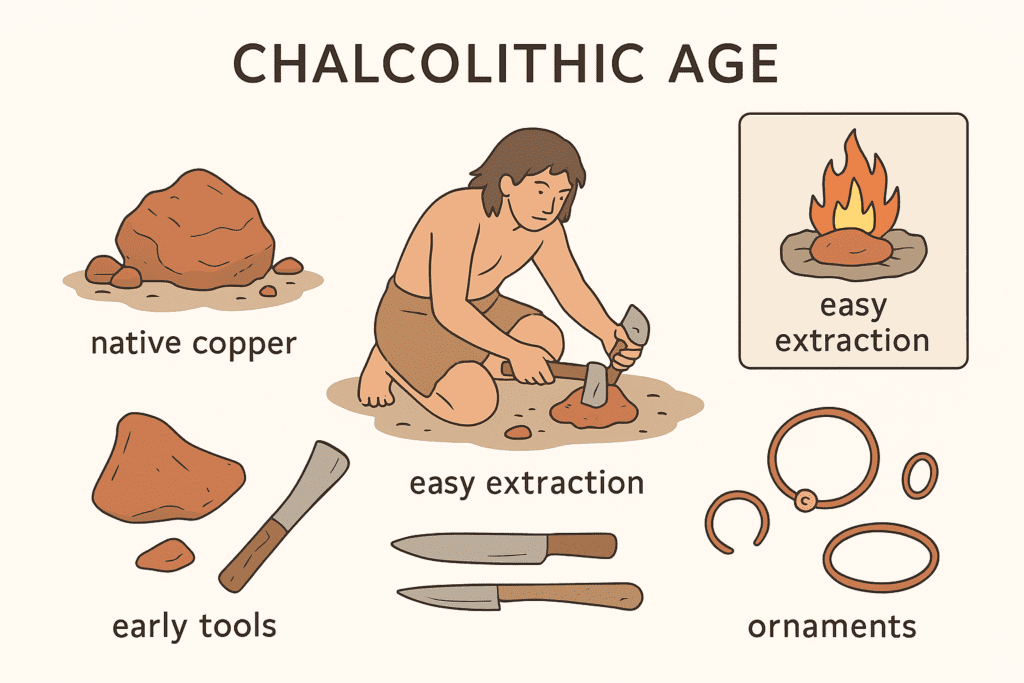
Copper was one of the earliest metals discovered and used by humans, primarily because it occurs in native form and can be easily extracted and shaped. Its low melting point and availability in nature made it ideal for early tools and ornaments, marking the beginning of the Chalcolithic Age.
Q5. Gobar gas contains mainly
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Methane
(c) Ethylene
(d) Carbon monoxide
Answer: (b) Methane
Explanation:
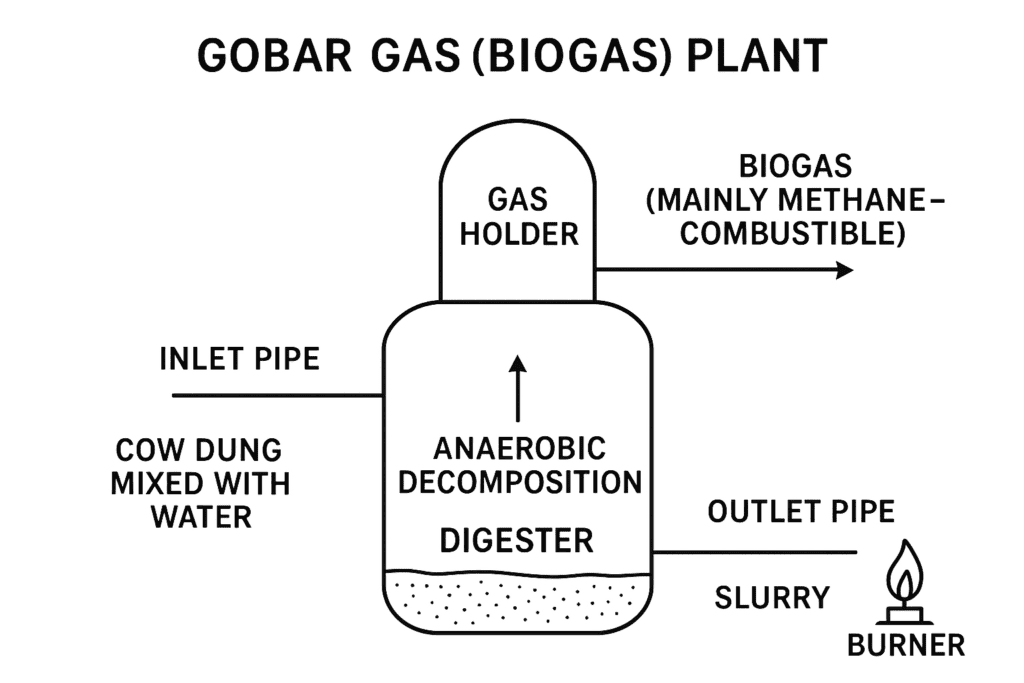
Gobar gas, produced from the anaerobic decomposition of cow dung, primarily consists of methane, which is a combustible gas. It is used as a renewable source of energy for cooking and lighting. The presence of methane makes it an efficient fuel.
Q6. The content of water is greater than fats, the plasma is more than proteins, proteins are more than fats and fats less than plasma. Which constitutes the major Part of the human body ?
(a) Fats
(b) Water
(c) Plasma
(d) Proteins
Answer: (b) Water
Explanation:
The human body is composed mostly of water, which makes up about 60–70% of body weight. It is more abundant than plasma, proteins, or fats, and plays a critical role in physiological processes like temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and cellular function.

Q7. Dialysis is used for a patient suffering from
(a) Kidney trouble
(b) Liver trouble
(c) Lung trouble
(d) Bronchitis
Answer: (a) Kidney trouble
Explanation:
Dialysis is a medical procedure used when the kidneys fail to filter waste products from the blood. It removes toxins, excess salts, and fluids, mimicking the function of healthy kidneys. It is essential for patients with renal failure.

Q8. Pulse reading is done by doctors to find out
(a) Temperature
(b) Heart beat
(c) Blood pressure
(d) Respiration rate
Answer: (b) Heart beat
Explanation:
Pulse reading involves feeling the rhythmic throbbing of arteries, which reflects the heartbeat. It helps assess the rate, rhythm, and strength of the heart, providing vital information about cardiovascular health.
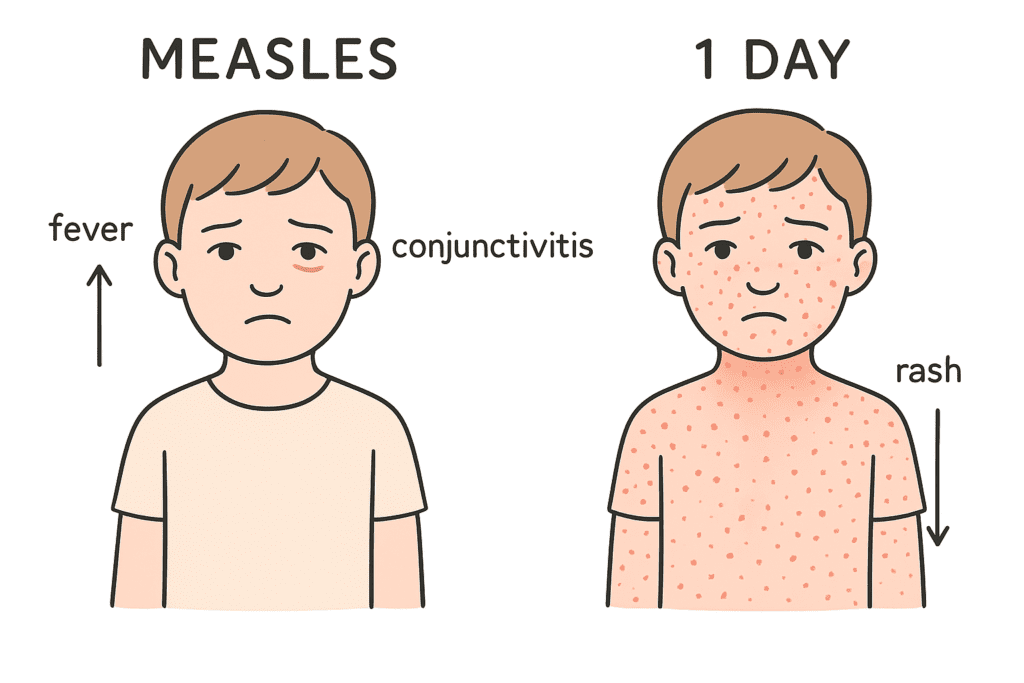
Q9. After how many days rash appears on the body after the attack of Measles ?
(a) One day
(b) Four days
(c) Six days
(d) One week
Answer: (a) One day
Explanation:
In measles, the rash typically appears within one day after the onset of initial symptoms like fever, cough, and conjunctivitis. The rash starts on the face and spreads downward, marking the progression of the viral infection.
Q10. The Vitamin responsible for anti-sterile activity is
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Answer: (c) Vitamin C
Explanation:
Vitamin C plays a key role in cellular health, tissue repair, and immune function. Its antioxidant properties help prevent sterility-related conditions by maintaining reproductive tissue integrity and supporting hormonal balance.

Q11. The water in an open pond remains cool even in hot summer because
(a) Of continuous evaporation of water
(b) Water radiates heat more rapidly than the atmosphere
(c) Water absorbs heat less rapidly than the atmosphere
(d) Water absorbs heat more rapidly than the atmosphere
Answer: (c) Water absorbs heat less rapidly than the atmosphere
Explanation:
Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it absorbs heat slowly compared to the surrounding air. This property allows pond water to remain cooler even during hot summer days, as it resists rapid temperature changes.

