Q1. Why the Indian farmers plough their fields during the time interval between two crops ?
(a) In order to keep the soil loose for further cultivation
(b) To increase the porosity of the soil
(c) To escape drought
(d) To prevent clodding
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (d) To prevent clodding
Explanation: Ploughing between crops helps break up soil clods, maintaining a fine tilth for the next sowing. It also aids in weed control, moisture retention, and aeration, preparing the field for better crop establishment.
Q2. Maximum production of paddy per unit water consumption can be best achieved in a
(a) Non-porous soil
(b) Porous soil
(c) Impervious soil
(d) Soil that allows slow percolation
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (d) Soil that allows slow percolation
Explanation: Paddy cultivation thrives in soil with slow percolation, which retains water longer, reducing irrigation needs and enhancing yield efficiency. Such soils prevent water loss and support continuous root hydration.
Q3. Which of the following statements about the cultivation of tea and coffee is true ?
(a) Tea grows at a higher altitude than coffee
(b) Coffee grows at a higher altitude than tea
(c) Both grow at about the same altitude
(d) There is no climatic relationship between the two crops
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (b) Coffee grows at a higher altitude than tea
Explanation: Coffee is typically cultivated at higher altitudes (1000–2000 meters) compared to tea, which grows well between 600–2000 meters. The cooler climate and shade at higher elevations favour coffee quality and flavour.

Q4. Which soil is best suited for paddy crop ?
(a) Black soil
(b) Loamy soil
(c) Hard soil
(d) Red soil
Answer: (b) Loamy soil
Explanation: Loamy soil is ideal for paddy cultivation because it retains moisture, has good drainage, and supports root development. Its balanced texture of sand, silt, and clay allows for slow percolation, which is essential for rice fields.

Q5. Operation Flood refers to
(a) Use of preventive measures for flood devastation
(b) A study about floods
(c) Dairy development for increased milk production
(d) None of these
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (c)
Explanation: Operation Flood was a landmark initiative launched by NDDB to boost milk production, making India the largest producer of milk. It revolutionized the dairy sector and empowered rural farmers.
Q6. Flame of the forest is
(a) A tree blossomed with flowers like flame in leafless season
(b) Fire developed in the forest due to strong wind
(c) A lady who worked for the development of the forests
(d) An insect which glows like a flame in the forest
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (a)
Explanation: Flame of the forest refers to the Butea monosperma tree, known for its bright orange-red flowers that bloom during the leafless season, giving the appearance of flames across the landscape. It is a symbolic and ornamental tree in India.
Q7. After sowing seeds, the fertilisers used are
(a) Phosphates
(b) Nitrates
(c) Green manures
(d) All of these
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (d)
Explanation: Post-sowing, a combination of phosphates, nitrates, and green manures is used to enhance soil fertility and support plant growth. These fertilisers supply essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
Q8. To keep the seeds in good condition, we should keep it in a place which is
(a) Warm and dry
(b) Warm and wet
(c) Cool and dry
(d) Cool and wet
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (c)
Explanation: Seeds remain viable longer when stored in cool and dry conditions, which prevent moisture absorption, fungal growth, and premature germination. This ensures preservation of genetic quality.
Q9. 200 cm of rainfall, 20°C of temperature and well drained land is ideal for the cultivation of
(a) Rice
(b) Tea
(c) Coffee
(d) Rubber
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (b)
Explanation: Tea cultivation thrives in regions with high rainfall, moderate temperature, and well-drained soil. These conditions are typically found in hilly areas, making them ideal for tea plantations.
Q10. The largest producer of tea in the world is
(a) China
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) India
(d) Malaysia
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (c)
Explanation: In the context of 1982, India was the largest producer of tea, with major production in Assam, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu. The country has a long history of tea cultivation and export.
Q11. Contour bunding is used
(a) To stop the winds in sandy deserts
(b) To irrigate desert areas
(c) To prevent erosion in hilly areas
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (c)
Explanation: Contour bunding involves building embankments along contour lines to reduce soil erosion and water runoff in hilly terrain. It helps in soil conservation and improves agricultural productivity.
Q12. Arrange the following fertilisers according to the decreasing order of their nitrogen content
I. Ammonium sulphate
II. Ammonium nitrate
III. Potassium nitrate
IV. Urea
(a) IV, II, III, I
(b) IV, II, I, III
(c) IV, III, II, I
(d) II, IV, III, I
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (b) IV, II, I, III
Explanation: Urea has the highest nitrogen content, followed by ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulphate, and potassium nitrate. This order reflects their effectiveness in supplying nitrogen for plant growth.
Q13. Which one is a high yielding variety of rice?
