Q1. 240, ?, 120, 40, 10, 2
(a) 240
(b) 120
(c) 180
(d) 200
Answer: (a) 240
Explanation:
This is a pattern of division. Starting from 240, divide by 2 to get 120, then divide by 3 to get 40, then by 4 to get 10, and finally by 5 to get 2.
The missing number must be 240 to maintain this sequence of progressive division.
Q2. 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, ?
(a) 7.5
(b) 6.5
(c) 8.5
(d) 9.5
Answer: (c) 8.5
Explanation:
The pattern alternates between multiplying by 2 and adding 1.5:
0.5 × 2 = 1
1 + 1.5 = 2.5
2.5 × 2 = 5
5 + 3.5 = 8.5
Hence, the next number is 8.5, following the alternating pattern of multiplication and addition.
Q3. 4, 7, 3, 6, 2, 5, ?
(a) 8
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer: (b) 1
Explanation:
The sequence alternates between adding 3 and subtracting 4:
4 + 3 = 7
7 − 4 = 3
3 + 3 = 6
6 − 4 = 2
2 + 3 = 5
5 − 4 = 1
Hence, the missing number is 1, following the alternating pattern.
Q4. B, D, G, I, L, ?
(a) M
(b) N
(c) O
(d) P
Answer: (b) N
Explanation:
The alphabetical positions are:
B (2), D (4), G (7), I (9), L (12)
The gaps are: +2, +3, +2, +3
Continuing the pattern:
L (12) + 2 = N (14)
So, the next letter is N, maintaining the alternating increment.
Q5. A, E, I, O, ?
(a) T
(b) P
(c) G
(d) U
Answer: (d) U
Explanation:
This is a sequence of vowels in alphabetical order:
A, E, I, O, U
Hence, the next vowel is U, completing the standard vowel set.
Q6. 1, 5, 8, 10, 11, ?
(a) 3
(b) 14
(c) 12
(d) 11
Answer: (d) 11
Explanation:
The sequence includes repetition and incremental jumps:
1 → +4 → 5
5 → +3 → 8
8 → +2 → 10
10 → +1 → 11
Then 11 repeats, so the next number is again 11, showing a decreasing increment pattern followed by repetition.
Q7. A, C, F, ?, O
(a) K
(b) H
(c) J
(d) I
Answer: (c) J
Explanation:
Alphabetical positions:
A (1), C (3), F (6) → gap of +2, +3
Next gap: +4 → F (6) + 4 = J (10)
Then +5 → J (10) + 5 = O (15)
So, the missing letter is J, following the increasing gap pattern.
Q8. CBA, WVU, IHG, TSR, ?
(a) NOM
(b) MON
(c) ONM
(d) NMO
Answer: (c) ONM
Explanation:
Each group is a reverse sequence of three consecutive letters:
CBA → W, V, U → I, H, G → T, S, R
Next group: O, N, M → reversed = ONM
Hence, the correct answer is ONM, continuing the reverse alphabetical trios.
Q9. HI, JI, KL, ML, NO, ?
(a) PO
(b) PQ
(c) OP
(d) QO
Answer: (a) PO
Explanation:
The second letter in each pair remains constant for two steps:
HI → JI (I repeats)
KL → ML (L repeats)
NO → PO (O repeats)
The first letter progresses alphabetically: H → J → K → M → N → P
So, the next pair is PO, following the alternating fixed-letter pattern.
Q10. DC, DE, FE, ?? , HG, HI
(a) DE
(b) ED
(c) FG
(d) GF
Answer: (c) FG
Explanation:
The sequence alternates between forward and backward alphabetical pairs:
DC (backward), DE (forward), FE (forward), FG (forward), HG (backward), HI (forward)
So, the missing pair is FG, continuing the forward sequence.
Q11. ? , 6, 30, 120, 360, 720
(a) 5
(b) 8
(c) 1
(d) 3
Answer: (c) 1
Explanation:
This is a sequence of factorials:
1! = 1
2! = 2
3! = 6
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
The missing number is 1, which fits the factorial progression starting from 1!.
Q12. 1, 3, 1, 9, 1, 81, 1 ?
(a) 4
(b) 1
(c) 243
(d) 6561
Answer: (d) 6561
Explanation:
The pattern alternates between 1 and powers of 3:
1, 3¹ = 3, 1, 3² = 9, 1, 3⁴ = 81, 1, 3⁸ = 6561
So, the next number is 6561, continuing the alternating exponential pattern.
Q13. 10, 12, 11; 14, 16, 15; ?; 22, 24, 23
(a) 18, 20, 19
(b) 18, 19, 20
(c) 17, 19, 18
(d) 21, 23, 24
Answer: (a) 18, 20, 19
Explanation:
Each group follows the pattern:
First number +2 → second
Second −1 → third
So:
10 + 2 = 12, 12 − 1 = 11
14 + 2 = 16, 16 − 1 = 15
Next:
18 + 2 = 20, 20 − 1 = 19
Hence, the correct trio is 18, 20, 19, maintaining the +2, −1 structure.
Q14. 2, 4, 8, 32, ?, 8192
(a) 256
(b) 128
(c) 64
(d) 32
Answer: (a) 256
Explanation:
The pattern is multiplication by increasing powers of 2:
2 × 2 = 4
4 × 2 = 8
8 × 4 = 32
32 × 8 = 256
256 × 32 = 8192
So, the missing number is 256, following the exponential multiplication pattern.
Q15. A, E, I, M, Q, U, ?
(a) Z
(b) Y
(c) J
(d) T
Answer: (b) Y
Explanation:
Alphabetical positions:
A (1), E (5), I (9), M (13), Q (17), U (21)
Each letter is 4 positions ahead of the previous
Next: U (21) + 4 = Y (25)
So, the next letter is Y, continuing the +4 alphabetical jump.
Q16. Doctor : Patient : : Politician : ?
(a) Voter
(b) Chair
(c) Money
(d) Public
Answer: (a) Voter
Explanation:
A doctor serves a patient, similarly a politician serves a voter
This is a profession-to-recipient analogy, where the correct match is voter.
Q17. Ignorance : Education : : Disease : ?
(a) Hospital
(b) Doctor
(c) Medicine
(d) Nurse
Answer: (c) Medicine
Explanation:
Education cures ignorance, just as medicine cures disease
This is a problem-to-solution analogy, making medicine the correct answer.
Q18. Man : Biography : : Nation : ?
(a) History
(b) Geography
(c) People
(d) Leader
Answer: (a) History
Explanation:
A biography records a man’s life, while history records a nation’s life
This is a subject-to-record analogy, where history fits the pattern.
Q19. Guilt : Past : : Hope : ?
(a) Present
(b) Sorrow
(c) Past
(d) Future
Answer: (d) Future
Explanation:
Guilt is tied to the past, while hope is tied to the future
This is a feeling-to-timeframe analogy, making future the correct match.
Q20. Telephone : Cable : : Radio : ?
(a) Microphone
(b) Electricity
(c) Wire
(d) Wireless
Answer: (d) Wireless
Explanation:
A telephone transmits via cable, while a radio transmits wirelessly
This is a device-to-medium analogy, where wireless completes the pair.
Q21. Who is regarded as the greatest lawgiver of ancient India ?
(a) Megasthanese
(b) Panini
(c) Manu
(d) Kautilya
Answer: (c) Manu
Explanation:
Manu is traditionally considered the greatest lawgiver in ancient India, known for the Manusmriti, which laid down social, legal, and moral codes for society.
Q22. At which place Gautama Buddha delivered his first sermon ?
(a) Sarnath
(b) Lumbini
(c) Bodh Gaya
(d) Vaishali
Answer: (a) Sarnath
Explanation:
Gautama Buddha delivered his first sermon at Sarnath, known as the Dharmachakra Pravartana, marking the beginning of his teaching journey.
Q23. Who was the founder of the Servants of India Society ?
(a) G. K. Gokhale
(b) K. M. Roy
(c) M. K. Gandhi
(d) B. G. Tilak
Answer: (a) G. K. Gokhale
Explanation:
Gopal Krishna Gokhale founded the Servants of India Society in 1905 to promote education, social reform, and national service.
Q24. Saka era commenced from
(a) 78 AD
(b) 120 AD
(c) 1000 AD
(d) 1953 AD
Answer: (a) 78 AD
Explanation:
The Saka Era began in 78 AD, introduced by King Kanishka, and is used in the Indian national calendar.
Q25. The year 1919 is associated with
(a) Dandi March by Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Jallianwala Bagh Tragedy
(c) Chauri Chaura Incident
(d) Partition of Bengal
Answer: (b) Jallianwala Bagh Tragedy
Explanation:
In 1919, the Jallianwala Bagh massacre occurred in Amritsar, where British troops fired on a peaceful gathering, leading to nationwide outrage.
Q26. Whose name is associated with Fatehpur Sikri ?
(a) Akbar
(b) Babar
(c) Shahjehan
(d) Humayun
Answer: (a) Akbar
Explanation:
Fatehpur Sikri was built by Emperor Akbar as his capital city, showcasing Mughal architecture and planning.
Q27. Who introduced the ‘Civil Services’ in India ?
(a) Lord Dalhousie
(b) Lord Curzon
(c) Lord Wellesley
(d) Lord Cornwallis
Answer: (d) Lord Cornwallis
Explanation:
Lord Cornwallis is credited with introducing the modern civil services in India, emphasizing merit-based recruitment and administrative reforms.
Q28. Who was the famous Deccan Hindu King whose fleet crossed the Bay of Bengal with an army and conquered a number of states in Sumatra, Java and Malaysia ?
(a) Rajaraja I
(b) Rajendra Chola
(c) Pulakesin
(d) Mahipala II
Answer: (b) Rajendra Chola
Explanation:
Rajendra Chola, son of Rajaraja I, led naval expeditions across the Bay of Bengal, expanding influence to Southeast Asia.
Q29. Why did India industrialise only gradually in the time of Britishers ?
(a) Capitalists helped to set up new industries
(b) Many technicians came from different parts of the world to set up new industries
(c) Britishers seized and handicapped Indian cottage industries
(d) People were fond of new machine made goods
Answer: (c) Britishers seized and handicapped Indian cottage industries
Explanation:
The British colonial policies led to the decline of traditional industries, causing slow industrial growth in India.
Q30. Which of the following was the most important characteristic of Kanishka’s rule ?
(a) Expansion of Buddhism outside India
(b) Re-emergence of Jainism
(c) Fourth Buddhist Council at Srinagar
(d) Gandhara School of Art
