The Heartland and Rimland Theories are two important geopolitical theories that attempt to explain the balance of power in the world. In this article, we will discuss the Heartland and Rimland theories in detail.
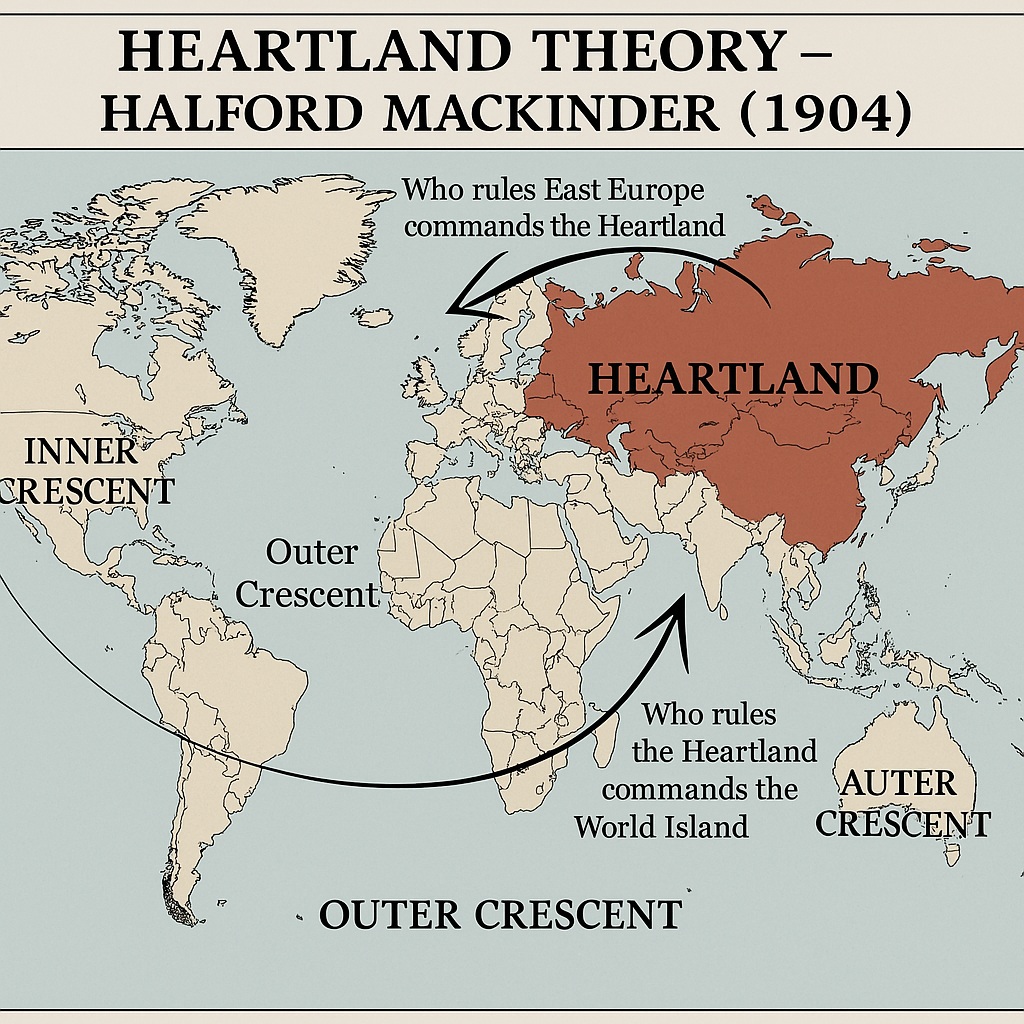
Who rules East Europe commands the Heartland!
Who rules Heartland commands the world island!
Who rules the world island commands the world!
Table of Contents
Mackinder’s Heartland Theory
The Heartland theory was proposed by British geographer Halford Mackinder in his famous paper titled ‘The Geographical Pivot of History’ in the year 1904. On the basis of the physical map of the world, he observed that in geopolitics, there is a continuous struggle between land power (controlling landmass) and sea power (controlling sea).