(a) IR-8
(b) IR-21
(c) K-64
(d) M-986
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (a) IR-8
Explanation: IR-8 is a high-yielding rice variety developed during the Green Revolution. It significantly increased rice production, especially in developing countries, due to its short growth cycle and resistance to pests.
Q14. Lucerne is a
(a) Foliage crop
(b) Cereal crop
(c) Fruit crop
(d) Fibre crop
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (a) Foliage crop
Explanation: Lucerne, also known as alfalfa, is a high-protein foliage crop used primarily as animal fodder. It is valued for its nutritional content and soil-enriching properties, making it a key component in livestock farming.
Q15. Indian agriculture largely depends for its water supply on
(a) Rivers
(b) Wells
(c) Monsoon rains
(d) Desalinised marine water
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (c) Monsoon rains
Explanation: Monsoon rains are the primary source of water for Indian agriculture, especially in rain-fed areas. The seasonal rainfall determines crop cycles, yields, and irrigation needs, making it crucial for farming.
Q16. “Mulching” the soil is a process whereby
(a) Big pieces of soil are broken down into smaller pieces
(b) The field is irrigated at regular intervals
(c) Transplanting of seedlings take place
(d) Loose material, dung, etc. are laid on the ground to prevent excessive evaporation or erosion of the soil
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (d) Loose material, dung, etc. are laid on the ground to prevent excessive evaporation or erosion of the soil
Explanation: Mulching involves covering the soil with organic or inorganic material to retain moisture, reduce erosion, and suppress weed growth. It enhances soil health and supports sustainable farming practices.

Q17. Sugarcane crop matures in about
(a) 2 months
(b) 4 months
(c) 8 months
(d) 12 months
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (d) 12 months
Explanation: Sugarcane is a long-duration tropical crop that typically takes about 12 months to mature. The growth period depends on climatic conditions, soil fertility, and irrigation, but in general, it requires a full year for optimal yield and sugar content.
Q18. Micro-elements needed to increase soil fertility are
(a) Nitrogen, hydrogen and calcium
(b) Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
(c) Iron, calcium and potassium
(d) Manganese, copper and zinc
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (d) Manganese, copper and zinc
Explanation: Micro-elements or micronutrients are required in small quantities but are essential for plant growth and soil fertility. Elements like manganese, copper, and zinc play key roles in enzyme activation, photosynthesis, and nutrient absorption.
Q19. New high yielding varieties of food crops are different from the conventional in that they need
(a) Less water
(b) Less fertilisers
(c) More water and more fertilisers
(d) Less water and more fertilizers
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (c) More water and more fertilisers
Explanation: High Yielding Varieties (HYVs) introduced during the Green Revolution are genetically designed for maximum productivity. However, they require intensive inputs, including more water, fertilizers, and pesticides, to achieve their potential yields.
Q20. Select the famous agricultural scientist who was awarded Nobel Prize for Peace ?
(a) Norman E. Borlaug
(b) M. S. Swaminathan
(c) N. S. Subba Rao
(d) None of these
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (a) Norman E. Borlaug
Explanation: Norman E. Borlaug was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in developing high-yielding crop varieties and promoting agricultural innovation, which helped avert famine in many developing countries. He is considered the father of the Green Revolution.
Q21. Which of the following is an insecticide ?
(a) TNT
(b) DDT
(c) Salicylic acid
(d) Ammonium phosphate
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (b) DDT
Explanation: DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane) is a synthetic insecticide used to control mosquitoes and agricultural pests. It was widely used in the mid-20th century but later banned in many countries due to its environmental and health impacts. It is not a fertilizer or explosive, unlike the other options.