Answer: (c) Fourth Buddhist Council at Srinagar
Explanation:
During Kanishka’s reign, the Fourth Buddhist Council was held at Srinagar, which played a key role in the spread of Mahayana Buddhism.
Q31. Gandhiji opposed the untouchability and he wanted
(a) The Harijans to revolt against it
(b) The people of India to give treatment of equality to the untouchables
(c) Untouchability to be declared a crime under law
(d) A social revolution to create a society based on equality
Answer: (b) The people of India to give treatment of equality to the untouchables
Explanation:
Gandhiji believed in social harmony and worked tirelessly for the upliftment of Harijans. He urged the people of India to treat untouchables with equality, promoting dignity and inclusion.
Q32. Which of the following is not a tenet of Gandhian Socialism
(a) Social justice
(b) Concern for the poor but not hatred for the rich
(c) Equality of opportunities of all
(d) Nationalisation of all means of production and distribution
Answer: (d) Nationalisation of all means of production and distribution
Explanation:
Gandhian Socialism emphasized decentralization, trusteeship, and moral responsibility, not state control. Hence, nationalisation contradicts the core Gandhian principles.
Q33. Neolithic period of age is not characterised by
(a) Agriculture
(b) Use of copper
(c) Domestication of animals
(d) Fishing
Answer: (b) Use of copper
Explanation:
The Neolithic period is known for stone tools, agriculture, and animal domestication, but not for the use of copper, which began in the Chalcolithic age.
Q34. Which one of the following was the cause of disintegration of the Mughal Empire ?
(a) War of succession among sons of Aurangzeb
(b) Attacks of Nadir Shah and Ahmad Shah Abdali
(c) Revolts of various communities like Jats, Sikhs, Rajputs, etc.
(d) All of the above mentioned factors contributed to the downfall of the Mughal Empire
Answer: (d) All of the above mentioned factors contributed to the downfall of the Mughal Empire
Explanation:
The Mughal Empire declined due to internal conflicts, external invasions, and regional uprisings, making multiple factors responsible for its disintegration.
Q35. Idol worship was started in
(a) Gupta period
(b) Vedic period
(c) Epic period
(d) Maurya period
Answer: (c) Epic period
Explanation:
Idol worship began during the Epic period, especially in the Ramayana and Mahabharata era, marking a shift from abstract rituals to personal deities.
Q36. Which of the following was the main feature of the policy of Dual Government of British rulers in India ?
(a) The English collected the revenues with the help of Indian Officials and they became virtually the head of the civil and military administration
(b) The general administrative body consisted of two categories of rulers
(c) Main items of administration were in the hands of local kings and rest were in the hands of British rulers
(d) Some portions of land were ruled by the local kings and rest by the British rulers
Answer: (a) The English collected the revenues with the help of Indian Officials and they became virtually the head of the civil and military administration
Explanation:
Under Dual Government, the British controlled revenue and military, while Indian officials handled civil administration, creating a split authority structure.
Q37. The basic education advocated by Gandhiji in Wardha Congress is related with
(a) Compulsory elementary education
(b) Social relevance of education to society
(c) Demand of separate institutions for minorities
(d) Compulsory military training for every student
Answer: (b) Social relevance of education to society
Explanation:
Gandhiji’s Wardha Scheme emphasized craft-based learning, linking education with productive work, and making it socially relevant and self-sustaining.
Q38. Which important event immediately preceded Jallianwala Bagh massacre ?
(a) Rowlatt Act enactment
(b) Communal award
(c) Coming of Simon Commission
(d) Quit India Movement
Answer: (a) Rowlatt Act enactment
Explanation:
The Rowlatt Act of 1919 allowed arrest without trial, sparking nationwide protests. The Jallianwala Bagh massacre occurred during one such peaceful protest.
Q39. Civil Disobedience Movement was suspended in 1921 because
(a) Violence broke out at Chauri Chaura
(b) Gandhiji was arrested for five years
(c) Government accepted the demands of Indian leaders
(d) People were not supporting this movement
Answer: (a) Violence broke out at Chauri Chaura
Explanation:
The Chauri Chaura incident involved violent clashes, prompting Gandhiji to suspend the Civil Disobedience Movement, as it violated his principle of non-violence.
Q40. Sultanates of Delhi have taken which of the following in their buildings from the ancient architecture?
(a) Mehrab
(b) Gumbaj
(c) Arched openings
(d) Decoration figures
Answer: (c) Arched openings
Explanation:
The Delhi Sultanate adopted arched openings from ancient Indian architecture, blending Islamic styles with local design elements in their monuments.
Q41. Who started Bhoodan Movement in India ?
(a) Gandhiji
(b) Jayaprakash Narayan
(c) Vinoba Bhave
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer: (c) Vinoba Bhave
Explanation:
The Bhoodan Movement was initiated by Vinoba Bhave in 1951, aiming to persuade landowners to voluntarily donate land to the landless, promoting non-violent land redistribution.
Q42. Name the God who lost his importance in the beginning of Christian era ?
(a) Indra
(b) Brahma
(c) Vishnu
(d) Mahesh
Answer: (a) Indra
Explanation:
Indra, once a prominent Vedic deity, gradually lost significance during the post-Vedic period, especially by the beginning of the Christian era, as Vaishnavism and Shaivism gained prominence.
Q43. Who were ‘Jagirdars’ during the reign of Akbar ?
(a) Large estate owners
(b) Officials of state who were given ‘jagir’ in place of cash pay
(c) Revenue collectors
(d) Autonomous rulers under Akbar
Answer: (a) Large estate owners
Explanation:
During Akbar’s reign, Jagirdars were large estate holders granted land (jagir) in lieu of salary, responsible for revenue collection and maintaining troops.
Q44. Which statement about Colombo Plan is incorrect ?
(a) The headquarters of the Colombo Plan are at Colombo
(b) This is a plan of economic development for South and South East Asian countries
(c) It is going to expire in 1981.
(d) The Colombo Plan celebrated its Silver Jubilee in 1976
Answer: (c) It is going to expire in 1981.
Explanation:
The Colombo Plan is an ongoing regional initiative for economic development, and the statement about its expiry in 1981 is incorrect, making it the right choice.
Q45. What was the impact of Western Industrial Revolution on India ?
(a) Handicrafts of India were ruined
(b) Machines were introduced in textile industry
(c) Heavy import duty was imposed on foreign goods
(d) All technical hands got employment
Answer: (a) Handicrafts of India were ruined
Explanation:
The Western Industrial Revolution led to the decline of Indian handicrafts, as machine-made goods flooded the market, causing economic hardship for artisans.
Q46. Which of the following is not a member of U.N.O. ?
(a) Switzerland
(b) Bahamas
(c) Mauritius
(d) Dominician Republic
Answer: (a) Switzerland
Explanation:
At the time of the 1980 exam, Switzerland was not a member of the U.N.O., maintaining a policy of neutrality, and joined only in 2002.
Q47. We can know about early Vedic period from
(a) Archaeological excavations
(b) Contemporary cultures
(c) Rigveda
(d) Jatak Katha
Answer: (c) Rigveda
Explanation:
The Rigveda is the primary source for understanding the early Vedic period, containing hymns, rituals, and social insights of that era.
Q48. Gandhiji was of the view that
(a) All old traditions should be followed
(b) All old traditions should be discarded
(c) Only scientifically based traditions should be followed
(d) Those traditions should not be followed which are against our moral values
Answer: (d) Those traditions should not be followed which are against our moral values
Explanation:
Gandhiji believed in ethical reform, advocating that traditions conflicting with moral values should be abandoned, while preserving constructive customs.
Q49. Upanishads are
(a) Religious books of Hindus
(b) Books dealing with ancient Hindu laws
(c) Books on social behaviour of man
(d) Prayers to God
Answer: (a) Religious books of Hindus
Explanation:
The Upanishads are philosophical texts forming the core of Hindu spiritual thought, exploring concepts like Brahman, Atman, and Moksha.
Q50. According to Gandhiji non-violence is
(a) A way to attain truth
(b) A way to win political freedom
(c) The only way to realise God
(d) An end in itself
Answer: (a) A way to attain truth
Explanation:
For Gandhiji, non-violence (Ahimsa) was the means to attain truth (Satya), forming the foundation of his philosophy and political action.