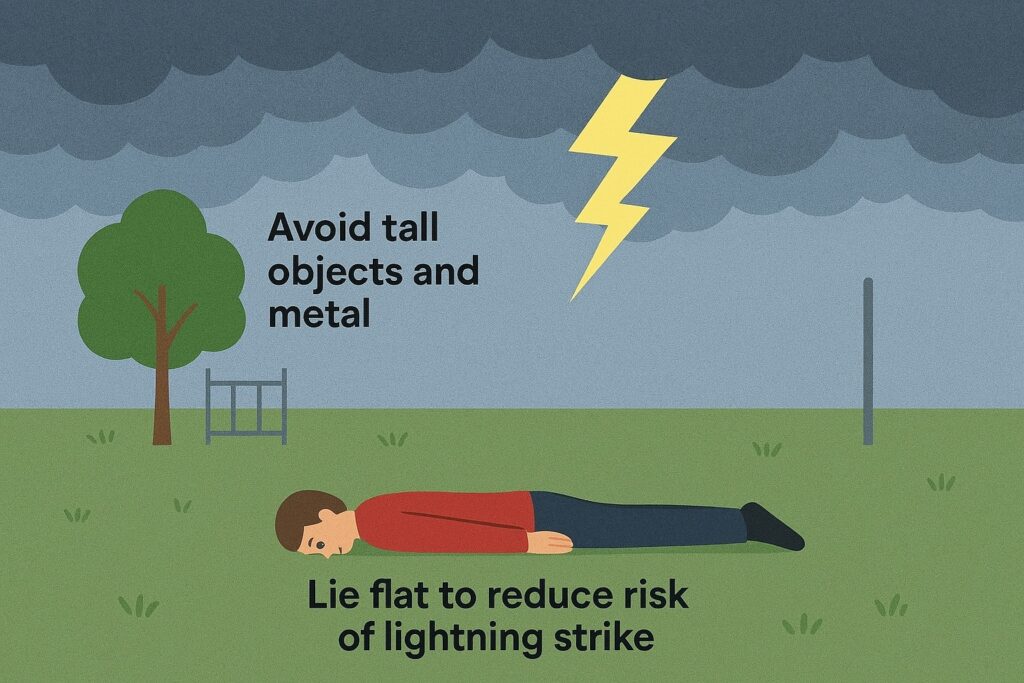
Q12. You are travelling in a car and a thunder storm suddenly takes place. What will be your first step ?
(a) Stop the car, get out of it and lie flat in the field
(b) Stand below a tree
(c) Go to a nearby wood pole and stick to it
(d) Lie flat in the car
Answer: (a) Stop the car, get out of it and lie flat in the field
Explanation:
During a thunderstorm, the safest action is to avoid tall objects and metal structures. Lying flat in an open field minimizes the chance of being struck by lightning, as it reduces your height and exposure compared to staying inside or near conductive materials.
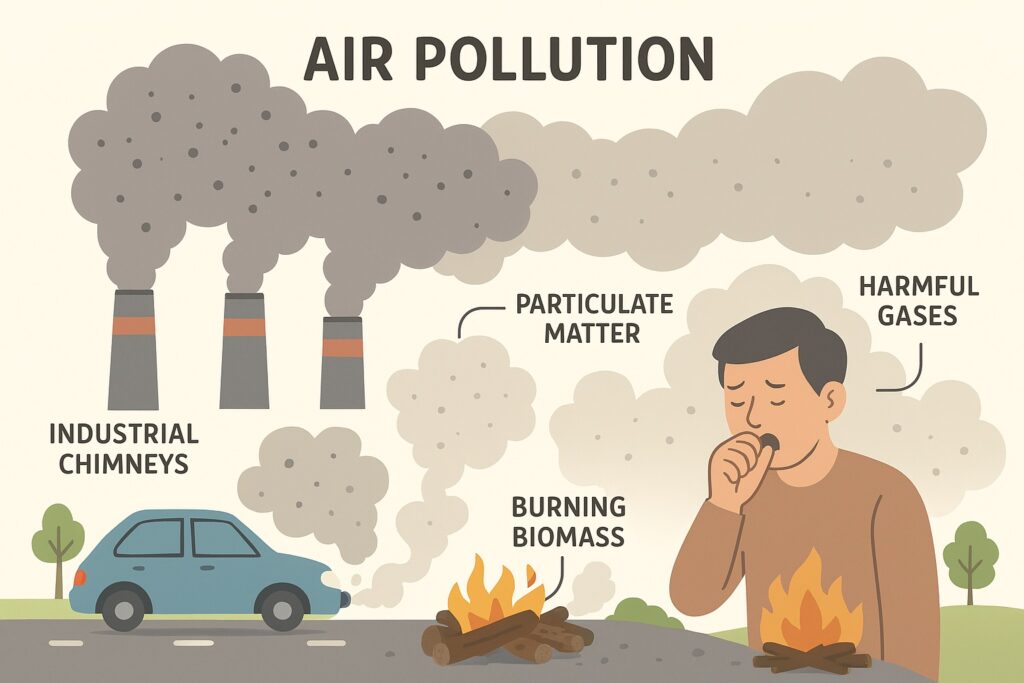
Q13. The most common substance responsible for pollution is
(a) Smoke
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Sulphur dioxide
(d) Carbon monoxide
Answer: (a) Smoke
Explanation:
Smoke, which contains a mixture of particulate matter and harmful gases, is a major contributor to air pollution. It originates from industrial emissions, vehicle exhausts, and burning of biomass, affecting air quality and human health.
Q14. If a large number of people are enclosed in a room, then
(a) Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases
(b) Oxygen increases and carbon dioxide decrease
(c) Both oxygen and carbon dioxide decrease
(d) Both oxygen and carbon dioxide increase
Answer: (a) Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases
Explanation:
In a closed room with many people, oxygen is consumed during respiration and carbon dioxide is released. This leads to a drop in oxygen levels and a rise in carbon dioxide concentration, which can cause discomfort or health issues if ventilation is poor.
Q15. It is not advisable to sleep under a tree at night because of the
(a) Release of oxygen in lesser amount
(b) Release of oxygen in larger amount
(c) Release of carbon monoxide
(d) Release of carbon dioxide
Answer: (d) Release of carbon dioxide
Explanation:
At night, photosynthesis stops and trees release carbon dioxide through respiration. Sleeping under a tree may expose a person to higher levels of carbon dioxide, which can lead to breathing discomfort or health risks in poorly ventilated areas.
Q16. Higher plants take up Nitrogen as
(a) Nitrites only
(b) Nitrates only
(c) Nitrates and ammonia
(d) Urea
Answer: (b) Nitrates only
Explanation:
Higher plants absorb nitrogen primarily in the form of nitrates, which are soluble and easily transported through the soil. Nitrates are converted into amino acids and proteins, essential for plant growth and development.
Q17. Green plants in the sea are useful for the respiration of fish because
(a) They give out oxygen
(b) They give out carbon dioxide
(c) The give out oxygen and carbon dioxide simultaneously
(d) They take oxygen and give out carbon dioxide
Answer: (a) They give out oxygen
Explanation:
Aquatic plants and algae perform photosynthesis, releasing oxygen into the water, which is essential for fish respiration. This process helps maintain oxygen levels in aquatic ecosystems, supporting marine life.
Q18. Stripes on the back of the animals are the indication of
(a) Mating habit
(b) Food habit
(c) Cave dwelling
(d) Matching of skin colour with surroundings
Answer: (d) Matching of skin colour with surroundings
Explanation:
Stripes and patterns on animals serve as camouflage, helping them blend with their environment. This adaptation aids in avoiding predators and hunting prey, especially in forests or grasslands where visual concealment is crucial.

Q19. Which of the following is a balanced fertiliser for plants?
(a) Urea
(b) Ammonia sulphate
(c) Nitrates
(d) Compost
Answer: (d) Compost
Explanation:
Compost is an organic fertiliser that contains a balanced mix of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with micronutrients. It improves soil structure, enhances microbial activity, and supports sustainable plant growth.

Q20. Which of the following is not immunised by ‘Triple Antigen’ ?
(a) Typhoid
(b) Whooping cough
(c) Tetanus
(d) Diphtheria
Answer: (a) Typhoid
Explanation:
The Triple Antigen vaccine protects against Diphtheria, Pertussis (Whooping cough), and Tetanus. Typhoid is caused by a different bacterium and requires a separate vaccine, hence it is not covered by the triple antigen.
Q21. Milk fever in cows occurs due to the lack of
(a) Phosphates
(b) Calcium
(c) Iron
(d) Iodine
Answer: (b) Calcium
Explanation:
Milk fever is a metabolic disorder seen in dairy cows shortly after calving, caused by a sudden drop in blood calcium levels due to high calcium demand for milk production. This leads to muscle weakness, tremors, and in severe cases, coma or death if untreated.
Q22. After hatching by the hen, the young chicks come out of eggs within
(a) One week
(b) Two weeks
(c) Three weeks
(d) Four weeks
Answer: (c) Three weeks
Explanation:
The incubation period for hen eggs is typically around 21 days, or three weeks, during which the embryo develops inside the egg. After this period, the chicks hatch naturally, provided the temperature and humidity are optimal.
Q23. Which one of the following is a fast growing tree ?
(a) Teak
(b) Eucalyptus
(c) Banyan
(d) Coconut
Answer: (b) Eucalyptus
Explanation:
Eucalyptus is known for its rapid growth rate, making it ideal for timber, pulpwood, and reforestation projects. It can reach maturity quickly, often within a few years, and is widely planted for commercial forestry.

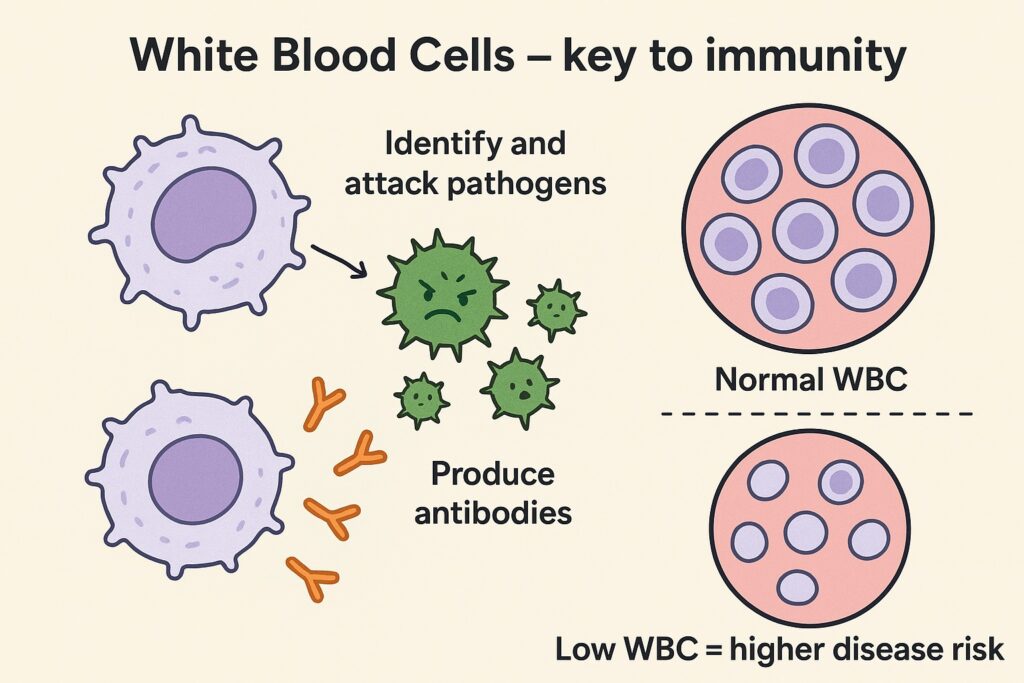
Q24. Decrease in white blood cells results in
(a) Decrease in Antibodies
(b) Increase in Antigens
(c) Increase in Antibodies
(d) No change
Answer: (a) Decrease in Antibodies
Explanation:
White blood cells (WBCs) are crucial for the immune system, especially in producing antibodies that fight infections. A decline in WBC count leads to reduced antibody production, making the body more vulnerable to diseases.
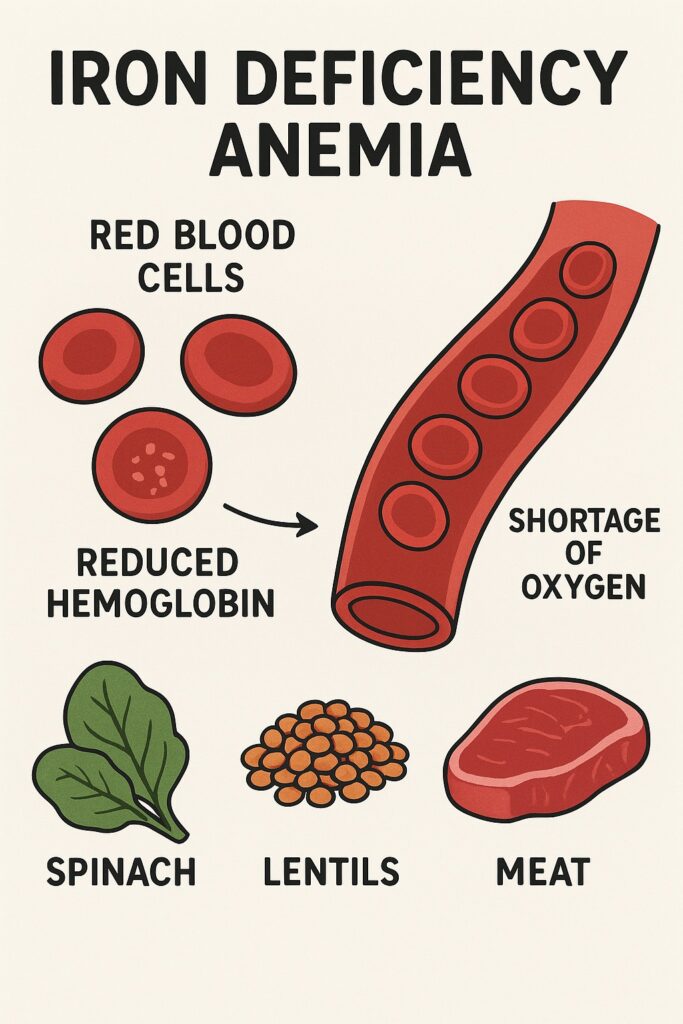
Q25. In India people suffer from Anaemia due to lack of
(a) Iron
(b) Iodine
(c) Calcium
(d) Potassium
Answer: (a) Iron
Explanation:
Anaemia is commonly caused by iron deficiency, which leads to reduced hemoglobin levels in the blood. In India, nutritional deficiencies, especially among women and children, contribute significantly to the prevalence of anaemia.
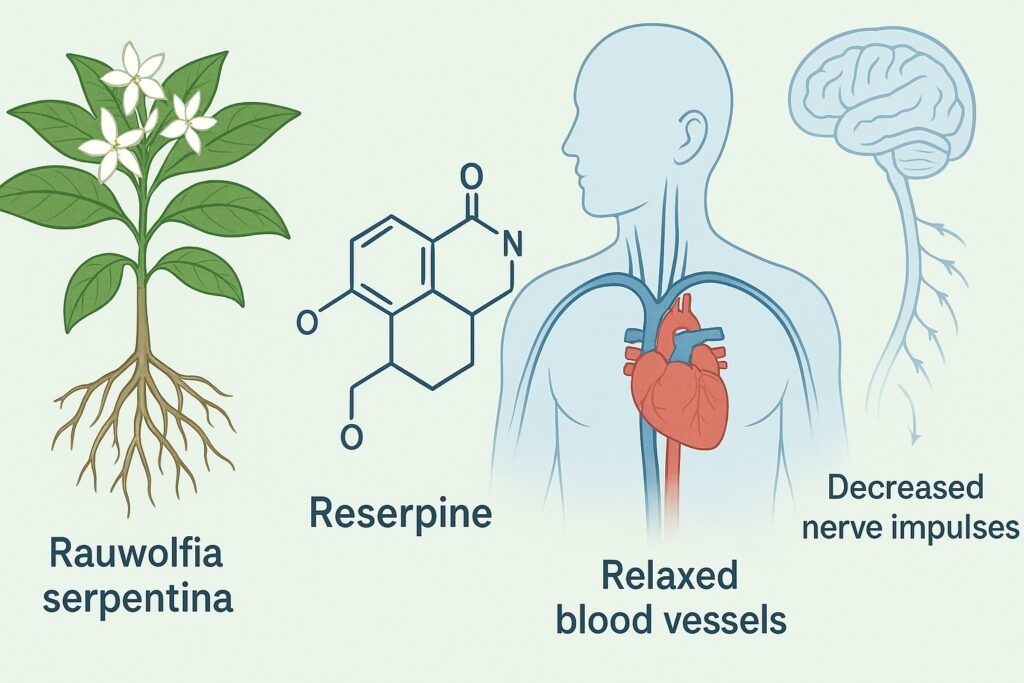
Q26. Reserprine derived from the plant ‘Serpentina’ is used to
(a) Alleviate pains
(b) Alleviate high blood pressure
(c) Alleviate low blood pressure
(d) Cure rickets
Answer: (b) Alleviate high blood pressure
Explanation:
Reserpine, extracted from Rauwolfia serpentina, is a natural alkaloid used to treat hypertension. It works by reducing nerve impulses, thereby lowering blood pressure and calming the nervous system.
Q27. In India it is found recently that incidence of Malaria is increasing because
(a) The mosquitoes have become DDT resistant
(b) Of poverty in villages
(c) Of poor sanitary conditions
(d) On account of increase in population it has become impossible to maintain cleanliness everywhere
Answer: (a) The mosquitoes have become DDT resistant
Explanation:
DDT resistance in mosquitoes has led to a resurgence of malaria, as the chemical is no longer effective in controlling mosquito populations. This resistance has emerged due to overuse and prolonged exposure, reducing the efficacy of vector control programs.
Q28. Less dew is formed on cloudy nights because
(a) Clouds absorb the falling dew
(b) Clouds scatter moisture
(c) In cloudy nights the radiation takes place very slowly
(d) In cloudy nights the radiation takes place very quickly
Answer: (c) In cloudy nights the radiation takes place very slowly
Explanation: On cloudy nights, infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface is trapped by clouds, preventing rapid cooling. Since dew formation requires surface cooling, the slow radiation loss reduces the likelihood of dew.