Therefore, he classified the world into two geographical regions: Continuous Land Mass (Europe, Asia, and Africa) and Isolated Islands (North America, South America, Australia, Great Britain, and Japan).
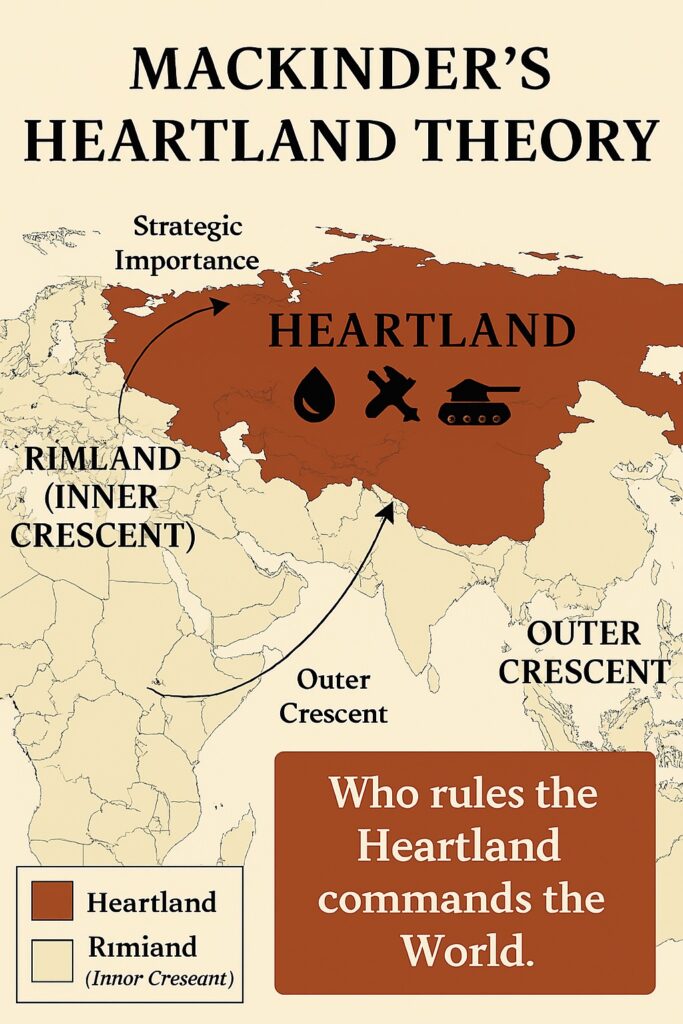
He argues that the power in the world is determined by control of the landmass of the Eurasian continent, particularly the vast expanse of land in the center of the continent, which he called the “Heartland.” According to Mackinder, whoever controlled the Heartland could dominate the world because of the region’s strategic location, difficulty to access by the sea powers, and contains vast resources.
Mackinder’s Heartland Theory Statement
The central statement of Mackinder’s Heartland Theory is that control of the heartland region, which stretches from Eastern Europe to Central Asia, is essential for achieving global dominance.
Mackinder believed that the state or empire that controlled the heartland would be the most powerful in the world and that this control required land power rather than sea power. He argued that throughout history, the great empires were those that controlled the heartland or its periphery and that a united and strong power controlling the heartland would be able to resist any attempts at external domination. Mackinder’s theory emphasized the importance of strategic thinking and policy-making and warned of the danger of a powerful state controlling the heartland and threatening the rest of the world.