Q51. Which dynasty was well-known for excellent village administration ?
(a) Pandyas
(b) Pallavas
(c) Cholas
(d) Chalukyas
Answer: (c) Cholas
Explanation:
The Chola dynasty is renowned for its efficient village administration, with local self-governance through sabhas and ur councils, ensuring grassroots participation in decision-making.
Q52. The Ajanta Caves were built during the period of
(a) Guptas
(b) Kushans
(c) Mauryas
(d) Chalukyas
Answer: (a) Guptas
Explanation:
The Ajanta Caves, known for their Buddhist murals and sculptures, were primarily constructed during the Gupta period, reflecting the golden age of Indian art and culture.
Q53. The Indus Valley people had contacts with
(a) Egyptians
(b) Sumerians
(c) Chinese
(d) Mesopotamians
Answer: (b) Sumerians
Explanation:
Archaeological evidence like seals and trade goods shows that the Indus Valley Civilization had commercial and cultural contacts with the Sumerians of Mesopotamia.
Q54. In which way Sarnath is associated with Lord Buddha ?
(a) He resided there
(b) He was born there
(c) He ruled there
(d) He preached his first Sermon there
Answer: (d) He preached his first Sermon there
Explanation:
Sarnath is the site where Lord Buddha delivered his first sermon, known as the Dharmachakra Pravartana, marking the beginning of the Buddhist Sangha.
Q55. Lothal is connected as excavation site of the civilisation of
(a) Indus Valley Civilisation
(b) Sumerians
(c) Mesopotamians
(d) Vedic Aryan
Answer: (a) Indus Valley Civilisation
Explanation:
Lothal, located in Gujarat, was a prominent port city of the Indus Valley Civilization, featuring a dockyard and advanced urban planning.
Q56. The DYARCHY as introduced by the Government of India Act, 1919 postulated which of the following ?
(a) A system of dual government in Bengal
(b) Backward classes were entitled to vote
(c) A few subjects were transferred to the Provincial Ministries and the rest retained by the Executive Council
(d) Hindus and Muslims could vote separately
Answer: (c) A few subjects were transferred to the Provincial Ministries and the rest retained by the Executive Council
Explanation:
The Dyarchy system divided provincial subjects into transferred and reserved categories, with Indian ministers handling transferred subjects and British officials retaining control over reserved ones.
Q57. Which of the following is not related to the Gandhara School of Art ?
(a) Ellora
(b) Ajanta
(c) Khajuraho
(d) Elephanta
Answer: (c) Khajuraho
Explanation:
The Gandhara School of Art is known for Greco-Buddhist sculptures, while Khajuraho is famous for erotic temple carvings, belonging to a different artistic tradition.
Q58. Which of the following is the most important cause for the decline of Buddhism after Ashoka?
(a) Non-patronage by the kings
(b) Condemnation of animal sacrifices
(c) Growth of licentious practices in Buddhist centres
(d) Allegiance to the middle path
Answer: (a) Non-patronage by the kings
Explanation:
After Ashoka, royal patronage for Buddhism declined, leading to reduced support, loss of monastic discipline, and eventual decline of the religion in India.
Q59. What was not the most important feature of land revenue system of Akbar ?
(a) Collection of land revenue in kind or cash
(b) Collection of land revenue based on accurate measurement of land
(c) Collection of land revenue directly at the central treasury
(d) Fixation of rates
Answer: (c) Collection of land revenue directly at the central treasury
Explanation:
Under Akbar’s revenue system, revenue was collected at the local level, not directly at the central treasury, making this option inaccurate.
Q60. What is true of Indian National Congress during World War II
(a) It demanded for its co-operation with the British that a provincial national government may be set up at the centre
(b) It extended full support to the Indian National Army to oust the British from India
(c) It decided to extend full support to the allied nations
(d) It worked for the defeat of the allied nations
Answer: (a) It demanded for its co-operation with the British that a provincial national government may be set up at the centre
Explanation:
During World War II, the Indian National Congress offered conditional support to the British, demanding the formation of a national government at the centre as a precondition.
Q61. Who is the new President of Iran ?
(a) Robert Mugabe
(b) Sharif Abdul Hamid Saraf
(c) Abolhasan Bani Sadr
(d) Babrak Karmal
Answer: (c) Abolhasan Bani Sadr
Explanation:
In 1980, Abolhasan Bani Sadr became the first President of Iran after the Islamic Revolution, marking a shift to theocratic governance.
Q62. Who among the following was the Chief Guest at the Republic Day celebrations of 1980 ?
(a) Valery Giscard d’Estaing
(b) Leonid Brezhnev
(c) Jimmy Carter
(d) J. R. Jayawardene
Answer: (a) Valery Giscard d’Estaing
Explanation:
The Chief Guest for India’s Republic Day in 1980 was Valery Giscard d’Estaing, then President of France, reflecting strong diplomatic ties.
Q63. The venue of 1980 Olympics was
(a) Tokyo
(b) Mexico
(c) Moscow
(d) Athens
Answer: (c) Moscow
Explanation:
The 1980 Summer Olympics were held in Moscow, USSR, notable for the boycott by several Western nations due to the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan.
Q64. Who got ‘Bharat Ratna’ award for 1980 ?
(a) Birendra Kumar Bhattacharya
(b) Mother Teresa
(c) Mrs. Indira Gandhi
(d) Jayaprakash Narayan
Answer: (b) Mother Teresa
Explanation:
In 1980, Mother Teresa was awarded the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honour, for her humanitarian work and service to the poor.
Q65. A well known Indian player who took part in Olympic Games several times died recently. His name was associated with which game
(a) Football
(b) Hockey
(c) Volleyball
(d) Basketball
Answer: (b) Hockey
Explanation:
The player referred to was associated with hockey, India’s national sport, and had represented the country in multiple Olympic Games, contributing to its golden era.
Q66. Abdus Salam of Pakistan was a joint winner of 1979 Nobel Prize for his pioneer work in
(a) Physics
(b) Medicine
(c) Chemistry
(d) Economics
Answer: (a) Physics
Explanation:
Abdus Salam, a Pakistani physicist, won the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on electroweak unification, a major breakthrough in particle physics.
Q67. Oil has been struck in which of the following places recently by the ONGC ?
(a) Gunupur
(b) Belonia
(c) Ankleshwar
(d) Krishna Godavari basin
Answer: (d) Krishna Godavari basin
Explanation:
The ONGC discovered oil reserves in the Krishna Godavari basin, a significant step in India’s energy exploration and self-reliance.
Q68. Who was India’s captain for the last cricket test match held at Calcutta in February, 1980 against Pakistan ?
(a) Sunil Gavaskar
(b) Vishwanath
(c) Kapil Dev
(d) Venkataraghavan
Answer: (b) Vishwanath
Explanation:
Gundappa Vishwanath captained India in the February 1980 Test match against Pakistan in Calcutta, known for his elegant batting style and leadership.
Q69. Prime Minister Mrs. Indira Gandhi visited Assam to talk with the leaders of the agitation on
(a) 12th April, 1983
(b) 6th April, 1980
(c) 19th April, 1980
(d) 20th April, 1980
Answer: (a) 12th April, 1983
Explanation:
Indira Gandhi visited Assam on 12th April 1983 to address the Assam agitation, which was focused on illegal immigration and electoral reforms.
Q70. Name the king of only Hindu Kingdom in the world, who visited India in March 1980
(a) Jigme Singhye Wangchuck
(b) Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev
(c) Rao Birendra Singh
(d) Surya Bahadur Thapa
Answer: (b) Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev
Explanation:
King Birendra of Nepal, the monarch of the world’s only Hindu kingdom at the time, visited India in March 1980, strengthening bilateral relations.
Q71. 1979 Jnanpith Award was given to
(a) Ashapurna Devi
(b) Tarashankar Banerjee
(c) Birendra Kumar Bhattacharjee
(d) S. H. Vatsyayan ‘Agyeya’
Answer: (d) S. H. Vatsyayan ‘Agyeya’
Explanation:
The Jnanpith Award for 1979 was conferred on S. H. Vatsyayan ‘Agyeya’, a prominent figure in modern Hindi literature, known for his experimental writing and poetry.
Q72. In November, 1979, few Iranian protesters seized the U.S. Embassy, an American culture centre in Teheran and held more than 50 Americans as hostage. What was the cause of it ?
(a) It was done to force U.S.A. to extradite the ailing former Shah who was undergoing treatment at that time in New York
(b) America refused to purchase crude oil from Iran at their fixed price
(c) America did not recognise Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini as the religious leader of Iran
(d) America planned to invade Iran