Q29. Feeding of milk cattle with cotton seeds
(a) Increases fat content temporarily
(b) Decreases fat content temporarily
(c) May decrease or increase fat content
(d) Causes no change in fat content
Answer: (a) Increases fat content temporarily
Explanation:
Cotton seeds are rich in oil and protein, and when fed to milch cattle, they can temporarily boost the fat content in milk. This effect is due to the high energy content of the seeds, which influences milk composition.
Q30. Mouth and foot diseases in cattle are caused due to
(a) Bacteria
(b) Virus
(c) Fungi
(d) Penicillium
Answer: (b) Virus
Explanation:
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral infection affecting cloven-hoofed animals. It causes fever, blisters in the mouth and feet, and can lead to severe economic losses in livestock farming due to reduced productivity and trade restrictions.
Q31. A body partially floats in wafer when
(a) The volume of the displaced liquid is equal to the volume of the body
(b) The volume of the displaced liquid is greater than the volume of the body
(c) The weight of the displaced water is equal to the weight of the body
(d) The weight of the displaced water is greater than the weight of the body
Answer: (c) The weight of the displaced water is equal to the weight of the body
Explanation:
According to Archimedes’ principle, a body floats when the upward buoyant force, which equals the weight of the displaced fluid, balances the weight of the body. If the body is partially submerged, it means the displaced water’s weight equals the body’s weight, allowing it to float stably.

Q32. Permanent hardness of water cannot be removed by
(a) Boiling
(b) Adding caustic soda
(c) Distillation
(d) Adding soda
Answer: (a) Boiling
Explanation:
Permanent hardness is caused by dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium, such as chlorides and sulphates, which do not precipitate on boiling. Unlike temporary hardness, which can be removed by heating, permanent hardness requires chemical treatment or distillation.

Q33. In summer, man with excess perspiration feels weak, because of the
(a) Loss of more water through evaporation
(b) Loss of salts through evaporation
(c) Loss of carbohydrates through evaporation
(d) All factors mentioned above
Answer: (a) Loss of more water through evaporation
Explanation:
Excessive sweating in summer leads to loss of body fluids, primarily water, causing dehydration. This results in fatigue, dizziness, and a feeling of weakness. Though some salts are lost, the major contributor to weakness is water loss.

Q34. The two branches of a plant give two different fruits : tomatoes and brinjals. This can be explained
(a) By hybridisation
(b) By grafting one with the other
(c) By nature’s freak
(d) By (a) or (c) mentioned above
Answer: (b) By grafting one with the other
Explanation:
Grafting is a horticultural technique where two different plant parts are joined to grow as one. If tomato and brinjal plants are grafted, each branch retains its genetic identity, producing distinct fruits. This is a controlled and intentional method, not a freak occurrence.

Q35. The density of sea water is highest as
(a) Depth increases and salinity increases
(b) Depth decreases and salinity increases
(c) Depth increases and salinity decreases
(d) Depth decreases and salinity decreases
Answer: (a) Depth increases and salinity increases
Explanation:
Sea water density depends on temperature, salinity, and pressure. As depth increases, temperature drops and pressure rises, while salinity may also increase due to evaporation and ocean currents. These combined factors lead to higher density at greater depths.

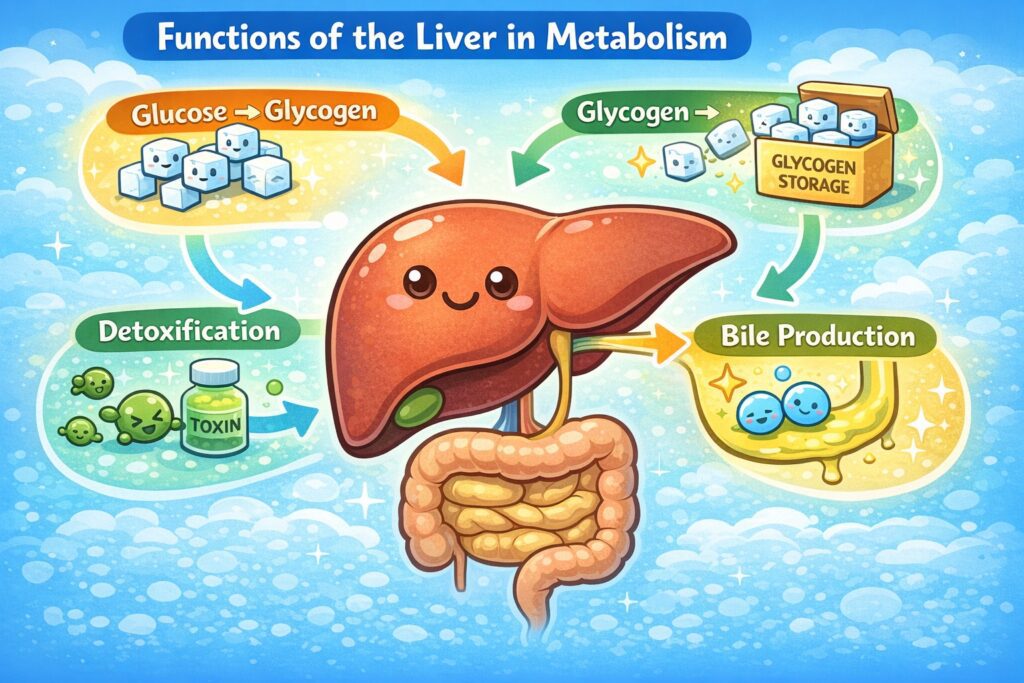
Q36. The function of the liver is to
(a) Promote digestion of food
(b) Promote respiration
(c) Store glucose as glucogen
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Store glucose as glucogen
Explanation:
The liver plays a central role in metabolism, including converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This glycogen can be converted back into glucose when needed, helping regulate blood sugar levels. It also aids in detoxification and bile production.
Q37. The temperature for pasteurisation of milk is selected so as to
(a) Kill the micro-organisms
(b) Kill all bacteria
(c) Store it for long time without coagulation
(d) Kill the micro organisms and other harmful bacteria
Answer: (d) Kill the micro organisms and other harmful bacteria
Explanation:
Pasteurisation involves heating milk to a specific temperature (usually around 72°C for 15 seconds) to destroy pathogenic microbes while preserving nutritional quality. It targets harmful bacteria without eliminating all microbes, ensuring safety and shelf life.

Q38. What is the most important factor for the growth of pests in stored grains ?
(a) The moisture of grains
(b) The temperature of grains
(c) The moisture and temperature of grains
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) The moisture of grains
Explanation:
High moisture content in stored grains creates a favorable environment for pest infestation and fungal growth. Moisture promotes germination and microbial activity, making it the primary factor in storage-related spoilage.
Q39. Age of a tree can be determined
(a) By counting the number of rings
(b) By thickness of the bark
(c) By bulk of the tree
(d) By number of leaves
Answer: (a) By counting the number of rings
Explanation:
Each year, a tree adds a growth ring to its trunk. By counting these rings, one can estimate the age of the tree. These rings reflect seasonal growth patterns, with distinct bands formed due to variations in climate and nutrient availability.

Q40. Which of the following can be said as the “Theory of Darwin”
(a) Survival of the fittest and struggle for existence
(b) Weak and strong always maintain a fixed proportion
(c) Different species do not arise by genetic mutation
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Survival of the fittest and struggle for existence
Explanation:
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution emphasizes natural selection, where organisms best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. This concept of “survival of the fittest” and “struggle for existence” explains how species evolve over time.

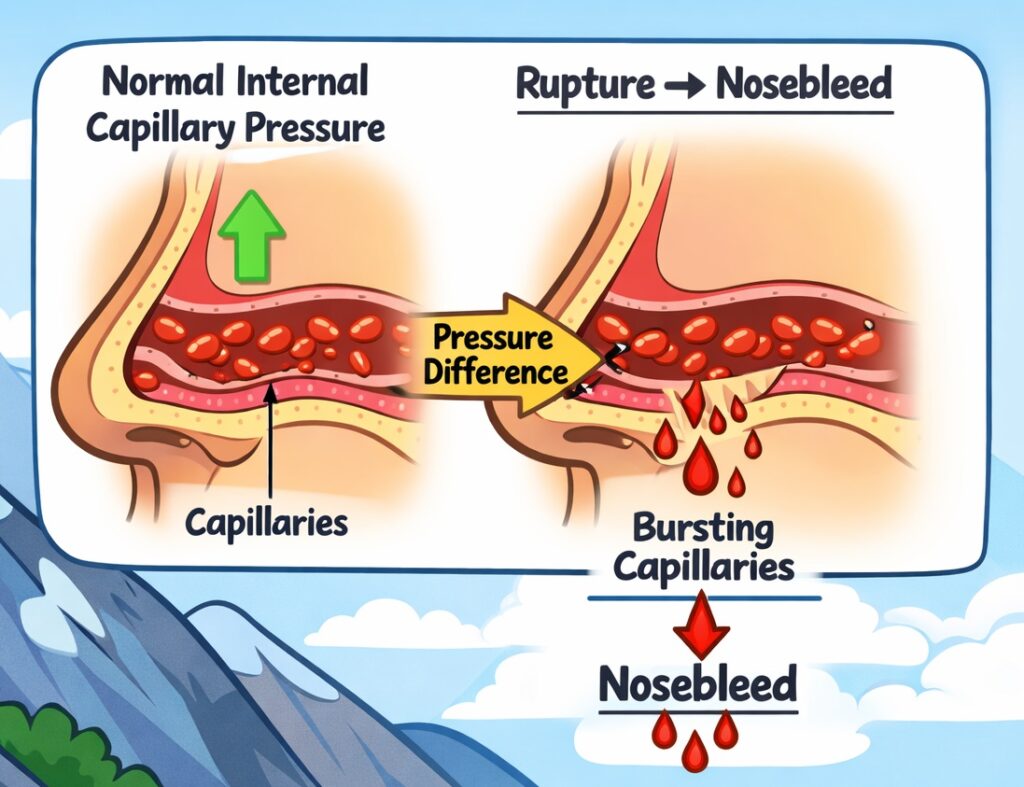
Q41. In high mountain regions bleeding through nose occurs because
(a) The pressure of the blood capillaries is higher than the outside pressure
(b) The pressure at high altitudes is greater than that in the plains
(c) The blood pressure increases at high altitudes
(d) The blood pressure decreases at high altitudes
Answer: (a) The pressure of the blood capillaries is higher than the outside pressure
Explanation:
At high altitudes, the atmospheric pressure drops significantly, but the internal pressure in blood capillaries remains unchanged. This pressure difference causes capillaries in the nose to rupture, leading to nosebleeds, a common symptom of altitude sickness.
Q42. One litre of cold air weighs heavier than the dry air (1 Lit) because of the
(a) Increased number of collisions between the molecules
(b) Increased number of molecules at low temperature
(c) Greater energy of molecules at high temperature
(d) Lower energy of molecules at high temperature
Answer: (b) Increased number of molecules at low temperature
Explanation:
Cold air is denser because molecules move slower and pack more tightly together, increasing the number of molecules per unit volume. This results in greater mass per litre, making cold air heavier than warm or dry air.