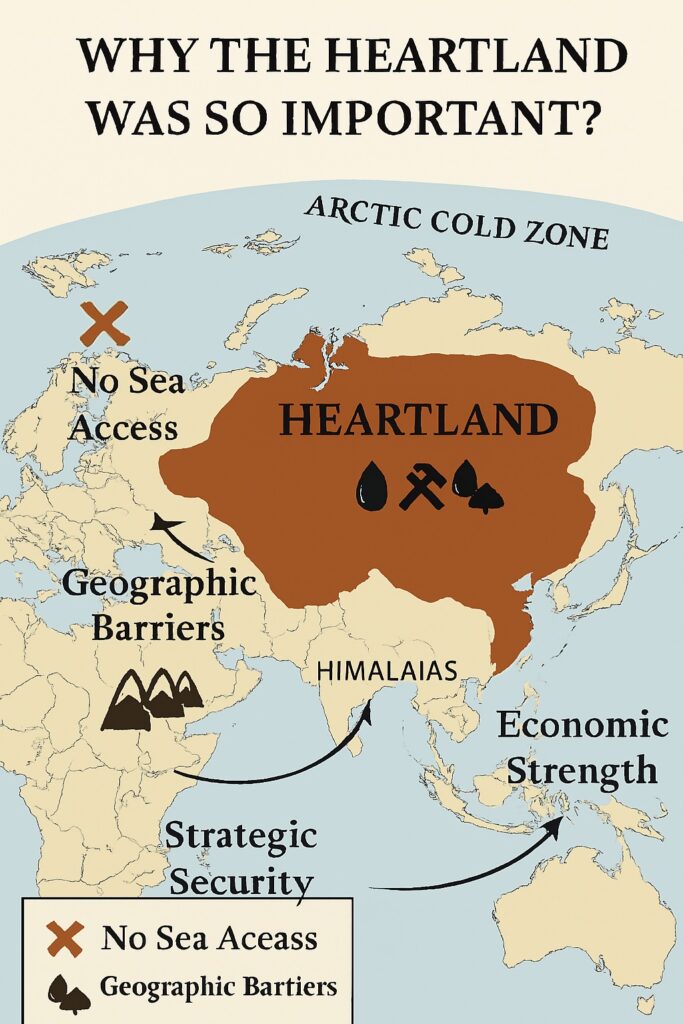
Why the heartland was so important?
- The region can not be accessed through the sea route as it is guarded by a geographical barrier like mountains and cold climatic zones of artic.
- It has vast natural resources.
Division of World by Mackinder
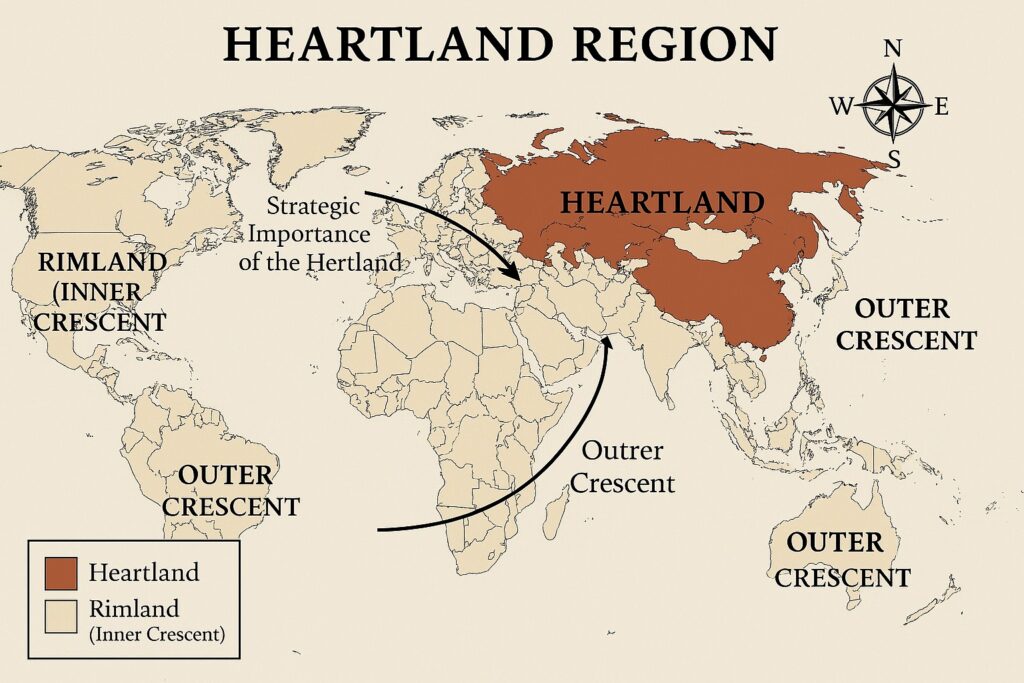
Mackinder’s theory proposed a division of the World Island into three regions, known as the Heartland, Inner Crescent, and Outer Crescent.