Answer: (a) It was done to force U.S.A. to extradite the ailing former Shah who was undergoing treatment at that time in New York
Explanation:
The Iran hostage crisis began when protesters demanded the extradition of the former Shah, who was receiving medical treatment in the U.S., viewing him as a symbol of tyranny.
Q73. An earnest, widely supported move to enlarge U. N. Security Council, was made during the General Assembly’s session. Which of the following countries voted against the above proposal ?
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) India
(d) U.S.S.R.
Answer: (d) U.S.S.R.
Explanation:
The U.S.S.R. opposed the proposal to enlarge the U.N. Security Council, reflecting its strategic interests in maintaining the existing power structure.
Q74. All responsibilities regarding elections in India are entrusted to
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Chief Justice
(d) Chief Election Commissioner
Answer: (d) Chief Election Commissioner
Explanation:
The Chief Election Commissioner heads the Election Commission of India, which is responsible for conducting free and fair elections across the country.
Q75. In 1980 Parliamentary elections which parties got the maximum number of seats in the descending order ?
(a) Congress (I), Lok Dal, C. P. I. (M)
(b) Lok Dal, C. P. I. (M), Congress (I)
(c) D. M. K., Congress (I), Lok Dal
(d) Janata, Congress (I), C. P. I. (M)
Answer: (a) Congress (I), Lok Dal, C. P. I. (M)
Explanation:
In the 1980 elections, Congress (I) secured the highest number of seats, followed by Lok Dal and CPI(M), marking a political shift in the Indian Parliament.
Q76. In which case a joint session of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha is convened by the President?
(a) When a Finance Bill is to be passed by the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha with 2/3rd majority
(b) To impeach the President
(c) If after a bill has been passed by one House and transmitted to the other House and the bill is rejected by the other House
(d) All of the above
Answer: (c) If after a bill has been passed by one House and transmitted to the other House and the bill is rejected by the other House
Explanation:
A joint session is called when a legislative deadlock occurs between the two Houses, especially when a bill is rejected or stalled, enabling resolution through combined voting.
Q77. 44th Amendment of the Constitution speaks of
(a) Right to property as no longer a Fundamental Right
(b) Suspension of individual liberty during emergency
(c) Barring the courts from interfering in the disputes regarding the election of Prime Minister
(d) Giving more importance to Directive Principles over Fundamental Rights
Answer: (a) Right to property as no longer a Fundamental Right
Explanation:
The 44th Amendment (1978) removed the Right to Property from the list of Fundamental Rights, making it a legal right under Article 300A.
Q78. The Constitution 45th Amendment Bill, passed by Parliament extended reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in Parliament and State Assemblies upto
(a) 1980
(b) 1985
(c) 1990
(d) 1995
Answer: (c) 1990
Explanation:
The 45th Amendment extended political reservation for SCs and STs in legislative bodies until 1990, ensuring continued representation.
Q79. Finance Commission is appointed after every
(a) 2 years
(b) 5 years
(c) 7 years
(d) 10 years
Answer: (b) 5 years
Explanation:
The Finance Commission is constituted every 5 years to recommend the distribution of financial resources between the Centre and States.
Q80. Rolling Plan can be best defined in context of India as
(a) Formulation of annual plans
(b) Perspective of Five-Year Plan with the provision of extending by one year at a time so that there would be a constant planning horizon of five years
(c) Aims and achievements reviewed every year in a Five-Year Plan
(d) Plan for full 5 years
Answer: (b) Perspective of Five-Year Plan with the provision of extending by one year at a time so that there would be a constant planning horizon of five years
Explanation:
The Rolling Plan concept allowed for annual revisions within a five-year framework, ensuring flexibility and continuous planning based on performance and priorities.
Q81. Council of Ministers of the Union of India is responsible to the
(a) Parliament
(b) President
(c) Prime Minister
(d) Chief Justice
Answer: (a) Parliament
Explanation:
The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha, which is part of the Parliament, ensuring accountability in a parliamentary democracy.
Q82. A candidate to become a member of Lok Sabha should not be less than
(a) 21 years
(b) 25 years
(c) 30 years
(d) 35 years
Answer: (b) 25 years
Explanation:
As per the Constitution of India, the minimum age to contest Lok Sabha elections is 25 years, ensuring maturity and civic understanding.
Q83. The word “secular” denotes
(a) Keeping away from all religions
(b) Belief in one God
(c) Freedom of religion and worship to all citizens
(d) Practising different religions
Answer: (c) Freedom of religion and worship to all citizens
Explanation:
In the Indian context, secularism means the state does not favor any religion, and guarantees freedom of faith and worship to all citizens.
Q84. What is the maximum period during which Parliament may not meet?
(a) Six months
(b) One year
(c) Two years
(d) Three years
Answer: (a) Six months
Explanation:
The Constitution mandates that there should not be a gap of more than six months between two sessions of Parliament, ensuring regular legislative activity.
Q85. Parliament consists of
(a) Prime Minister and other Ministers
(b) President, Prime Minister and other Ministers
(c) President, Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha
(d) President, Chief Justice and Lok Sabha
Answer: (c) President, Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha
Explanation:
The Indian Parliament is composed of the President, the Rajya Sabha (Upper House), and the Lok Sabha (Lower House), forming the legislative framework.
Q86. Rajya Sabha can delay the Money Bill passed by the Lok Sabha for a period not exceeding
(a) 9 days
(b) 14 days
(c) 15 days
(d) 30 days
Answer: (b) 14 days
Explanation:
As per Article 110, the Rajya Sabha can delay a Money Bill for a maximum of 14 days, after which it is deemed passed, preserving financial supremacy of Lok Sabha.
Q87. Highest per capita income is in
(a) Punjab
(b) West Bengal
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Gujarat
Answer: (a) Punjab
Explanation:
In 1980, Punjab had the highest per capita income, attributed to its agricultural prosperity, especially due to the Green Revolution.
Q88. Hong Kong is
(a) A free port
(b) An independent state
(c) A free exchange market
(d) All of the above
Answer: (c) A free exchange market
Explanation:
Hong Kong was known for its free exchange market, with minimal trade restrictions, making it a global financial hub.
Q89. Antyodaya scheme is meant
(a) To help the Muslims
(b) To help the Harijans
(c) To help the minorities
(d) To help the economically weakest sections of the society
Answer: (d) To help the economically weakest sections of the society
Explanation:
The Antyodaya scheme targets the poorest of the poor, aiming to uplift the economically weakest sections through employment and welfare programs.
Q90. The trouble in Assam in 1980 was caused
(a) Due to infiltration of foreign guerrillas in the area
(b) Due to inclusion of foreigners in the electoral rolls of the State
(c) Postponement of Lok Sabha elections in all the constituencies of the State
(d) Due to prorogation of the State Assembly
Answer: (b) Due to inclusion of foreigners in the electoral rolls of the State
Explanation:
The Assam agitation in 1980 was triggered by the inclusion of illegal immigrants in the electoral rolls, raising concerns over identity, security, and representation.
Q91. Which country is known as the ‘Land of the Morning Calm’
(a) Japan
(b) Korea
(c) Taiwan
(d) Netherlands
Answer: (b) Korea
Explanation:
Korea is traditionally referred to as the ‘Land of the Morning Calm’ due to its serene natural beauty and peaceful landscapes, especially during sunrise.
Q92. Country known as the Sugar Bowl of the World is
(a) Cuba
(b) India
(c) Burma
(d) Norway
Answer: (a) Cuba
Explanation:
Cuba earned the title ‘Sugar Bowl of the World’ because of its large-scale sugarcane cultivation and dominance in global sugar exports during the 20th century.
Q93. Bustard King is found in
(a) Assam
(b) Himalayan Range
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Answer: (c) Rajasthan
Explanation:
The Great Indian Bustard, often called the Bustard King, is primarily found in Rajasthan, especially in the Thar Desert, and is a critically endangered species.
Q94. Thyagaraja of 18th century was
(a) The greatest musician who composed his songs in Telugu