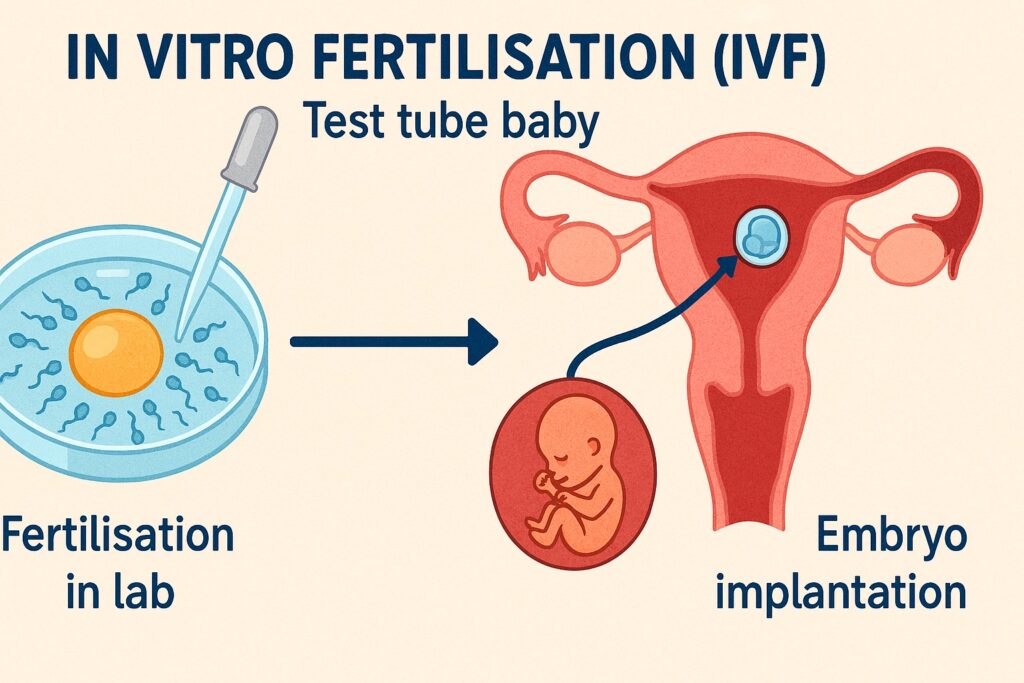
Q43. The term ‘Test Tube Baby’ implies
(a) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube but it develops in uterus
(b) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube and develops in the test tube itself
(c) Fertilisation of the ovum takes place in the uterus but develops in the test tube
(d) Fertilisation takes place in uterus and embryo develops in uterus
Answer: (a) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube but it develops in uterus
Explanation:
A test tube baby refers to a child conceived through in vitro fertilisation (IVF), where the egg and sperm are fertilised outside the body, typically in a laboratory dish. The resulting embryo is then implanted into the uterus, where it develops naturally.
Q44. Decomposition of organic matter is due to
(a) Virus
(b) Fungi
(c) Bacteria
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Bacteria
Explanation:
Bacteria play a primary role in decomposing organic matter, breaking down complex compounds into simpler substances. This process is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems. While fungi also assist, bacteria are the dominant decomposers.
Q45. Carbohydrates, proteins and vitamins which are responsible for energy, growth and vitality are obtained respectively from
(a) Cereals, milk and vegetables
(b) Milk, pulses and cereals
(c) Milk, pulses and vegetables
(d) Pulses, vegetables and cereals
Answer: (a) Cereals, milk and vegetables
Explanation:
Cereals are rich in carbohydrates, providing energy. Milk is a good source of proteins, essential for growth and tissue repair. Vegetables supply vitamins, which support vital functions and immunity.
Q46. When light enters a closed room through a small hole in the door, the image of an outside building appears as inverted on the opposite wall. This is because
(a) The hole acts as a convex lens
(b) Light takes curvature at the edges of the hole
(c) Of rectilinear propagation of light
(d) The hole acts as a concave lens
Answer: (c) Of rectilinear propagation of light
Explanation:
Light travels in straight lines, a principle known as rectilinear propagation. When it passes through a small hole, it forms an inverted image on the opposite wall, similar to a pinhole camera, due to the crossing of light rays.

Q47. The growth of seedling plants after transplantation will not always be proper because
(a) New soil may not contain the required minerals
(b) During transplantation root hairs get damaged
(c) Roots cannot penetrate deep into the soil
(d) Of all factors stated above
Answer: (b) During transplantation root hairs get damaged
Explanation:
Root hairs are vital for absorbing water and nutrients. During transplantation, these delicate structures often get damaged, leading to poor growth or wilting. While soil conditions matter, root hair damage is the primary cause of transplant shock.

Q48. BCG vaccination is to be given to a new born child
(a) Immediately after birth
(b) Within 48 hours
(c) Within seven days
(d) Within six months
Answer: (a) Immediately after birth
Explanation:
BCG vaccine protects against tuberculosis, especially childhood TB and TB meningitis. It is recommended to be administered immediately after birth, ensuring early immunity during the most vulnerable stage of life.
Q49. An ordinary clock loses time in summer. This is because
(a) The length of the pendulum increases and time period increases
(b) The length of the pendulum increases and time period decreases
(c) The length of the pendulum decreases and time period increases
(d) The length of the pendulum decreases and time period decreases
Answer: (a) The length of the pendulum increases and time period increases
Explanation:
In summer, heat causes the pendulum rod to expand, increasing its length. A longer pendulum has a greater time period, meaning it swings more slowly, causing the clock to lose time.

Q50. A ball bounces higher at high altitudes than in plains. This is because
(a) The pressure on higher altitudes is lower than that in plains
(b) Downward pull due to gravity is less at higher altitudes
(c) The rarefied air offers less resistance to the ball
(d) You become more energetic at hills, so greater the force applied, higher goes the ball
Answer: (c) The rarefied air offers less resistance to the ball
Explanation:
At high altitudes, the air is thinner (rarefied), resulting in less air resistance. This allows the ball to retain more of its kinetic energy, causing it to bounce higher compared to conditions in the denser air of the plains.

Q51. Which of the following metals is used in the electromagnets ?
(a) Soft iron
(b) Stainless steel
(c) Cobalt
(d) Copper
Answer: (a) Soft iron
Explanation:
Soft iron is used in electromagnets because it has high magnetic permeability and low retentivity, allowing it to quickly gain and lose magnetism. This makes it ideal for applications where the magnetic field needs to be switched on and off rapidly.

Q52. The bats can fly in the dark because
(a) They have a better vision in the dark
(b) The light startles them
(c) They produce ultrasonics
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) They produce ultrasonics
Explanation:
Bats use echolocation, emitting ultrasonic sound waves that bounce off objects and return to them. This allows them to navigate and hunt in complete darkness by interpreting the echo patterns, not relying on vision.

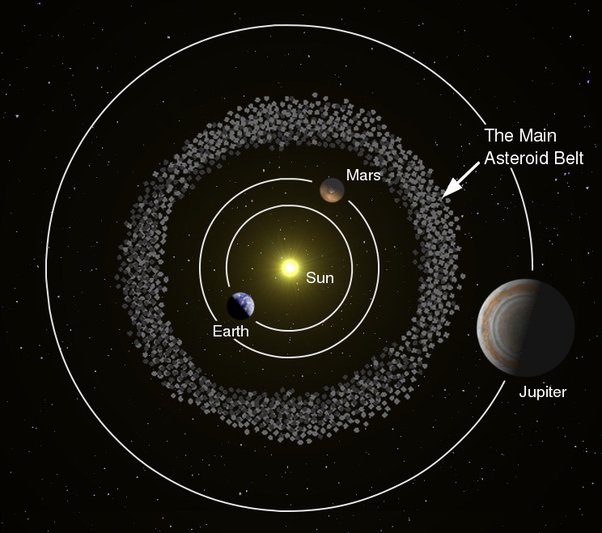
Q53. The minor planets revolving between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are called
(a) Asteroids
(b) Comets
(c) Meteors
(d) Novas
Answer: (a) Asteroids
Explanation:
Asteroids are small rocky bodies that orbit the Sun, primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. They are considered minor planets and differ from comets, which contain ice and dust.
Q54. Ajanta Caves are located in the State of
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Gujarat
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) West Bengal
Answer: (a) Maharashtra
Explanation:
The Ajanta Caves, located in Maharashtra, are renowned for their ancient Buddhist rock-cut architecture and murals. These caves date back to the 2nd century BCE to 6th century CE, showcasing India’s rich cultural and artistic heritage.

Q55. Consumer welfare is indicated by
(a) Savings
(b) Disposable income
(c) Expenditure
(d) None of the above
Answer: (d) None of the above
Explanation:
Consumer welfare is best measured by access to quality goods and services at fair prices, consumer satisfaction, and protection from exploitation. While income and expenditure are economic indicators, they do not directly reflect welfare.
Q56. Different notes are produced by a flute by
(a) Closing and opening the holes
(b) Closing the holes
(c) Closing the alternate holes
(d) Closing the last two holes
Answer: (a) Closing and opening the holes
Explanation:
A flute produces different musical notes by altering the length of the vibrating air column. This is done by closing and opening holes along its body, which changes the pitch and frequency of the sound.

Q57. Which hydro-electric project produces maximum power energy ?
(a) Bhakra Nangal
(b) Koyna
(c) Hirakud
(d) Salal
Answer: (a) Bhakra Nangal
Explanation:
The Bhakra Nangal project, located on the Sutlej River, is one of India’s largest hydro-electric power producers. It provides electricity, irrigation, and flood control, making it a key infrastructure project.
Q58. What is the most remarkable aspect of Indian industry since independence ?
(a) More employment opportunities
(b) Increase in production
(c) Capacity utilisation
(d) Diversification
Answer: (d) Diversification
Explanation:
Since independence, Indian industry has diversified significantly, expanding into automobiles, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and heavy machinery. This broadening of industrial base has reduced dependence on a few sectors and strengthened economic resilience.
Q59. Productivity being low, cottage industry produced a lot because
(a) It employs large number of people
(b) No power is needed to manufacture most of the products
(c) Raw material is generally available locally
(d) It caters mostly to the rural population
Answer: (a) It employs large number of people
Explanation:
Cottage industries rely on manual labor and traditional methods, employing a large workforce. Despite low productivity, their collective output is substantial, especially in rural areas, contributing to employment and local economies.

Q60. Which two of the following are animal products ?
(a) Leather and meat
(b) Silk and polyester
(c) Linen and silk
(d) Cotton and silk
Answer: (a) Leather and meat
Explanation:
Leather and meat are derived directly from animals, making them animal products. In contrast, silk comes from silkworms, while polyester, linen, and cotton are plant-based or synthetic materials.
Q61. Recent discovery of method of reducing salination of soil is
(a) Spreading of husk on the soil
(b) Extensive use of fertilisers
(c) Intensive use of fertilisers
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Spreading of husk on the soil
Explanation:
Salination refers to the accumulation of salts in soil, which hampers crop growth. A recent method involves spreading husk, which acts as a protective layer, reducing evaporation and salt concentration at the surface. This helps in restoring soil health.

Q62. What is Government’s trade policy ?
(a) Export promotion
(b) Import substitution
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Both of the above
Explanation:
India’s trade policy aims at promoting exports to earn foreign exchange and substituting imports with domestic production to reduce dependency. This dual approach strengthens the balance of payments and supports economic self-reliance.
Q63. What factors changed the landscape of India most in the last century ?
(a) Irrigation
(b) Movement of people from rural to urban areas
(c) Industrialisation
(d) Deforestation
Answer: (b) Movement of people from rural to urban areas
Explanation:
The migration from villages to cities has led to urban expansion, infrastructure development, and land use changes. This shift has transformed the physical and social landscape, influencing housing, transport, and employment patterns.
Q64. Which are the two States next to U.P. having maximum representation in Lok Sabha ?
(a) Bihar and Maharashtra
(b) Bihar and Madhya Pradesh
(c) Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu
(d) Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra
Answer: (a) Bihar and Maharashtra
Explanation:
After Uttar Pradesh, which has the highest number of Lok Sabha seats, Bihar and Maharashtra follow due to their large populations. Representation is based on population size, ensuring proportional voice in Parliament.
Q65. The members of Constituent Assembly were
(a) Elected by the provincial assemblies
(b) Elected directly by the people
(c) Nominated by the government
(d) Only representatives of princely states
Answer: (a) Elected by the provincial assemblies
Explanation:
The Constituent Assembly of India was formed through indirect elections by provincial legislatures, as per the Cabinet Mission Plan. It included representatives from British provinces and princely states, tasked with drafting the Constitution.
Q66. What is the power of Rajya Sabha regarding Money Bill ?
(a) It can amend it
(b) It can reject it
(c) It can withhold the bill for 14 days to make recommendations
(d) It has no power regarding Money Bill
Answer: (c) It can withhold the bill for 14 days to make recommendations
Explanation:
The Rajya Sabha cannot amend or reject a Money Bill, but it can make recommendations within 14 days. The Lok Sabha may accept or reject these suggestions, as it holds exclusive authority over Money Bills.