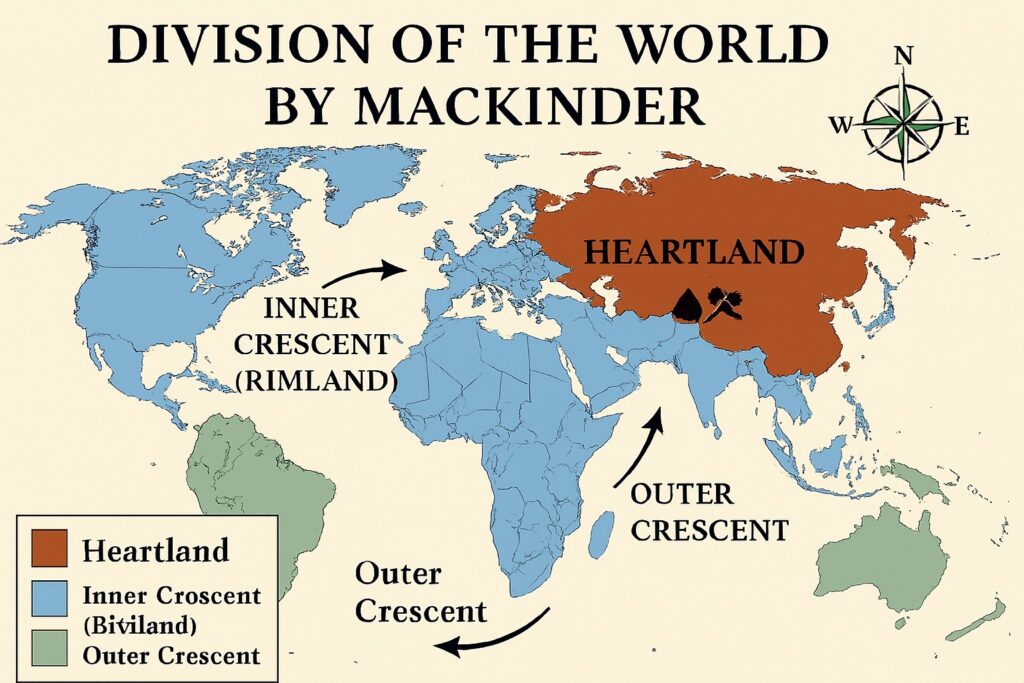
- The Heartland: This is the central region of the World Island, which stretches from Eastern Europe to Central Asia. Mackinder believed that the Heartland was the most important geopolitical region in the world and that its control was essential for global dominance.
- The Inner Crescent: This is the ring of land surrounding the Heartland, which includes Western Europe, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent. Mackinder believed that the Inner Crescent was important because it was the gateway to the Heartland and could therefore influence events in the Heartland.
- The Outer Crescent: This is the outer ring of land surrounding the Inner Crescent, which includes the Americas, Africa, and Australia. Mackinder believed that the Outer Crescent was less important than the other two regions but could still play a role in global affairs.
Mackinder believed that the balance of power between these three regions was critical for understanding the dynamics of global politics. He argued that whoever controlled the Heartland would have the greatest geopolitical power, but that the Inner Crescent could influence events in the Heartland through its access to maritime trade routes and resources.
Applications of Heartland Theory
The heartland theory has several applications in the field of international relations and geopolitics.