(b) The greatest Kathak dancer
(c) The greatest playwright of Tamil
(d) The greatest Sanskrit poet
Answer: (a) The greatest musician who composed his songs in Telugu
Explanation:
Thyagaraja was a legendary Carnatic composer of the 18th century, known for his devotional compositions in Telugu, dedicated to Lord Rama.
Q95. How many judges are there in the International Court of Justice ?
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 15
(d) 20
Answer: (c) 15
Explanation:
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) consists of 15 judges, elected for nine-year terms, representing the principal legal systems of the world.
Q96. Mixed economy refers to
(a) The coexistence of heavy, small scale and cottage industries
(b) The promotion of agriculture as well as cottage industries
(c) The coexistence of rich as well as poor
(d) Co-existence of public as well as private sector
Answer: (d) Co-existence of public as well as private sector
Explanation:
A mixed economy blends government-owned enterprises with private businesses, allowing both state and market forces to drive economic development.
Q97. The only State in India that shows excess of females over males is
(a) U.P.
(b) Kerala
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer: (b) Kerala
Explanation:
Kerala has consistently shown a higher female-to-male ratio, attributed to better healthcare, education, and social awareness, setting it apart from other states.
Q98. The term ‘Fourth Estate’ refers to
(a) A very backward State
(b) Judiciary
(c) Parliament
(d) Press
Answer: (d) Press
Explanation:
The ‘Fourth Estate’ refers to the press or media, highlighting its role as a watchdog of democracy, alongside the three formal branches of government.
Q99. Qantas Airways belongs to
(a) Australia
(b) West Germany
(c) East Germany
(d) New Zealand
Answer: (a) Australia
Explanation:
Qantas Airways is the flag carrier of Australia, known for being one of the world’s oldest airlines, with a reputation for safety and service.
Q100. Whose signatures are found on a hundred rupee note ?
(a) President of India
(b) Governor of Reserve Bank of India
(c) Prime Minister
(d) Finance Minister
Answer: (b) Governor of Reserve Bank of India
Explanation:
Every Indian currency note, including the ₹100 note, bears the signature of the RBI Governor, signifying its authenticity and legal tender status.
Q101. To ensure the efficiency, economic condition; etc. there are Control Boards for each major project except one for which a statutory corporation has been set up. That project is
(a) Farakka Project
(b) Bhakra Nahgal Project
(c) Damodar Valley Project
(d) Ramgangq Project
Answer: (c) Damodar Valley Project
Explanation:
The Damodar Valley Project is managed by a statutory corporation, unlike other major projects which are overseen by Control Boards, making it an exception in administrative structure.
Q102. The Bhilai Steel Plant was set up with the collaboration of the U.S.S.R., the Rourkela Steel Plant with the collaboration of West Germany, the Durgapur Steel Plant was constructed with the collaboration of
(a) Britain
(b) Japan
(c) U.S.A.
(d) Romania
Answer: (a) Britain
Explanation:
The Durgapur Steel Plant was built with British collaboration, forming part of India’s early industrial development under the Second Five-Year Plan.
Q103. Silent Valley Project in Kerala was dropped because
(a) Ecologists pointed out that the project will set up an environmental imbalance
(b) India will have to spend a huge amount of foreign exchange to complete the project
(c) Skilled labour and cheap power were not available
(d) Some political controversy arose regarding the project
Answer: (a) Ecologists pointed out that the project will set up an environmental imbalance
Explanation:
The Silent Valley Project was abandoned due to concerns raised by ecologists about its impact on the unique rainforest ecosystem, highlighting environmental conservation priorities.
Q104. 1980 Republic Day award ‘Padma Vibhushan’ was awarded to an exponent of Hindustani classical music who is
(a) Vani Jairam
(b) Bismillah Khan
(c) Ravi Shankar
(d) Rai Krishna Dass
Answer: (b) Bismillah Khan
Explanation:
Bismillah Khan, the legendary shehnai maestro, received the Padma Vibhushan in 1980 for his contribution to Indian classical music, especially in popularizing the shehnai.
Q105. Skylab crashed on July 11, 1979 in
(a) Pacific Ocean
(b) Atlantic Ocean
(c) Mediterranean Sea
(d) Indian Ocean near western Australia
Answer: (d) Indian Ocean near western Australia
Explanation:
Skylab, America’s first space station, re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and crashed in the Indian Ocean near western Australia, marking the end of its orbital mission.
Q106. Farakka agreement between Bangladesh and India implies
(a) Sharing of river water of Ganges
(b) Free navigation
(c) Mutual understanding of border areas
(d) A peace treaty
Answer: (a) Sharing of river water of Ganges
Explanation:
The Farakka agreement was signed to resolve disputes over the distribution of Ganges water, ensuring equitable sharing between India and Bangladesh.
Q107. Who was the second President of the Indian Republic ?
(a) Dr. Zakir Hussain
(b) Dr. S. Radhakrishnan
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(d) V. V Giri
Answer: (b) Dr. S. Radhakrishnan
Explanation: Dr. S. Radhakrishnan served as the second President of India from 1962 to 1967, known for his philosophical scholarship and statesmanship.
Q108. Who designed the city of Chandigarh ?
(a) Le Corbusier
(b) Jacob Epstein
(c) Rodhin Auguste
(d) Ferdinand M. V. De Lesseps
Answer: (a) Le Corbusier
Explanation:
The modern city of Chandigarh was designed by Le Corbusier, a Swiss-French architect, blending urban planning with modernist architecture.
Q109. India has launched Symphonic Satellite Telecommunication Experiment Project (STEP). It is a joint project of the
(a) P and T Department and Indian Space Research Organisation
(b) Ministry of Energy and Space Commission
(c) Ministry of Defence and Indian Space Research Organisation
(d) Indian Space Research Organisation and Ministry of Industry
Answer: (a) P and T Department and Indian Space Research Organisation
Explanation:
The STEP project was a collaboration between the Post and Telegraph Department and ISRO, aimed at testing satellite-based communication systems.
Q110. The Muslims march seven times round the Kaaba as part of their Haj pilgrimage in the city of
(a) Riyadh
(b) Mecca
(c) Rabat
(d) Jeddah
Answer: (b) Mecca
Explanation:
During Haj, Muslims perform Tawaf, circling the Kaaba seven times in the holy city of Mecca, which is the spiritual center of Islam.
Q111. Largest Nationalised Bank in India is
(a) Central Bank of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) State Bank of India
(d) Bank of India
Answer: (c) State Bank of India
Explanation:
The State Bank of India (SBI) is the largest nationalised bank in India, known for its extensive branch network, customer base, and role in public sector banking.
Q112. Andrei Sakharov came into news in January 1980 because
(a) He was set to internal exile in Gorky
(b) He bagged Nobel Prize in medicine in 1979
(c) He wrote a famous book named Gulag Archipelago
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) He was set to internal exile in Gorky
Explanation:
Andrei Sakharov, a prominent Soviet physicist and dissident, was exiled to Gorky in 1980 due to his criticism of Soviet policies, drawing global attention.
Q113. Range of Television Broadcasting is confined to a limited distance because
(a) Long waves are used
(b) Short waves are absorbed by atmosphere
(c) Energy of the waves is dissipated
(d) Earth is spherical in shape
Answer: (d) Earth is spherical in shape
Explanation:
Television signals use line-of-sight transmission, and due to the curvature of the Earth, the range is limited, making the spherical shape the key factor.
Q114. Another name of Vitamin C is
(a) Folic acid
(b) Ascorbic acid
(c) Niacin
(d) Acetic acid
Answer: (b) Ascorbic acid
Explanation:
Vitamin C is also known as Ascorbic acid, essential for immune function, collagen synthesis, and preventing scurvy.
Q115. Unit of distance used in navigation is
(a) Nautical mile
(b) Kilometre
(c) Light year
(d) Yard
Answer: (a) Nautical mile
Explanation:
A nautical mile is the standard unit in marine and air navigation, equivalent to 1.852 kilometers, based on the Earth’s circumference.
Q116. What type of mirror is used by motorists to see the road behind them ?
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
(c) Plane
(d) Concavo-convex
Answer: (a) Convex
Explanation:
Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view, allowing motorists to see more area behind them, making them ideal for rear-view mirrors.