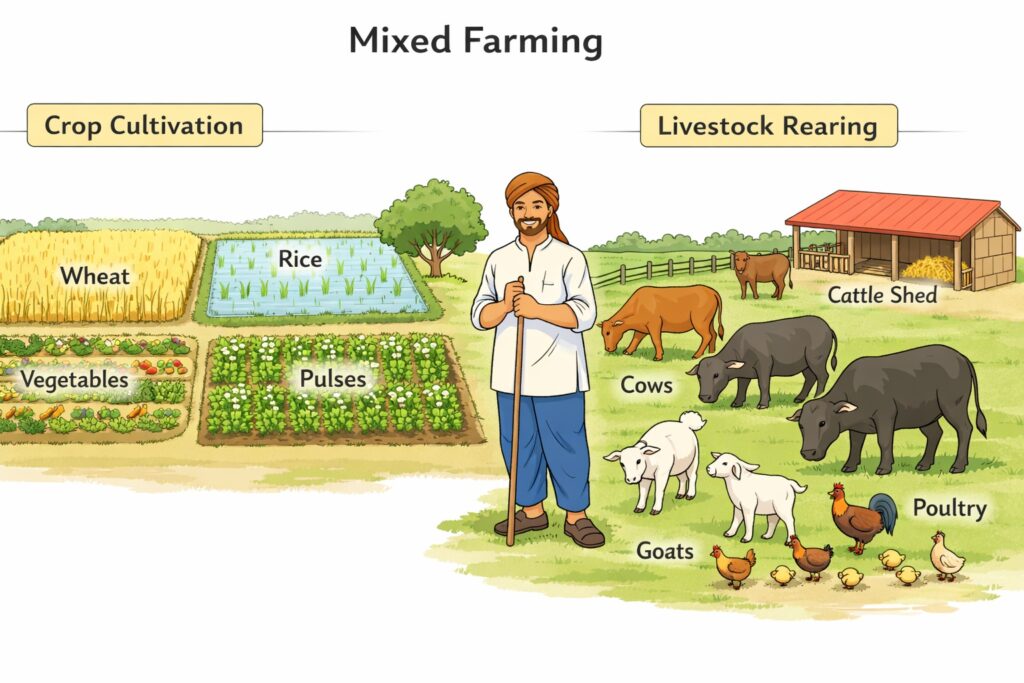
Q22. Mixed farming means
(a) Simultaneous cultivation of a number of crops in a single field
(b) Alternate cropping in a field
(c) Growing fruits and vegetables in the same field
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Simultaneous cultivation of a number of crops in a single field
Explanation:
Mixed farming involves the simultaneous cultivation of multiple crops and often includes livestock rearing on the same farm. This method promotes diversification, risk reduction, and efficient resource use, enhancing farm productivity and sustainability.
Q23. Economy of Brazil is mostly dependent on
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Tobacco
(d) Sugar
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (b) Coffee
Explanation: Brazil has long been the world’s largest producer and exporter of coffee, making it a cornerstone of its agricultural economy. The country’s climate and soil conditions are ideal for coffee cultivation, and it contributes significantly to employment and foreign exchange earnings.
Q24. Assertion (A): Our agricultural growth rate is small even after proper planning and huge investments.
Reason (R): The land reform measures are not carried up to the mark
(a) A and R both are incorrect
(b) A is correct but R is incorrect
(c) A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (c) A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Despite planning and investment, agricultural growth has been limited due to ineffective land reforms. Issues like land ceiling evasion, poor redistribution, and lack of tenancy protection have hindered productivity, making the reason a valid explanation.
Q25. The International Rice Research Institute is located in
(a) The Philippines
(b) Thailand
(c) Indonesia
(d) Malaysia
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) The Philippines
Explanation: The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is headquartered in Los Baños, Philippines. It is a leading global research organization dedicated to rice science and agricultural innovation. Its location in the Philippines reflects the country’s central role in rice cultivation and research across Asia.
Q26. Uttar Pradesh tops the list of sugarcane producing States in India. Which of the following States occupies the second position in this regard ?
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Bihar
(c) Karnataka
(d) Madhya Pradesh
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) Maharashtra
Explanation: Maharashtra ranks second in sugarcane production in India after Uttar Pradesh. The state’s favorable climate and irrigation infrastructure support extensive cultivation, especially in regions like Pune, Satara, and Kolhapur.
Q27. In India, the rise in food production between 1960-61 and 1980-81 was approximately
(a) 25 per cent
(b) 40 per cent
(c) 60 per cent
(d) 100 per cent
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (c) 60 per cent
Explanation: Between 1960–61 and 1980–81, India witnessed a 60% increase in food production, largely due to the Green Revolution, which introduced high-yielding varieties, irrigation, and fertilizers.
Q28. Of the total food grains produced in India during 1981-82, the percentage of pulses produced was approximately
(a) 9
(b) 12
(c) 25
(d) 50
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) 9
Explanation: During 1981–82, pulses accounted for approximately 9% of India’s total foodgrain production. Though essential for protein intake, pulses occupy a smaller share compared to cereals like rice and wheat.
Q29. Which of the following is a weedkiller ?
(a) Insecticide
(b) Methyl salicylate
(c) Heribicide
(d) None of these
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (c) Heribicide
Explanation: A herbicide is a chemical used to kill unwanted plants or weeds. It differs from insecticides, which target insects. Methyl salicylate is not a weedkiller; it’s used in medicinal applications.
Q30. Assertion (A): France produces the best wine in the world.
Reason (R): The Champagne district of France is famous for the best quality of grape-wines.
(a) if A and R both are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) if A and R both are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) if A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) if A is correct but R is incorrect
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (b) if A and R both are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: While France is renowned for its wine, and the Champagne district is famous for sparkling wine, it is not the sole reason for France’s global reputation. Hence, both statements are correct, but not causally linked.
Q31. Which of the following crops is a tropical monsoon crop ?