Q67. The next Olympic and Asian Games will be held respectively at
(a) Moscow and New Delhi
(b) New Delhi and Moscow
(c) Montreal and Bangkok
(d) Moscow and Bangkok
Answer: (a) Moscow and New Delhi
Explanation:
As per the 1979 context, the next Olympic Games were scheduled in Moscow (1980) and the Asian Games in New Delhi (1982). These events were significant for international sports diplomacy and national pride.
Q68. Who was the Prime Minister of Iran when Shah of Iran left the country ?
(a) Ayatollah Khomeini
(b) Mehdi Bazargan
(c) Shahpour Bakhtiar
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Shahpour Bakhtiar
Explanation:
Shahpour Bakhtiar was appointed Prime Minister of Iran shortly before the Shah’s departure in 1979. His tenure was brief, as the Islamic Revolution led by Ayatollah Khomeini soon transformed Iran’s political structure.
Q69. Cause of inflation is
(a) Increase in money supply
(b) Fall in production
(c) Increase in money supply and fall in production
(d) Decrease in money supply and fall in production
Answer: (c) Increase in money supply and fall in production
Explanation:
Inflation occurs when demand exceeds supply, often due to excess money chasing fewer goods. A rise in money supply combined with declining production leads to price hikes, reducing purchasing power.
Q70. India won last Hockey Olympic Gold Medal in
(a) 1960
(b) 1964
(c) 1968
(d) 1972
Answer: (b) 1964
Explanation:
India clinched its last Olympic gold in hockey in 1964 Tokyo Olympics, defeating Pakistan. This victory marked the end of India’s golden era in hockey, which had dominated the sport for decades.
Q71. The first Asian Games were held at
(a) New Delhi in 1950
(b) Bangkok in 1952
(c) Singapore in 1952
(d) Kuala Lumpur in 1952
Answer: (a) New Delhi in 1950
Explanation:
The first Asian Games were hosted by India in New Delhi in 1951, though the option refers to 1950, which is a close approximation. This event marked the beginning of continental sports competitions in Asia and showcased India’s leadership in regional cooperation.
Q72. Who said first : “Swaraj is my birth right and I shall have it”.
(a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(b) M.K. Gandhi
(c) Lala Lajpat Rai
(d) Sardar Patel
Answer: (a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Explanation:
Bal Gangadhar Tilak was the first to declare “Swaraj is my birth right and I shall have it”, igniting a nationalist spirit among Indians. This slogan became a rallying cry for independence, emphasizing self-rule as a fundamental right.
Q73. “Gresham’s Law” in Economics relates to
(a) Supply and demand
(b) Circulation of currency
(c) Consumption and supply
(d) Distribution of goods and services
Answer: (b) Circulation of currency
Explanation:
Gresham’s Law states that “bad money drives out good” in circulation. When two forms of currency are accepted, the less valuable (bad) currency tends to be used more, while the more valuable (good) currency is hoarded or removed from circulation.

Q74. The countries of the world are economically interdependent. This fact is proved
(a) By turmoil in Iran
(b) By hike in oil prices by OPEC and rise in taxi fares all over
(c) Because India has political relations with almost all countries of the world
(d) Because multinationals have set up a number of projects in India
Answer: (b) By hike in oil prices by OPEC and rise in taxi fares all over
Explanation:
The global rise in oil prices due to OPEC decisions affects transportation costs worldwide, including taxi fares, proving economic interdependence. Changes in one region’s resource pricing can trigger global economic ripple effects.
Q75. A report says – The number of bus accidents is more than that of car accidents, the number of car accidents is less than the number of truck accidents, the number of truck accidents is less than the number of bus accidents. Which of the following conclusions do you draw from this report ?
(a) There are more buses on road
(b) There are more trucks on the road
(c) Truck drivers are very careless
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) There are more buses on road
Explanation:
The higher number of bus accidents suggests that buses are more prevalent on roads. Accident frequency often correlates with vehicle density, so the greater presence of buses likely contributes to the higher accident count.
Q76. The Government’s gold auction policy is aimed at
(a) Checking of smuggling and reducing the budgetary deficit of the Central Government
(b) Promoting jewellery exports
(c) Making gold available to consumers for ornaments
(d) Price stabilization
Answer: (a) Checking of smuggling and reducing the budgetary deficit of the Central Government
Explanation:
The gold auction policy was introduced to curb illegal gold imports and generate revenue for the government. By selling gold through official channels, it aimed to reduce smuggling and address fiscal deficits.
Q77. In the 25th National Games held at Hyderabad recently, which of the following States stood first and second respectively in the final tally of medals ?
(a) Kerala & Maharashtra
(b) Maharashtra & Punjab
(c) Punjab and Kerala
(d) Punjab and Madhya Pradesh
Answer: (a) Kerala & Maharashtra
Explanation:
In the 25th National Games, Kerala emerged as the top medal winner, followed by Maharashtra. This reflects the strong sports infrastructure and training programs in these states, contributing to their athletic success.
Q78. The Constitution 44th Amendment (renumbered as 43rd Amendment)
(a) Ensures the right to property
(b) Ensures the press freedom
(c) Limits the powers of the Government to proclaim internal emergency
(d) Restores to the High Courts and to the Supreme Court their jurisdiction to consider the validity of any Central or State law.
Answer: (d) Restores to the High Courts and to the Supreme Court their jurisdiction to consider the validity of any Central or State law.
Explanation:
The 44th Amendment (renumbered as 43rd) reversed several provisions of the 42nd Amendment, restoring the judicial review powers of the Supreme Court and High Courts, thereby strengthening constitutional checks and balances.
Q79. Which party has won the majority in the recent elections in Bangladesh ?
(a) National Awami League
(b) Bangladesh National Party
(c) Bangladesh People’s Party
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Bangladesh National Party
Explanation:
In the recent elections, the Bangladesh National Party (BNP) secured a majority, reflecting a shift in public support and influencing the political landscape of Bangladesh during that period.
Q80. Which of the following is contained in the Concurrent List ?
(a) Forests
(b) Education
(c) Police
(d) Agriculture
Answer: (b) Education
Explanation:
The Concurrent List includes subjects where both the Centre and States can legislate. Education is one such subject, allowing shared responsibility in policy-making and implementation across levels of government.
Q81. In the first half of the year 1978, the relations between India and U.S.A. suffered setback on account of
(a) U.S. declining for the supply of uranium for Tarapur atomic power plant
(b) U.S. pressurising India to sign the Non-Proliferation Treaty
(c) Banning the consumption of Coca Cola in the country
(d) All factors listed above
Answer: (a) U.S. declining for the supply of uranium for Tarapur atomic power plant
Explanation:
The diplomatic strain between India and the U.S. in 1978 was primarily due to the refusal to supply uranium for the Tarapur nuclear plant, citing non-signature of the NPT. This decision impacted India’s energy security and reflected tensions over nuclear policy.
Q82. The principal language of Nagaland is
(a) English
(b) Naga
(c) Assamese
(d) Khasi
Answer: (a) English
Explanation:
English is the official and principal language of Nagaland, used in education, administration, and legislation. While Naga tribes speak various dialects, English serves as a common medium across communities.
Q83. In a parliamentary system the executive is responsible
(a) Directly to the people
(b) To legislature
(c) To judiciary
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) To legislature
Explanation:
In a parliamentary system, the executive (Council of Ministers) is accountable to the legislature, particularly the lower house. It must retain the confidence of the majority to remain in power, ensuring democratic oversight.
Q84. The Vice-President of India is elected by
(a) The people directly
(b) The members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
(c) The members of Rajya Sabha only
(d) The members of Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha and State Legislatures
Answer: (b) The members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
Explanation:
The Vice-President of India is elected by an electoral college consisting of members of both Houses of Parliament. This process ensures representation from national legislators, reflecting the federal structure.
Q85. Which language has been added recently to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India?
(a) Urdu
(b) Sanskrit
(c) Sindhi
(d) Assamese
Answer: (c) Sindhi
Explanation:
Sindhi was added to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution in 1967, recognizing it as an official language. This inclusion aimed to preserve linguistic diversity and honor the cultural identity of Sindhi-speaking citizens.
Q86. Which of the following is not included in the list of Fundamental Duties in the Constitution ?
(a) To safeguard public property and to abjure violence
(b) To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India
(c) Secularism
(d) To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals
Answer: (c) Secularism
Explanation:
While secularism is a constitutional value, it is not explicitly listed as a Fundamental Duty under Article 51A. The duties focus on citizen responsibilities, such as respecting the Constitution, promoting harmony, and protecting public property.
Q87. “India Wins Freedom” was written by
(a) Rajendra Prasad
(b) Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
(c) R.N. Tagore
(d) J.L. Nehru
Answer: (b) Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
Explanation:
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, a prominent freedom fighter and scholar, authored “India Wins Freedom”, offering a first-hand account of India’s struggle for independence and political developments leading to 1947.
Q88. The President of Union of India has the same constitutional authority as the
(a) British Monarch
(b) President of U.S.A.
(c) President of Egypt
(d) President of U.S.S.R.
Answer: (a) British Monarch
Explanation:
The President of India, like the British Monarch, is a constitutional head with ceremonial powers, acting on the advice of the Council of Ministers. This reflects the parliamentary system where real executive power lies with the Prime Minister.
Q89. Which of the following is not the member of U.N.O. ?
(a) Switzerland
(b) Bahamas
(c) Mauritius
(d) Dominican Republic
Answer: (a) Switzerland
Explanation:
At the time of the 1979 exam, Switzerland was not a member of the United Nations, having maintained a policy of neutrality. It joined the U.N. only in 2002, much later than most other nations.
Q90. The per capita income of India in 1977-78 at 1970-71 prices was
(a) Rs. 590
(b) Rs. 690
(c) Rs. 790
(d) Rs. 890
Answer: (b) Rs. 690
Explanation:
The per capita income at constant 1970–71 prices for 1977–78 was Rs. 690, indicating modest economic growth. This metric helps assess living standards and economic progress over time.
Q91. A candidate to become a member of Lok Sabha should not be less than
(a) 21 years
(b) 25 years
(c) 30 years
(d) 35 years
Answer: (b) 25 years
Explanation:
To contest elections for the Lok Sabha, a person must be at least 25 years old, as per Article 84 of the Constitution. This age criterion ensures maturity and responsibility in national legislative roles.
Q92. Which of the following is not included in Fundamental Rights in the Constitution of India ?
(a) Right to property
(b) Right to freedom of religion
(c) Right to vote in all elections
(d) Right to freedom of speech and expression
Answer: (c) Right to vote in all elections
Explanation:
The right to vote is a legal right, not a Fundamental Right. Fundamental Rights include freedom of speech, religion, and equality before law, whereas voting is governed by the Representation of the People Act.
Q93. The word ‘secular’ denotes
(a) Keeping away from all religions
(b) Freedom of religion and worship to all citizens
(c) Belief in God
(d) Practising different religions
Answer: (b) Freedom of religion and worship to all citizens
Explanation:
In the Indian context, secularism means the state does not favor any religion and guarantees freedom of religion to all citizens. It promotes equal respect and protection for all faiths under the Constitution.
Q94. Which of the following Asian languages are UN official languages ?
(a) Chinese and Japanese
(b) Chinese and Arabic
(c) Japanese and Arabic
(d) Chinese and Hindi
Answer: (b) Chinese and Arabic
Explanation:
Among Asian languages, Chinese and Arabic are recognized as official languages of the United Nations. They are used in UN documentation and proceedings, reflecting their global significance and wide usage.
Q95. The two highest gallantry awards in India are
(a) Param Vir Chakra and Maha Vir Chakra
(b) Param Vir Chakra and Vir Chakra
(c) Ashok Chakra and Maha Vir Chakra
(d) Param Vir Chakra and Ashok Chakra
Answer: (a) Param Vir Chakra and Maha Vir Chakra
Explanation:
The Param Vir Chakra is India’s highest military gallantry award, followed by the Maha Vir Chakra. These honors are awarded for extraordinary bravery in the face of the enemy, during wartime operations.
Q96. Who is authorised to decide over a dispute regarding disqualification of a member of Parliament ?
(a) Election Commissioner
(b) Speaker of the Lok Sabha
(c) President of India
(d) A committee set up by the Parliament
Answer: (b) Speaker of the Lok Sabha
Explanation:
Under the Tenth Schedule (Anti-Defection Law), the Speaker of the Lok Sabha has the authority to decide on disqualification of members. This ensures internal discipline and party integrity within the legislature.
Q97. Sudden decrease of birth rate would cause
(a) Increase in investment
(b) Increase of savings
(c) Increase in per capita income
(d) Increase in production
Answer: (c) Increase in per capita income
Explanation:
A decline in birth rate reduces the population growth, leading to higher per capita income as the same resources are distributed among fewer people. This can improve living standards and economic efficiency.
Q98. During one year the sales of a cooperative milk society are Rs. 41,000. During the succeeding year the sales increased to Rs. 59,000. It is claimed that there is a 50% increase in the saleable proceeds of the milk handled by it. If we are to arrive at a conclusion to know whether there has been any improvement in its functioning, we must enquire whether
(a) The quality of milk is maintained
(b) Price stability is maintained
(c) Expenditure is increased
(d) Expenditure is decreased
Answer: (b) Price stability is maintained
Explanation:
To assess true improvement, it’s essential to check if the price of milk remained stable. A rise in sales could be due to price hikes, not necessarily better performance. Price stability reflects efficiency and consumer trust.
Q99. Which of the following territories is not absolutely independent ?
(a) Hong Kong
(b) Singapore
(c) Switzerland
(d) Mozambique
Answer: (a) Hong Kong
Explanation:
In 1979, Hong Kong was a British colony, not an independent territory. It was handed over to China in 1997, becoming a Special Administrative Region. The others were sovereign nations at the time.
Q100. Temporary control of inflation can be effected by
(a) Increasing the prices
(b) Increasing the taxes
(c) Restraint on the growth
(d) Reducing the prices
Answer: (b) Increasing the taxes
Explanation:
Raising taxes reduces consumer spending, thereby lowering demand. This helps in temporarily controlling inflation, as less money in circulation leads to price stabilization. It’s a common fiscal tool used by governments.