Q117. The escape velocity from the earth’s surface is about
(a) 30 km/sec
(b) 6 km/sec
(c) 11.2 km/sec
(d) 300 km/sec
Answer: (c) 11.2 km/sec
Explanation:
Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed to break free from Earth’s gravitational pull, which is approximately 11.2 km/sec.

Q118. The chief constituent of gabar gas is
(a) Methane
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Acetylene
(d) Ethylene
Answer: (a) Methane
Explanation:
Gobar gas, produced from cow dung and organic waste, primarily contains methane, used as a renewable fuel source.
Q119. The radiant energy of the sun is due to
(a) Nuclear fission
(b) Nuclear fusion
(c) Sinking of the sun
(d) Violent explosions
Answer: (b) Nuclear fusion
Explanation:
The sun’s energy comes from nuclear fusion, where hydrogen nuclei combine to form helium, releasing vast amounts of energy.

Q120. In microphone, transformation of energy takes place from
(a) Sound into electrical energy
(b) Electrical into sound energy
(c) Sound into mechanical energy
(d) Mechanical into sound energy
Answer: (a) Sound into electrical energy
Explanation:
A microphone converts sound waves into electrical signals, enabling amplification, recording, or transmission of audio.

Q121. Fuel used in a nuclear reactor is
(a) Uranium
(b) Heavy water
(c) Barium
(d) Cadmium
Answer: (a) Uranium
Explanation:
Uranium is the primary fuel used in nuclear reactors, where its fission reactions release energy for electricity generation.
Q122. The heater element in an electric iron is made of
(a) Nichrome
(b) Tungsten
(c) Copper
(d) Iron
Answer: (a) Nichrome
Explanation:
Nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium, is used in heater elements due to its high resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without oxidizing.