(a) Rice
(b) Wheat
(c) Ragi
(d) Jowar
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (a) Rice
Explanation: Rice thrives in hot and humid climates with abundant rainfall, making it a typical tropical monsoon crop. It requires standing water during its growth phase, which is provided by the monsoon rains.
Q32. Operation Flood II refers to
(a) Krishna-Cauvery link
(b) Cleaning of Ganga water
(c) Decreasing floods in the country
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (d) None of the above
Explanation: Operation Flood II was part of India’s White Revolution, aimed at increasing milk production and creating a national milk grid. It had no connection with rivers or flood control.
Q33. Mixed farming means
(a) Growing two crops at one time
(b) Growing different crops in succession
(c) Using different soils
(d) Agriculture involving crops and livestock
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (d) Agriculture involving crops and livestock
Explanation: Mixed farming integrates crop cultivation with livestock rearing, enhancing resource utilization and income diversification. It is a sustainable agricultural practice.
Q34. Rotation of crops means
(a) Different crops are grown in succession to maintain the soil fertility
(b) Growing two crops at the same time
(c) Same crop is grown after some time
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (a) Different crops are grown in succession to maintain the soil fertility
Explanation:
Crop rotation involves growing different crops in a planned sequence to prevent soil nutrient depletion, control pests, and improve soil health.
Q35. The maximum cropped area of the country is in
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Punjab
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (d) Uttar Pradesh
Explanation: Uttar Pradesh has the largest cropped area in India due to its fertile plains, extensive irrigation infrastructure, and dominance in agricultural production, especially of wheat and sugarcane.
Q36. Which of the following pairs is/are correct ?
(A) Main root – Storage
(B) Lateral root – Absorption
(C) Root hair – Conduction
(a) Only A
(b) A and C
(c) All are correct
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Only A
Explanation:
- Main root stores nutrients – correct
- Lateral roots help in anchorage, not absorption
- Root hairs are responsible for absorption, not conduction
Hence, only statement A is correct.
Q37. In India, the problem of utilisation of agriculture wastes is in
(a) Conversion of starch into alcohol
(b) Conversion of sugar into carbohydrates
(c) Conversion of bran into molasses
(d) Conversion of cellulose into sugar
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (d) Conversion of cellulose into sugar
Explanation: Agricultural waste like straw and husks contains cellulose, which is difficult to convert into sugar due to its complex structure. This conversion is a major challenge in biofuel and waste management technologies.
9. Match List I with List II
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| (A) Groundnut | (i) Leguminosae |
| (B) Cotton | (ii) Graminae |
| (C) Sugarcane | (iii) Malvaceae |
Select the correct answer:
(a) A-(i) B-(ii) C-(iii)
(b) A-(i) B-(iii) C-(ii)
(c) A-(ii) B-(i) C-(iii)
(d) A-(iii) B-(i) C-(ii)
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Groundnut belongs to the Leguminosae family. Cotton is classified under the Malvaceae family. Sugarcane is a member of the Graminae family.
Therefore, the correct matching is A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii).
Q39. Which of the following fertilisers leaves acidic residue ?
(a) Ammonium phosphate
(b) Ammonium sulphate
(c) Urea
(d) Sulphate of potash
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (d) Sulphate of potash
Explanation: Sulphate of potash tends to leave acidic residues in the soil after application, affecting soil pH. The other fertilizers are either neutral or mildly acidic, but potassium sulphate is known for its acidifying effect.
Q40. Mixed cropping is useful when
(a) Crops with varying maturity periods are sown together.
(b) Crops with same maturity period are sown together.
(c) Different soils are used for the same crops.
(d) Crops with different nutritional requirements are grown.
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (d) Crops with different nutritional requirements are grown
Explanation: Mixed cropping involves growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field. It is most effective when the crops have different nutritional needs, reducing competition for resources and improving soil health and yield stability.
Q41. Which of the following is the correct group of Kharif crops ?
(a) Rice, Millet, Maize, Cotton
(b) Groundnut, Bajra, Barley, Sorghum, Wheat
(c) Jowar, Bajra, Rice, Cotton, Jute, Gram
(d) Wheat, Barley, Gram, Mustard
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (a) Rice, Millet, Maize, Cotton
Explanation: Kharif crops are sown at the beginning of the monsoon season and harvested in autumn. Rice, millet, maize, and cotton are typical Kharif crops, thriving in warm, wet conditions.
Q42. Opium is obtained from
(a) Tablet type latex
(b) Latex juice
(c) Seed capsule of opium poppy
(d) Poppy leaves
Answer: (c) Seed capsule of opium poppy
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Explanation:
Opium is extracted from the seed capsule of the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum). The milky latex that oozes from incisions in the capsule is dried and processed to produce opium, which contains alkaloids like morphine and codeine.