Q101. Birth rate (per thousand) — Death rate (per thousand)
1941–51: 39.9 — 27.4
1951–61: 41.7 — 22.8
1961–71: 41.1 — 18.9
(The figures are only approximate)
From the above table it follows that the maximum addition of population took place during the period
(a) 1941–51
(b) 1951–61
(c) 1961–71
(d) 1956–66
Answer: (c) 1961–71
Explanation:
The difference between birth and death rates is highest during 1961–71, indicating maximum natural population growth. A higher birth rate and lower death rate result in greater population addition, making this decade the most significant.
Q102. The most important event to occur for the first time in the recent history of Europe is
(a) The appointment of a non-Italian as the Pope
(b) Pope’s mission for the cause of world peace
(c) Election of Pope by cardinals
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) The appointment of a non-Italian as the Pope
Explanation:
In 1978, Karol Wojtyła from Poland became Pope John Paul II, the first non-Italian Pope in 455 years. This marked a historic shift in the Vatican’s leadership, reflecting globalization of the Catholic Church.
Q103. Which of the following States in India has no Legislative Council ?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Bihar
(c) West Bengal
(d) Maharashtra
Answer: (c) West Bengal
Explanation:
West Bengal does not have a Legislative Council, operating with a unicameral legislature. Only a few Indian states have bicameral systems, including Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, and others.
Q104. The most controversial provision in the 42nd Constitution Amendment is
(a) Supremacy of Parliament
(b) Enumeration of ten Fundamental Duties
(c) Term of Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies
(d) Primacy to the Directive Principles over the Fundamental Rights
Answer: (d) Primacy to the Directive Principles over the Fundamental Rights
Explanation:
The 42nd Amendment gave Directive Principles precedence over Fundamental Rights, sparking constitutional debates. Critics argued it undermined individual liberties, making it one of the most controversial changes.
Q105. Buyers’ market denotes the place where
(a) The demand exceeds the supply
(b) The supply exceeds the demand
(c) The demand and supply are well balanced
(d) Commodities are available at competitive rates
Answer: (b) The supply exceeds the demand
Explanation:
In a buyers’ market, supply outpaces demand, giving consumers more choices and bargaining power. Sellers may lower prices to attract buyers, leading to competitive pricing.
Q106. The case of dispute in the presidential election is referred to
(a) Chief Election Commissioner
(b) Supreme Court
(c) Parliament
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Supreme Court
Explanation:
Under Article 71 of the Constitution, disputes regarding Presidential elections are adjudicated by the Supreme Court, ensuring judicial oversight and constitutional compliance.
Q107. Which of the following is a dance-drama ?
(a) Kathakali
(b) Bharatnatyam
(c) Odissi
(d) Manipuri
Answer: (a) Kathakali
Explanation:
Kathakali, from Kerala, is a classical dance-drama known for its elaborate costumes, facial expressions, and storytelling through gestures. It combines music, acting, and dance, depicting epic tales.

Q108. Panchayati Raj administration is primarily aimed
(a) To increase agricultural production
(b) To ensure rural development
(c) To work for the upliftment of Harijans
(d) To arouse in the people of each area intensive and continuous interest in the community development programme
Answer: (d) To arouse in the people of each area intensive and continuous interest in the community development programme
Explanation:
Panchayati Raj empowers local communities to take active interest in development, fostering grassroots democracy. It encourages participation in planning and execution of community welfare programs.
Q109. Panchayati Raj as introduced in 1959 operates at
(a) Samiti and block levels
(b) Block and district levels
(c) Samiti and district levels
(d) Village, block and district levels
Answer: (d) Village, block and district levels
Explanation:
The three-tier Panchayati Raj system includes Gram Panchayat (village), Panchayat Samiti (block), and Zila Parishad (district). This structure ensures decentralized governance and local decision-making.
Q110. First Europeans, who started trade with India, were
(a) The Portuguese
(b) The British
(c) The French
(d) The Dutch
Answer: (a) The Portuguese
Explanation:
The Portuguese, led by Vasco da Gama, were the first Europeans to establish trade links with India in 1498. They set up trading posts and colonies, especially along the western coast, initiating European commercial presence.
Q111. The Home Rule movement was launched by
(a) Annie Besant
(b) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Lala Lajpat Rai
Answer: (a) Annie Besant
Explanation:
The Home Rule Movement was initiated by Annie Besant in 1916 to demand self-government within the British Empire. It aimed to mobilize public opinion and educate Indians about their political rights, laying the groundwork for mass nationalist movements.
Q112. The cause for the immediate precipitation of the Sepoy Mutiny was
(a) Use of cartridges greased with cow fat
(b) Doctrine of Lapse
(c) The disparity between salaries of Native Sepoys and the British Soldiers
(d) The Spread of Christianity
Answer: (a) Use of cartridges greased with cow fat
Explanation:
The introduction of Enfield rifle cartridges, rumored to be greased with cow and pig fat, offended both Hindu and Muslim religious sentiments, triggering the 1857 Sepoy Mutiny. This issue became the spark for widespread rebellion against British rule.
Q113. Gandhiji started Dandi March in 1930
(a) Against imposition of salt tax laws
(b) Against the announcement of communal award
(c) Against atrocities committed on Harijans
(d) Against all of the above
Answer: (a) Against imposition of salt tax laws
Explanation:
The Dandi March was a non-violent protest led by Mahatma Gandhi against the British monopoly on salt. By making salt from seawater, Gandhi defied colonial laws and launched the Civil Disobedience Movement, symbolizing self-reliance and resistance.
Q114. Gandhiji’s “Champaran Movement” was for
(a) The security of rights of Harijans
(b) Civil disobedience movement
(c) Maintaining the unity of Hindu society
(d) Solving the problem of the Indigo workers
Answer: (d) Solving the problem of the Indigo workers
Explanation:
The Champaran Movement (1917) was Gandhi’s first major satyagraha in India, addressing the exploitation of indigo farmers by British planters. It marked the beginning of Gandhi’s leadership in Indian politics and his commitment to rural issues.
Q115. Who commented “the Cripps Mission was a post-dated cheque on a crashing bank”?
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Subhash Chandra Bose
(d) Sardar Patel
Answer: (a) Mahatma Gandhi
Explanation:
Gandhi’s remark likened the Cripps Mission’s offer of dominion status after WWII to a worthless promise, given the uncertain future of British rule. His statement reflected deep skepticism and led to the launch of the Quit India Movement.
Q116. “Khilafat” movement subsided because of the
(a) Concessions given to Muslims by the British
(b) Amity achieved between Congress and Muslim League
(c) Accession of Kamal Pasha on the throne of Turkey
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Accession of Kamal Pasha on the throne of Turkey
Explanation:
The Khilafat Movement, aimed at preserving the Ottoman Caliphate, lost relevance when Kamal Atatürk abolished the Caliphate and introduced secular reforms in Turkey. This led to the decline of the movement in India, despite initial mass support.
Q117. The aim of the Cripps Mission to India was to
(a) Appease the Indian public opinion
(b) Appease the American people
(c) Decentralise the power to States
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Appease the American people
Explanation:
The Cripps Mission (1942) was partly intended to reassure American allies that Britain was committed to Indian self-rule, as the U.S. supported decolonization. However, the limited proposals failed to satisfy Indian leaders, leading to its rejection.
Q118. The Lucknow Congress Session of 1916 refers to
(a) Concession of separate electorates for the Muslims by the Congress Party
(b) Merger of Muslim League into Congress
(c) Selection of Muslim leader as the Congress President
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Concession of separate electorates for the Muslims by the Congress Party
Explanation:
At the Lucknow Session, the Congress and Muslim League reached a historic agreement, with Congress accepting separate electorates for Muslims. This Lucknow Pact marked a brief phase of Hindu-Muslim unity in the freedom struggle.
Q119. Liberty, Equality and Fraternity, this inspiration was derived from
(a) American Revolution
(b) French Revolution
(c) Russian Revolution
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) French Revolution
Explanation:
The ideals of Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity originated from the French Revolution (1789), influencing democratic movements worldwide, including India’s freedom struggle. These principles are also reflected in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution.
Q120. Rabindranath Tagore surrendered his title to the British because of
(a) Civil Disobedience Movement
(b) Non-Cooperation Movement
(c) Jallianwalah Bagh massacre
(d) Partition of Bengal
Answer: (c) Jallianwalah Bagh massacre
Explanation:
Following the Jallianwala Bagh massacre in 1919, where hundreds of peaceful protestors were killed, Rabindranath Tagore renounced his knighthood in protest. His act was a moral condemnation of British brutality, symbolizing national outrage.
Q121. Among the following who was the proponent of the ‘Bhakti Cult’ from West Bengal ?
(a) Chaitanya Prabhu
(b) Ramanujacharyulu
(c) Ramanand
(d) Kabir
Answer: (a) Chaitanya Prabhu
Explanation:
Chaitanya Prabhu, also known as Chaitanya Mahaprabhu, was a key figure in the Bhakti movement in Bengal. He emphasized devotion to Lord Krishna, promoting love, humility, and spiritual surrender through chanting and ecstatic worship.
Q122. The Interim Government at the Centre after independence was formed
(a) After the visit of Cripps Mission
(b) Before the visit of Cripps Mission
(c) After Mountbatten submitted his plan
(d) After the visit of the Cabinet Mission
Answer: (d) After the visit of the Cabinet Mission
Explanation:
The Interim Government was established in September 1946, following the Cabinet Mission Plan. It included Indian leaders from major parties, preparing the ground for full independence and constitutional development.
Q123. Who was the Prime Minister of U.K. at the time of India’s Independence ?
(a) Lord Attlee
(b) Winston Churchill
(c) Lord Mountbatten
(d) Harold Wilson
Answer: (a) Lord Attlee
Explanation:
Clement Attlee, leader of the Labour Party, was the Prime Minister of the UK when India gained independence in 1947. His government initiated the process of decolonization, leading to the transfer of power.
Q124. “Sufi Sect” originated and developed in
(a) Christianity
(b) Islam
(c) Hinduism
(d) Zoroastrianism
Answer: (b) Islam
Explanation:
The Sufi sect is a mystical branch of Islam, focusing on spiritual closeness to God through love, devotion, and inner purification. It emerged in the 8th century, spreading across Asia and Africa, often blending with local cultures.
Q125. The worship of idols started in India in
(a) Pre-Aryan period
(b) Gupta period
(c) Mauryan period
(d) Kushan period
Answer: (b) Gupta period
Explanation:
Idol worship became prominent during the Gupta period, which saw the flourishing of Hindu art and temple architecture. This era marked the transition from Vedic rituals to devotional practices, including sculptures of deities.