- Military Strategy: The theory has been used to develop military strategies by various nations throughout history. For example, during the Cold War, the United States developed the “containment” strategy to prevent the Soviet Union from expanding its influence into the heartland. This led to the establishment of military bases and alliances in Europe and Asia, as well as the development of nuclear weapons as a deterrent.
- Economic Development: Understanding the strategic importance of certain regions can also inform economic policies and development strategies. Countries can invest in infrastructure and resources in the heartland to gain access to its vast resources and markets, as well as to secure their supply chains.
- Geopolitical Analysis: The heartland theory is often used as a framework for analyzing global power dynamics and predicting future trends. It helps policymakers and analysts to understand the importance of certain regions and the potential impact of geopolitical events on global stability and security.
- Energy Security: The heartland is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, making it a crucial region for energy security. Nations can invest in exploration and development in the heartland to reduce their dependence on foreign sources of energy.
Overall, the heartland theory has practical applications in various areas of international relations and can be used to inform strategic decision-making and policy development.
Criticism of the theory
The heartland theory has been subject to various criticisms over the years.
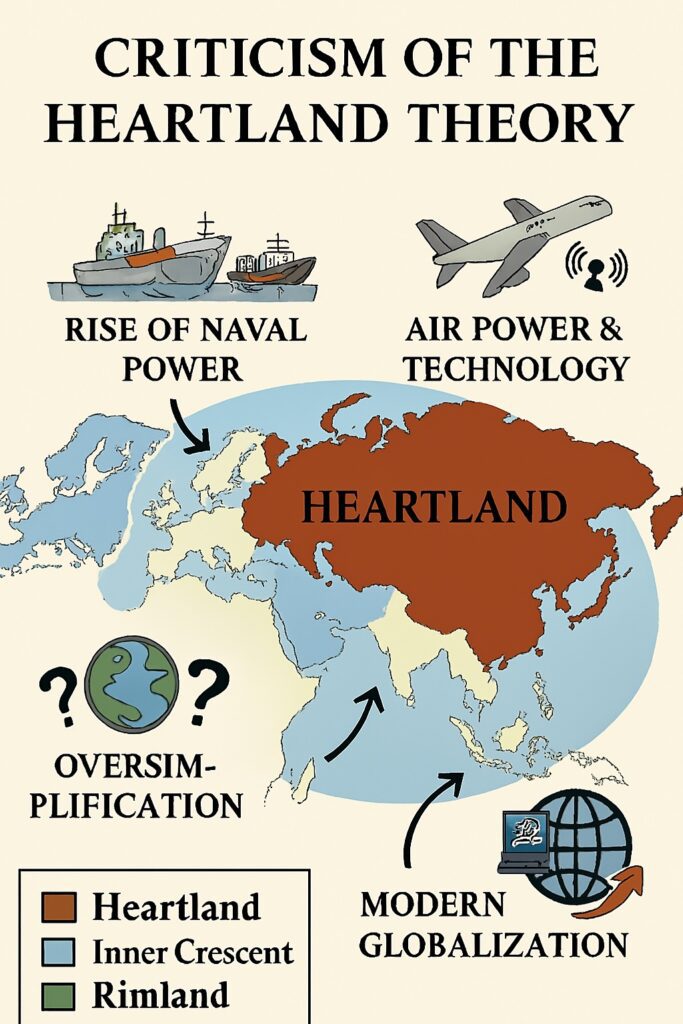
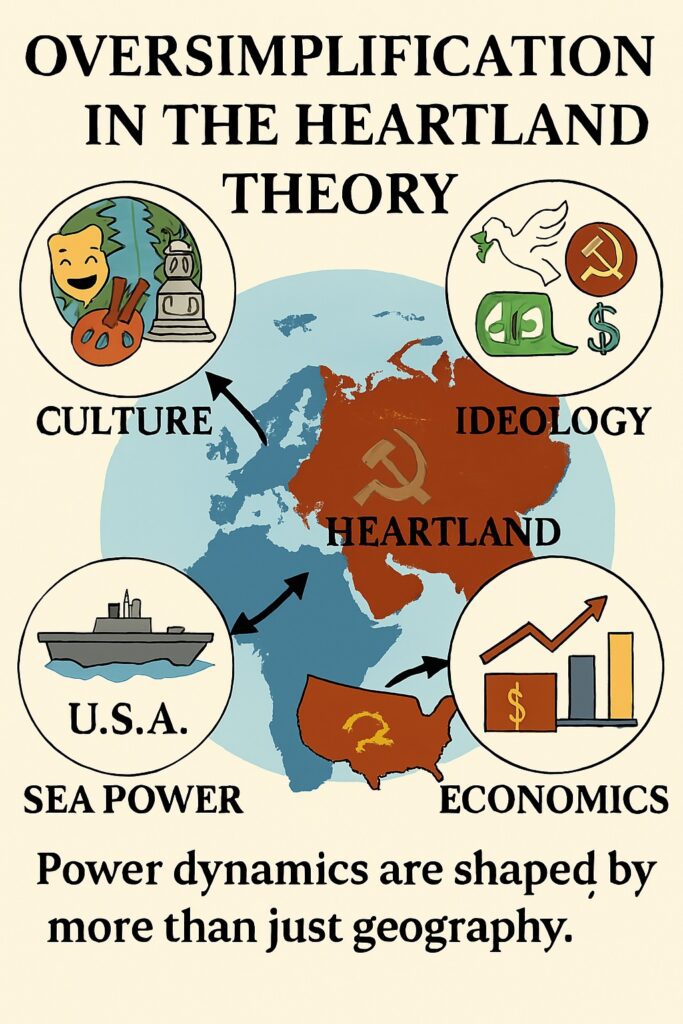
- Oversimplification: Critics argue that the theory oversimplifies the complexities of global power dynamics by reducing them to a single geographic region. The theory does not take into account other factors such as culture, ideology, and economics. Today the USA is the largest economy and it is a sea power.

Oversimplification as the Criticism of Heartland Theory - Historical Context: The heartland theory was developed in the early 20th century and was influenced by the geopolitical context of that time, particularly the rivalry between Britain and Russia. Critics argue that the theory does not adequately account for changes in global politics since then, including the rise of non-state actors and the decline of nation-states as the primary actors in international relations.