Q123. Dialysis is used for a patient suffering from
(a) Kidney trouble
(b) Liver trouble
(c) Lung trouble
(d) Heart trouble
Answer: (a) Kidney trouble
Explanation:
Dialysis is a medical process that removes waste and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys fail to function properly.
Q124. Green colour of plants is due to the presence of
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) Sugar
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Xylem
Answer: (a) Chlorophyll
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that plays a key role in photosynthesis, absorbing sunlight to convert into chemical energy.

Q125. Dry ice is
(a) Solid carbon dioxide
(b) Ice dust
(c) Liquified nitrogen
(d) Liquified hydrogen
Answer: (a) Solid carbon dioxide
Explanation:
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide, used for cooling and preservation, and it sublimates directly into gas without leaving liquid residue.

Q126. Neil Armstrong was the first person to reach on the moon. While walking on the moon
(a) His mass remained the same but weight increased
(b) His mass remained the same but weight decreased
(c) His mass as well as weight decreased
(d) His mass increased but weight remained the same
Answer: (b) His mass remained the same but weight decreased
Explanation:
Mass remains constant, but weight depends on gravity. Since the moon’s gravity is weaker, Neil Armstrong’s weight decreased, though his mass stayed the same.
 Q127. Distance of stars is measured in(a) Light years
Q127. Distance of stars is measured in(a) Light years
(b) Kilometres per second
(c) Kilometres only
(d) Nautical miles
Answer: (a) Light years
Explanation:
Astronomers measure stellar distances in light years, which represent the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers.

Q128. The deficiency of Vitamin D causes
(a) Rickets
(b) Night blindness
(c) Pellagra
(d) Scurvy
Answer: (a) Rickets
Explanation:
Vitamin D deficiency leads to rickets, a condition where bones become soft and weak, especially in children, due to poor calcium absorption.
Q129. Isotopes of the same element differ in the number of
(a) Protons
(b) Neutrons
(c) Electrons
(d) Positrons
Answer: (b) Neutrons
Explanation:
Isotopes have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses but similar chemical properties.

Q130. Stainless steel contains which of the following ?
(a) Aluminium and Zinc
(b) Chromium and Carbon
(c) Zinc and Mercury
(d) Copper and Cadmium
Answer: (b) Chromium and Carbon
Explanation:
Stainless steel is an alloy primarily made of iron, chromium, and carbon, where chromium provides corrosion resistance and carbon adds strength.

Q131. During processing and cooking which part of food is mostly destroyed ?
(a) Proteins
(b) Vitamins
(c) Carbohydrates
(d) Fats
Answer: (b) Vitamins
Explanation:
Vitamins are sensitive to heat, light, and air, and are often destroyed during cooking, especially water-soluble vitamins like Vitamin C and B-complex.

Q132. When iron rusts, the weight
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
(d) First increases then decreases
Answer: (a) Increases
Explanation:
Rusting is a chemical reaction where iron combines with oxygen, forming iron oxide, which adds mass, causing the weight to increase.

Q133. What is mainly obtained from bauxite ?
(a) Copper
(b) Aluminium
(c) Iron
(d) Gold
Answer: (b) Aluminium
Explanation:
Bauxite is the primary ore of aluminium, and is processed to extract alumina, which is then refined into aluminium metal.

Q134. Which one of the following is secreted by Pancreas and regulates the amount of sugar in the body
(a) Renin
(b) Creatin
(c) Vitamin
(d) Insulin
Answer: (d) Insulin
Explanation:
Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells.

Q135. Which substance is commonly used in refrigerators ?
(a) Freon
(b) Oxygen
(c) Ammonia
(d) Sulphur dioxide
Answer: (a) Freon
Explanation:
Freon is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) used as a refrigerant in cooling systems due to its stability and efficiency, though now being phased out for environmental reasons.

Q136. Radar is used for
(a) Detecting objects by using light waves
(b) Reflecting sound waves to detect objects
(c) Determining the presence and location of objects with radio waves
(d) Tracking rain-bearing clouds
Answer: (c) Determining the presence and location of objects with radio waves
Explanation:
Radar uses radio waves to detect the distance, speed, and direction of objects, commonly used in aviation, weather forecasting, and defense.