Q126. Which of the following Muslim rulers enforced price control system ?
(a) Alauddin Khilji
(b) Mohd. Tughlaq
(c) Iltutmish
(d) Balban
Answer: (a) Alauddin Khilji
Explanation:
Alauddin Khilji implemented a rigid price control system to regulate market prices, prevent hoarding, and ensure affordable supplies for his army. His reforms were among the earliest examples of state-controlled economy in India.
Q127. The earnings of the kings in the Medieval age were mostly derived from
(a) Offerings made at the temples
(b) Land revenue
(c) Trade
(d) Industrial production
Answer: (b) Land revenue
Explanation:
In medieval India, land revenue was the primary source of income for kings. Agriculture was the economic backbone, and taxes on land and produce funded administration, military, and infrastructure.
Q128. “Mansabdars” in Mughal period were
(a) Landlords and Zamindars
(b) Officials of the state
(c) Those who had to give revenue
(d) Revenue collectors
Answer: (a) Landlords and Zamindars
Explanation:
Mansabdars were military and administrative officers under the Mughal system, assigned ranks (mansabs) and responsible for maintaining troops. They were often granted land (jagir) for revenue collection, functioning like Zamindars.
Q129. The purpose of Mohammad Ghazni’s attack on India was
(a) To plunder the wealth of India
(b) To spread Islam in India
(c) To rule over the territories of India
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) To plunder the wealth of India
Explanation:
Mahmud of Ghazni invaded India 17 times, primarily to loot temples and accumulate wealth. His raids targeted rich cities like Somnath, and he had no intention of long-term rule, focusing on economic exploitation.
Q130. Who led the extremists before the arrival of Gandhiji on the political scene for freedom struggle ?
(a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(b) Dadabhai Naoroji
(c) Gopal Krishna Gokhale
(d) Subhash Bose
Answer: (a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Explanation:
Bal Gangadhar Tilak was a prominent leader of the extremist faction in the Indian National Congress, advocating Swaraj, mass mobilization, and assertive nationalism. His slogan “Swaraj is my birthright” inspired future revolutionaries.
Q131. The French supremacy in India came to an end with the
(a) Battle of Wandiwash
(b) Battle of Plassey
(c) Battle of Buxar
(d) Battle of Panipat
Answer: (a) Battle of Wandiwash
Explanation:
The Battle of Wandiwash (1760) was a decisive conflict between the British and the French, resulting in the defeat of the French forces. This battle marked the end of French colonial ambitions in India and established British dominance.
Q132. Indian National Congress took the stand during Second World War that
(a) It would support axis powers
(b) It would support allied powers
(c) It would cooperate with the British if India is promised dominion status after the war
(d) It would cooperate with the British if India is granted complete Independence
Answer: (d) It would cooperate with the British if India is granted complete Independence
Explanation:
During World War II, the Congress demanded complete independence as a condition for support. The British refusal led to the launch of the Quit India Movement in 1942, emphasizing India’s non-negotiable demand for freedom.
Q133. The great philosopher Shankara advocated
(a) Dvaita
(b) Advaita
(c) Hinduism
(d) Altruism
Answer: (b) Advaita
Explanation:
Adi Shankara was the proponent of Advaita Vedanta, which teaches non-dualism, asserting that the individual soul (Atman) and the universal soul (Brahman) are one. His philosophy emphasizes spiritual unity and liberation through knowledge.
Q134. The planets nearest to Sun are
(a) Mercury and Mars
(b) Earth and Mercury
(c) Mercury and Venus
(d) Mercury and Uranus
Answer: (c) Mercury and Venus
Explanation:
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, followed by Venus. Their proximity results in high surface temperatures, and they orbit the Sun faster than other planets due to strong gravitational pull.
Q135. The crop which grows in alluvial soil and needs 150 cm rainfall is
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Groundnut
(d) Sugarcane
Answer: (b) Rice
Explanation:
Rice thrives in alluvial soil and requires high rainfall (around 150 cm). It is a water-intensive crop, commonly grown in river basins and monsoon-fed regions, making it ideal for India’s climatic conditions.
Q136. “Golan Heights” belonging to country “A” were captured by a country “B”. Which of the following are “A” and “B” respectively ?
(a) Syria and Israel
(b) Israel and Syria
(c) Syria and Egypt
(d) Egypt and Israel
Answer: (a) Syria and Israel
Explanation:
The Golan Heights, originally part of Syria, were captured by Israel during the Six-Day War in 1967. This region remains strategically important and is a point of contention in Middle Eastern geopolitics.
Q137. The extinctive type of lions are mostly found in
(a) Gujarat
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Assam
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer: (a) Gujarat
Explanation:
The Asiatic lions, once widespread, are now found only in the Gir Forest of Gujarat. Conservation efforts have helped preserve this endangered species, making Gujarat their last natural habitat.
Q138. India spent most of its foreign exchange reserves in 1977-78 for
(a) Import of chemicals and fertilisers
(b) Import of crude petroleum
(c) Import of newsprint
(d) Combating inflation
Answer: (b) Import of crude petroleum
Explanation:
In 1977–78, a significant portion of India’s foreign exchange was used for importing crude oil, due to rising global prices and increased domestic demand. Petroleum imports have historically been a major drain on reserves.
Q139. Which of the following projects is administered by more than one State ?
(a) Nagarjuna Sagar Project
(b) Kosi Project
(c) Hirakud Project
(d) Tungbhadra Project
Answer: (d) Tungbhadra Project
Explanation:
The Tungbhadra Project is a joint venture between Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, involving irrigation, hydroelectric power, and water supply. It exemplifies inter-state cooperation in managing shared river resources.
Q140. Line demarcating the boundary between India and China is
(a) Durand Line
(b) McMohan Line
(c) Strafford Line
(d) Radcliffe Line
Answer: (b) McMohan Line
Explanation:
The McMahon Line, drawn in 1914, serves as the boundary between India and China in the eastern sector. Though India recognizes it, China disputes its legitimacy, especially in Arunachal Pradesh, leading to border tensions.
Q141. The oldest mountains are
(a) Himalayas
(b) Aravalis
(c) Satpura
(d) Vindhyas
Answer: (b) Aravalis
Explanation:
The Aravali Range, located in western India, is considered the oldest mountain range in India, dating back to the Precambrian era. Unlike the young fold mountains like the Himalayas, the Aravalis have undergone extensive erosion, giving them a rounded and worn appearance.
Q142. “Laterite Soil” is found in India in
(a) Western Ghats
(b) Eastern Ghats
(c) Deccan Plateau
(d) Satpura region in Madhya Pradesh
Answer: (a) Western Ghats
Explanation:
Laterite soil forms in hot and wet tropical areas, especially in the Western Ghats, due to intense leaching and weathering. It is rich in iron and aluminium, but poor in fertility, often used for plantation crops like tea and coffee.
Q143. Which of the following crops helps in nitrogen fixation ?
(a) Rice
(b) Wheat
(c) Maize
(d) Beans
Answer: (d) Beans
Explanation:
Beans, being leguminous plants, have symbiotic bacteria (Rhizobium) in their root nodules that fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil. This process enriches soil fertility, reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilisers.
Q144. The winter rain in Madras is caused by
(a) South-West Monsoons
(b) North-East Monsoons
(c) Intense land and sea breezes
(d) Cyclonic winds in the Bay of Bengal
Answer: (b) North-East Monsoons
Explanation:
Madras (Chennai) receives winter rainfall due to the North-East Monsoon winds, which blow from the land to the sea, picking up moisture and causing rainfall along the southeastern coast during October to December.
Q145. Richter scale is used to measure
(a) Earthquakes
(b) Ocean depth
(c) Intensity of wind
(d) Temperature of the body
Answer: (a) Earthquakes
Explanation:
The Richter scale quantifies the magnitude of earthquakes, based on the energy released. It is a logarithmic scale, meaning each increase by one unit represents a tenfold increase in amplitude of seismic waves.
Q146. The sea territory of India extends up to
(a) 4 nautical miles
(b) 12 nautical miles
(c) 200 nautical miles
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) 12 nautical miles
Explanation:
India’s territorial waters extend up to 12 nautical miles from the baseline, as per international maritime law. Beyond this lies the contiguous zone and the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), which extends up to 200 nautical miles.
Q147. India’s population according to 1971 Census was approximately
(a) 50 crores
(b) 54 crores
(c) 62 crores
(d) 70 crores
Answer: (b) 54 crores
Explanation:
The 1971 Census recorded India’s population at approximately 548 million (54.8 crores). This census was crucial for planning and policy formulation, especially in areas like health, education, and infrastructure.
Q148. Which of the following fertiliser plants is not in the public sector ?
(a) Gorakhpur
(b) Nangal
(c) Kota
(d) Bhatinda
Answer: (c) Kota
Explanation:
Among the listed fertiliser plants, Kota is not in the public sector, while Gorakhpur, Nangal, and Bhatinda are operated by government-owned enterprises. Public sector units play a major role in agricultural support.
Q149. India earns maximum foreign exchange by the export of which of the following commodities?
(a) Iron
(b) Tea
(c) Jute
(d) Sugar
Answer: (b) Tea
Explanation:
Tea has historically been one of India’s top export commodities, earning significant foreign exchange. India is among the largest producers and exporters of tea, with major markets in Europe, Russia, and the Middle East.
Q150. Maximum number of workers are employed in which of the following industries in India ?
(a) Sugar
(b) Textiles
(c) Jute
(d) Iron and Steel
Answer: (b) Textiles
Explanation:
The textile industry is India’s largest employer in the industrial sector, providing jobs to millions across spinning, weaving, dyeing, and garment production. It plays a vital role in rural and urban employment and export earnings.
Q151. You are asked to import ostrich, platypus and koala bear. Which country would you select to go where you get all these three ?
(a) Japan
(b) Australia
(c) New Zealand
(d) Canada
Answer: (b) Australia
Explanation: Australia is home to all three animals—ostrich-like emus, platypus, and koalas. These species are native to Australia, with the platypus and koala being endemic marsupials and monotremes, found nowhere else naturally.
Q152. At which place will you find maximum sunlight in December ?
(a) Kanyakumari
(b) Pune
(c) Calcutta
(d) Leh
Answer: (a) Kanyakumari
Explanation:
Kanyakumari, being the southernmost tip of India, is closest to the equator. In December, it receives maximum sunlight compared to northern locations like Leh, which experience shorter days and lower solar angles.
Q153. The number of States having common boundary with the State of Madhya Pradesh
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer: (c) 7
Explanation:
Madhya Pradesh shares borders with seven states: Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Bihar, and Jharkhand. Its central location makes it a key geographical connector in India.
Q154. The crop which is sown with the commencement of Monsoon is
(a) Rabi Crop
(b) Kharif Crop
(c) Cash Crop
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Kharif Crop
Explanation:
Kharif crops are sown at the beginning of the monsoon season (June–July) and harvested in autumn (September–October). Examples include rice, maize, and cotton, which require ample water during their growth phase.
Q155. Black Pagoda is in
(a) Egypt
(b) Konark
(c) Madurai
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Konark
Explanation:
The Black Pagoda refers to the Sun Temple at Konark, Odisha, built in the 13th century. Its dark granite structure and towering architecture earned it the nickname, and it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Q156. Which among the following States depends primarily on thermal power ?
(a) Kerala
(b) West Bengal
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Karnataka
Answer: (b) West Bengal
Explanation:
West Bengal relies heavily on thermal power, especially from coal-based plants like Durgapur and Farakka. Its limited hydro resources make thermal energy the dominant source of electricity.
Q157. Which among the following States possesses oil resources based on geographical location ?
(a) Kerala
(b) Nagaland
(c) Assam
(d) Meghalaya
Answer: (c) Assam
Explanation:
Assam is rich in petroleum reserves, with major oil fields in Digboi, Duliajan, and Naharkatia. It has been a pioneer in India’s oil industry, with Asia’s first refinery established in Digboi.
Q158. In which of the following States the yield of forest wealth per acre is highest ?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Kerala
(d) Assam
Answer: (d) Assam
Explanation:
Assam’s dense forests and favorable climate contribute to high per-acre forest yield, including timber, bamboo, and medicinal plants. Its biodiversity and rainfall support rich forest productivity.
Q159. The maximum percentage of the tribal population in India constitutes
(a) Bhils
(b) Santhals
(c) Mundas
(d) Nagas
Answer: (b) Santhals
Explanation:
The Santhals are one of the largest tribal communities in India, primarily found in Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, and West Bengal. Their population size and cultural presence make them the most populous tribal group.
Q160. The great Indian Bustard is found in
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Assam
(d) Nagaland
Answer: (b) Rajasthan
Explanation:
The Great Indian Bustard, a critically endangered bird, is mainly found in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan. Conservation efforts are focused in Desert National Park, where its habitat is under threat from human activity.
Q161. The cutting of forests leads to
(a) Soil erosion and incontrollable floods
(b) Desilting and denaturation
(c) Increase of rainfall and humidity
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Soil erosion and incontrollable floods
Explanation: Deforestation removes the vegetative cover that stabilizes soil and absorbs rainwater. Without trees, soil erosion intensifies, and rainwater flows unchecked, leading to flooding. Forests also regulate the water cycle, so their loss disrupts natural balance.
Q162. Underground Railways are being built in India at
(a) Bombay
(b) Calcutta
(c) Hyderabad
(d) Madras
Answer: (b) Calcutta
Explanation:
Calcutta (Kolkata) was the first Indian city to build an underground railway system, known as the Kolkata Metro, inaugurated in 1984. It marked a milestone in urban transport, easing congestion and improving connectivity.
Q163. The construction of Marmugao port has been fast in recent years because of
(a) Increased Imports
(b) Exporting iron ore from hinterland
(c) Decreasing the congestion caused due to heavy traffic at the Bombay port
(d) All factors listed above
Answer: (c) Decreasing the congestion caused due to heavy traffic at the Bombay port
Explanation:
Marmugao port, located in Goa, was developed rapidly to divert traffic from the congested Bombay port. Its strategic location and proximity to iron ore mines also support exports, but the primary driver was easing pressure on Bombay.
Q164. Allocation for power sector during the 6th Five-Year Plan (1978–83) is
(a) 23%
(b) 28%
(c) 33%
(d) 38%
Answer: (a) 23%
Explanation:
The Sixth Five-Year Plan emphasized energy development, allocating 23% of total outlay to the power sector. This investment aimed to boost industrial growth, rural electrification, and infrastructure modernization.
Q165. Gondwana hills are located in
(a) Punjab
(b) Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) Nagaland
Answer: (c) Madhya Pradesh
Explanation:
The Gondwana Hills, named after the Gond tribe, are situated in Madhya Pradesh. This region is rich in coal deposits and has significant geological importance, linked to the ancient Gondwana landmass.
Q166. ‘Jhum Cultivation’ is connected with
(a) Tribal people
(b) Delta cultivation
(c) Dry farming
(d) Hilly people
Answer: (d) Hilly people
Explanation:
Jhum cultivation, or slash-and-burn agriculture, is practiced by tribal communities in hilly regions, especially in North-East India. It involves clearing forest patches, growing crops temporarily, and then shifting to new areas.
Q167. The Supersonic jets tend to cause
(a) Destruction of ozone layer
(b) Sound pollution
(c) Nervous system breakdown
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) Destruction of ozone layer
Explanation:
Supersonic jets, flying at high altitudes, release nitrogen oxides that can deplete the ozone layer. Though they also contribute to noise pollution, their environmental impact on the stratosphere is a major concern.

Q168. It has been found recently that the acidity of the soil increases because of
(a) Leaching away of bases
(b) Increased use of ammonia
(c) Increased use of urea
(d) Increased use of rock phosphate
Answer: (a) Leaching away of bases
Explanation:
Soil acidity rises when basic nutrients like calcium and magnesium are leached away due to heavy rainfall or irrigation, leaving behind acidic residues. This affects crop productivity and soil health.
Q169. China attacked Vietnam because
(a) Of armed provocations and encroachment against Chinese territory
(b) Of Vietnam’s alliance with U.S.S.R.
(c) Of Vietnam’s involvement in Kampuchea
(d) Of Paracel Islands dispute
Answer: (c) Of Vietnam’s involvement in Kampuchea
Explanation:
In 1979, China invaded Vietnam in response to Vietnam’s military intervention in Kampuchea (Cambodia), which ousted the Khmer Rouge regime, a Chinese ally. This conflict reflected regional tensions and Cold War dynamics.
Q170. “Socialistic Pattern” comes through
(a) Free Economy
(b) Mixed Economy
(c) Public Sector
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Mixed Economy
Explanation:
India adopted a socialistic pattern of development through a mixed economy, combining public and private sectors. This model aimed to ensure economic growth with social justice, balancing state control and market freedom.
Q171. Which of the following has not declared itself as an Islamic Republic ?
(a) Pakistan
(b) Iran
(c) Algeria
(d) Saudi Arabia
Answer: (d) Saudi Arabia
Explanation:
While countries like Pakistan, Iran, and Algeria have officially declared themselves as Islamic Republics, Saudi Arabia is a monarchy governed by Islamic law, but it does not use the term “Islamic Republic” in its official designation.
Q172. Which head of state has based his foreign policy largely on Human Rights ?
(a) President Zia-ur-Rahman of Bangladesh
(b) President Jimmy Carter of U.S.A.
(c) President Anwar Sadat of Egypt
(d) President Julius Nyerere of Tanzania
Answer: (b) President Jimmy Carter of U.S.A.
Explanation:
President Jimmy Carter emphasized human rights as a central theme of his foreign policy, advocating for democratic values, freedom, and civil liberties in international relations, especially during the Cold War era.
Q173. “Chipko movement” in Uttar Pradesh relates to
(a) Prevention of felling green trees
(b) Prevention of felling of old trees by unauthorised persons
(c) Prevention of felling of dead trees by governmental agencies
(d) Planting trees on private plots
Answer: (a) Prevention of felling green trees
Explanation:
The Chipko Movement, initiated in the 1970s in Uttar Pradesh, involved villagers hugging trees to prevent their felling by contractors. It was a non-violent ecological protest aimed at preserving forests and promoting environmental awareness.
Q174. What is a Scheduled Bank ?
(a) A bank having Rs. 1000 crore deposits
(b) A bank included in the Second Schedule of the RBI
(c) A bank having Rs. 10 crore deposits
(d) A bank having Rs. 100 crore deposits
Answer: (b) A bank included in the Second Schedule of the RBI
Explanation:
A Scheduled Bank is one that is listed in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. These banks must meet certain criteria regarding capital and operations, and they are eligible for RBI facilities like refinancing.
Q175. Which of the following cows gives maximum milk yield ?
(a) Jersey
(b) Holstein
(c) Red Sindhi
(d) Sahiwal
Answer: (a) Jersey
Explanation:
The Jersey cow, originally from Jersey Island, is known for its high milk yield and butterfat content. It is widely used in dairy farming due to its efficiency, adaptability, and low maintenance requirements.
Q176. China intends to purchase from U.K.
(a) Hunters
(b) Harriers
(c) Sabers
(d) Jaguars
Answer: (b) Harriers
Explanation:
In the late 1970s, China expressed interest in purchasing Harrier jets from the United Kingdom. The Harrier is a vertical/short takeoff and landing aircraft, valued for its maneuverability and versatility in combat operations.
Q177. The sculpture with the three faces of Brahma, Vishnu and Mahesh known as “Trimurti” appears in
(a) Ajanta caves
(b) Ellora caves
(c) Kalva caves
(d) Elephanta caves
Answer: (d) Elephanta caves
Explanation:
The Trimurti sculpture in the Elephanta Caves near Mumbai is a masterpiece of Indian rock-cut art, depicting the three aspects of the divine—creation (Brahma), preservation (Vishnu), and destruction (Mahesh/Shiva)—in a single unified form.
Q178. During Aurangzeb’s reign, which of the following were not included in his government ?
(a) Rajputs
(b) Pathans
(c) Marathas
(d) All of these
Answer: (c) Marathas
Explanation:
Aurangzeb’s administration excluded the Marathas, who were seen as rebellious and expansionist. While Rajputs and Pathans were part of his military and administrative structure, the Marathas resisted Mughal authority, leading to prolonged conflict.
Q179. What was the important reason for the fall of Vijayanagar Empire ?
(a) Unity among the Muslim rulers
(b) Internal instability and weakness of Princes
(c) Moplah’s rebellion
(d) Economic bankruptcy
Answer: (a) Unity among the Muslim rulers
Explanation:
The Battle of Talikota (1565) saw a coalition of Deccan Sultanates unite against the Vijayanagar Empire, leading to its decisive defeat and decline. This rare unity among Muslim rulers was a key factor in the empire’s downfall.
Q180. “Inquilab Zindabad” slogan was given by
(a) Chandra Shekhar Azad
(b) Subhash Chandra Bose
(c) Bhagat Singh
(d) Iqbal
Answer: (c) Bhagat Singh
Explanation: Bhagat Singh, the revolutionary freedom fighter, coined the slogan “Inquilab Zindabad” (Long Live the Revolution) to inspire mass resistance against British rule. It became a symbol of patriotic fervor and youth activism in India’s independence movement.
Q181. “Red Shirts” movement aimed at
(a) To throw out Britishers from India
(b) To promote Communist organisational activities
(c) To promote trade union activities
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) To throw out Britishers from India
Explanation:
The Red Shirts movement, led by Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, was a non-violent nationalist movement in the North-West Frontier Province. Its goal was to end British colonial rule and promote social reform, aligning with the Indian freedom struggle.
Q182. Which of the following was not the outcome of Jallianwalah Bagh massacre ?
(a) Suspension of Gen. Dyer
(b) Change in Gandhiji’s outlook towards Britishers
(c) Temporary peace in Punjab
(d) Renunciation of British titles and positions by many Indians
Answer: (c) Temporary peace in Punjab
Explanation:
The Jallianwala Bagh massacre led to widespread outrage, not peace. It caused Gandhiji to lose faith in British intentions, and many Indians renounced British titles in protest. General Dyer’s actions were condemned, but no peace followed—instead, it intensified the freedom movement.
Q183. “Bijanti” government is compared to the Chola’s for
(a) Rural democracy
(b) Administrative system
(c) Land revenue collection system
(d) Display of wealth
Answer: (d) Display of wealth
Explanation:
The Bijanti government, likely referring to Vijayanagar rulers, is compared to the Cholas for their grand architecture, temples, and royal patronage, reflecting a display of wealth and cultural grandeur, similar to Chola traditions.
Q184. Who evolved the national consciousness as a formal concept ?
(a) B.G. Tilak
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru
(d) Surendranath Bannerjee
Answer: (d) Surendranath Bannerjee
Explanation:
Surendranath Bannerjee was among the first Indian leaders to articulate national consciousness, emphasizing political awareness, unity, and self-governance. His efforts laid the ideological foundation for the freedom movement.
Q185. Why could British only succeed in trade and commerce in India ?
(a) Because of government backing
(b) Quality of merchandise
(c) Naval superiority
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation:
The British succeeded in Indian trade due to state support, superior naval power, and competitive goods. Their East India Company had monopoly privileges, and their military and maritime strength enabled dominance over rivals.
Q186. Which is not the Indo-Aryan language?
(a) Gujarati
(b) Tamil
(c) Oriya
(d) Marathi
Answer: (b) Tamil
Explanation:
Tamil belongs to the Dravidian language family, not Indo-Aryan. In contrast, Gujarati, Oriya, and Marathi are Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Sanskrit and Prakrit roots, spoken mainly in northern and central India.
Q187. Who participated the least in the Indian National Movement ?
(a) Capitalists
(b) Landlords and Merchants
(c) Princes of States
(d) Government officials
Answer: (c) Princes of States
Explanation:
The Princes of Indian States largely remained loyal to the British, fearing loss of privileges and autonomy. Their limited participation contrasts with active roles played by capitalists, landlords, and even some government officials.
Q188. The name Pahlavi Dynasty in Iran is derived from the
(a) Language
(b) King
(c) Religion
(d) River
Answer: (a) Language
Explanation:
The Pahlavi Dynasty, founded by Reza Shah, took its name from the Pahlavi language, an ancient Persian script. This choice reflected a desire to revive Persian cultural identity, distancing Iran from Arab influences.
Q189. Which of the following throws light on Harappan Culture ?
(a) Archaeological excavations
(b) The script on copper sheets
(c) Rock edicts
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) Archaeological excavations
Explanation:
Our understanding of Harappan Civilization comes primarily from archaeological digs at sites like Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, revealing urban planning, drainage systems, and artifacts. The script remains undeciphered, and rock edicts are from a later period.
Q190. The Prime Minister of Interim Government of India after Independence was
(a) Gandhi
(b) Nehru
(c) Jinnah
(d) Rajgopalachari
Answer: (b) Nehru
Explanation:
Jawaharlal Nehru headed the Interim Government formed in 1946, before full independence. He became India’s first Prime Minister after August 15, 1947, leading the country through its transition to a sovereign republic.
Q191. Swadeshi movement started during
(a) Anti-Bengal partition movement
(b) Non-Cooperation Movement
(c) Civil Disobedience Movement
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Anti-Bengal partition movement
Explanation:
The Swadeshi Movement began in 1905 as a response to the partition of Bengal by the British. It encouraged boycott of foreign goods and promotion of indigenous products, becoming a symbol of economic nationalism.
Q192. Aim of Swaraj Party was to
(a) Enter the Legislative Councils by contesting elections in order to wreck the legislatures from within
(b) Boycott the foreign goods
(c) Launch a non-cooperation movement against the British
(d) Adopt Swadeshi in piece goods on a vast scale
Answer: (a) Enter the Legislative Councils by contesting elections in order to wreck the legislatures from within
Explanation:
Founded in 1923 by Motilal Nehru and C.R. Das, the Swaraj Party aimed to enter legislative councils and obstruct colonial governance from within, challenging British policies through constitutional means.
Q193. Which of the following countries did not suffer imperial aggression ?
(a) Ethiopia
(b) Somalia
(c) Mauritania
(d) Liberia
Answer: (d) Liberia
Explanation:
Liberia, founded by freed American slaves, remained independent during the colonial era, unlike Ethiopia, Somalia, and Mauritania, which faced European imperial aggression. Liberia is one of Africa’s oldest republics.
Q194. Swaraj Party was founded by
(a) Motilal Nehru
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) B.G. Tilak
(d) C. Rajagopalachari
Answer: (a) Motilal Nehru
Explanation:
The Swaraj Party was established by Motilal Nehru and Chittaranjan Das to continue the fight for self-rule through legislative participation, following the suspension of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
Q195. Which party was in power in U.K. when India became independent
(a) Labour
(b) Conservative
(c) Liberal
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Labour
Explanation:
The Labour Party, led by Clement Attlee, was in power in the United Kingdom when India gained independence in 1947. His government initiated the process of decolonization, granting freedom to India and other colonies.
Q196. What is the likely impact of decrease of population on economy ?
(a) Increase in per capita income
(b) Decrease in per capita income
(c) Increase in investment
(d) Decrease in savings
Answer: (a) Increase in per capita income
Explanation:
A decline in population means resources are shared among fewer people, leading to a rise in per capita income. It can improve living standards, though it may also pose challenges for labor supply and growth.
Q197. Which State is the biggest producer of cashewnuts ?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Assam
(c) Kerala
(d) Punjab
Answer: (c) Kerala
Explanation:
Kerala is India’s leading producer of cashewnuts, with favorable climatic conditions and a strong processing industry. It contributes significantly to domestic consumption and exports.
Q198. Which of the following States has no Panchayati Raj setup ?
(a) Nagaland
(b) Assam
(c) Kerala
(d) West Bengal
Answer: (a) Nagaland
Explanation:
Due to its unique tribal governance system, Nagaland does not follow the standard Panchayati Raj structure. Instead, it relies on traditional village councils under customary laws, as recognized by the Constitution.
Q199. Unemployment insurance will result in
(a) Maintenance of consumption level
(b) Decrease in consumption level
(c) Decrease in savings
(d) Increase in savings
Answer: (a) Maintenance of consumption level
Explanation:
Unemployment insurance provides financial support during job loss, helping individuals maintain their consumption levels. This stabilizes the economy, prevents demand shocks, and supports social welfare.
Q200. From the graph it follows that
(1) India generally produces more rice than wheat
(2) Production of wheat increases marginally around 4 percent
(3) India exports more sugar than wheat
(4) The cultivable area under sugar is higher than under rice
(a) Only 1 and 3 are correct
(b) Only 1 and 2 are correct
(c) Only 1 and 4 are correct
(d) Only 2 and 4 are correct
Answer: (b) Only 1 and 2 are correct
Explanation:
The graph indicates that rice production exceeds wheat, and wheat shows a marginal increase of around 4%. There is no clear evidence from the graph about exports or cultivable area, making statements 1 and 2 correct.