Q137. Municipal water in India is generally treated with
(a) Chlorine
(b) Potassium permanganate
(c) Sodium Chloride
(d) Sodium Carbonate
Answer: (a) Chlorine
Explanation:
Chlorine is widely used to disinfect municipal water, killing pathogens and ensuring safe drinking water.
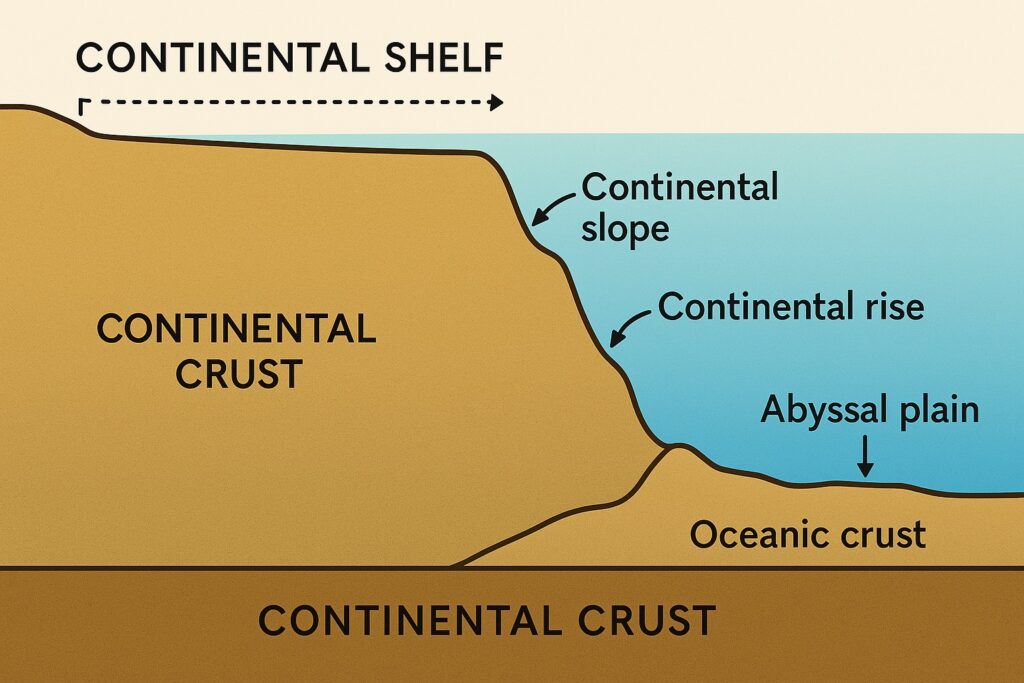
Q138. What is a continental shelf ?
(a) It is a part of the ocean which is really an extension of the land mass, but submerged
(b) It is that part where the ocean commences
(c) It is a land mass which is surrounded by water on all sides
(d) It is a part of the continent that is submerged in relatively shallow sea
Answer: (d) It is a part of the continent that is submerged in relatively shallow sea
Explanation:
A continental shelf is the submerged extension of a continent, found in shallow seas, and is rich in marine resources.
Q139. International date line
(a) Roughly corresponds to 180th meridian, the regions to the east of which are counted as being one day earlier in their calendar dates than regions to the west
(b) Roughly corresponds to 180th meridian, the region to the west of which are counted as being one day earlier in their calendar dates than regions to the east
(c) Roughly corresponds to 90th meridian which falls on the opposite side of the Greenwich meridian
(d) Roughly corresponds to 135th meridian which falls on the opposite side of the Greenwich meridian
Answer: (a) Roughly corresponds to 180th meridian, the regions to the east of which are counted as being one day earlier in their calendar dates than regions to the west
Explanation:
The International Date Line lies near the 180° longitude, and crossing it eastward subtracts a day, while crossing westward adds a day, maintaining global time consistency.
Q140. In which type of rocks, fossils are more abundantly found ?
(a) Igneous
(b) Metamorphic
(c) Sedimentary
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Sedimentary
Explanation:
Sedimentary rocks form from layers of deposited material, often preserving organic remains, making them the primary source of fossils.
Q141. Doldrums refer to
(a) A belt of calm and light variable winds near the equator
(b) A particular area in the centre of the Pacific Ocean
(c) The region of the upper atmosphere extending upward from the tropopause to about 20 kms. above the earth
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) A belt of calm and light variable winds near the equator
Explanation:
The doldrums are a low-pressure zone near the equator where winds are weak and variable, often causing calm conditions that affect maritime navigation.
Q142. A narrow strip of land, bordered on both sides by water, connecting to larger bodies of land is called
(a) Dune
(b) Equinox
(c) Isthmus
(d) Strait
Answer: (c) Isthmus
Explanation:
An isthmus is a narrow land bridge connecting two larger land masses, bordered by water on both sides, such as the Isthmus of Panama.

Q143. When it is 8 A.M. on Wednesday of Greenwich
(a) It is 10.30 P.M. on Wednesday at London
(b) It is 6.15 A.M. on Tuesday at New York
(c) It is 3.00 P.M. on Wednesday at Hong Kong
(d) It is 5.00 P.M. on Wednesday at Tokyo
Answer: (d) It is 5.00 P.M. on Wednesday at Tokyo
Explanation:
Tokyo is approximately 9 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), so when it is 8 A.M. in Greenwich, it is 5 P.M. in Tokyo, reflecting global time zone differences.
Q144. Tallest four-legged animal is
(a) Zebra
(b) Elephant
(c) Giraffe
(d) Ostrich
Answer: (c) Giraffe
Explanation: The giraffe is the tallest four-legged animal, with its long neck and legs, reaching heights of up to 18 feet, adapted for feeding on tall trees.
Q145. Reptile that is well known for its intense colour change is
(a) Lizard
(b) Chameleon
(c) Glass Snake
(d) Turtle
Answer: (b) Chameleon
Explanation:
Chameleons are famous for their ability to change skin colour, which helps in camouflage, temperature regulation, and communication.
Q146. Which bird has a chisel like bill ?
(a) Parrot
(b) Nightingale
(c) Woodpecker
(d) Woodchuck
Answer: (c) Woodpecker
Explanation:
The woodpecker has a chisel-shaped bill designed for drilling into wood, allowing it to search for insects and build nests.
Q147. Heavy rainfall affects soil by
(a) Increasing its acidity
(b) Increasing its alkalinity
(c) Reducing its fertility
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Reducing its fertility
Explanation:
Heavy rainfall can cause soil erosion, washing away nutrients, and leading to reduced fertility, especially in unprotected or sloped areas.
Q148. Pampas are the vast grassy plains of
(a) South America
(b) North America
(c) Africa
(d) Eurasia
Answer: (a) South America
Explanation:
The Pampas are extensive fertile grasslands in Argentina and Uruguay, known for agriculture and cattle ranching, forming part of South America’s landscape.
Q149. India ranks first in the production of in the world
(a) Tea
(b) Sugar
(c) Rice
(d) Wheat
Answer: (a) Tea
Explanation:
India has historically been the largest producer of tea, especially in regions like Assam and Darjeeling, contributing significantly to the global tea market.
Q150. The rising of evening star Venus indicates
(a) South pole
(b) North pole
(c) East
(d) West
Answer: (d) West
Explanation:
Venus, known as the evening star, appears in the western sky after sunset, helping in directional orientation and celestial navigation.