- Ignoring Rimland: The theory places too much emphasis on the heartland and ignores the importance of the “rimland” – the coastal regions surrounding the heartland. As Nicholas Spykman argued, control over the rimland is just as important as control over the heartland in maintaining global power.
- Inaccurate Predictions: Critics argue that the theory’s predictions about the future of global power dynamics have not always been accurate. For example, the theory predicted that the Soviet Union would dominate the heartland and thus become the dominant global power, which did not come to pass.

Inaccurate Prediction by Heartland Theory - Science and Technology: The theory ignores the development of new technologies like missiles, Fighter Aircraft, etc. A country located deep within the ocean like North Korea has become powerful and physically attack a nation in the heartland from its soil.
Despite these criticisms, the heartland theory remains a valuable framework for understanding the strategic significance of certain regions and their potential impact on global power dynamics. However, it should be used in conjunction with other theories and frameworks to provide a more nuanced understanding of international relations.
Skypman Rimland Theory
The Rimland theory was proposed by American political scientist Nicholas Spykman in his book titled “The Geography of Peace” in the year 1944. The Rimland Theory is a key geopolitical concept that challenges Halford Mackinder’s Heartland Theory. Instead of emphasizing the landlocked interior of Eurasia (the Heartland), Spykman argued that the surrounding coastal regions—known as the Rimland—hold the most strategic importance.
He argues that the power in the world is determined by control of the coastal regions surrounding the Heartland, which he called the “Rimland”. Spykman believed that whoever controlled the Rimland could prevent the Heartland from expanding its power and could potentially challenge the Heartland’s dominance.
Who controls the Rimland, rules Eurasia!
One who rules Eurasia controls the world !
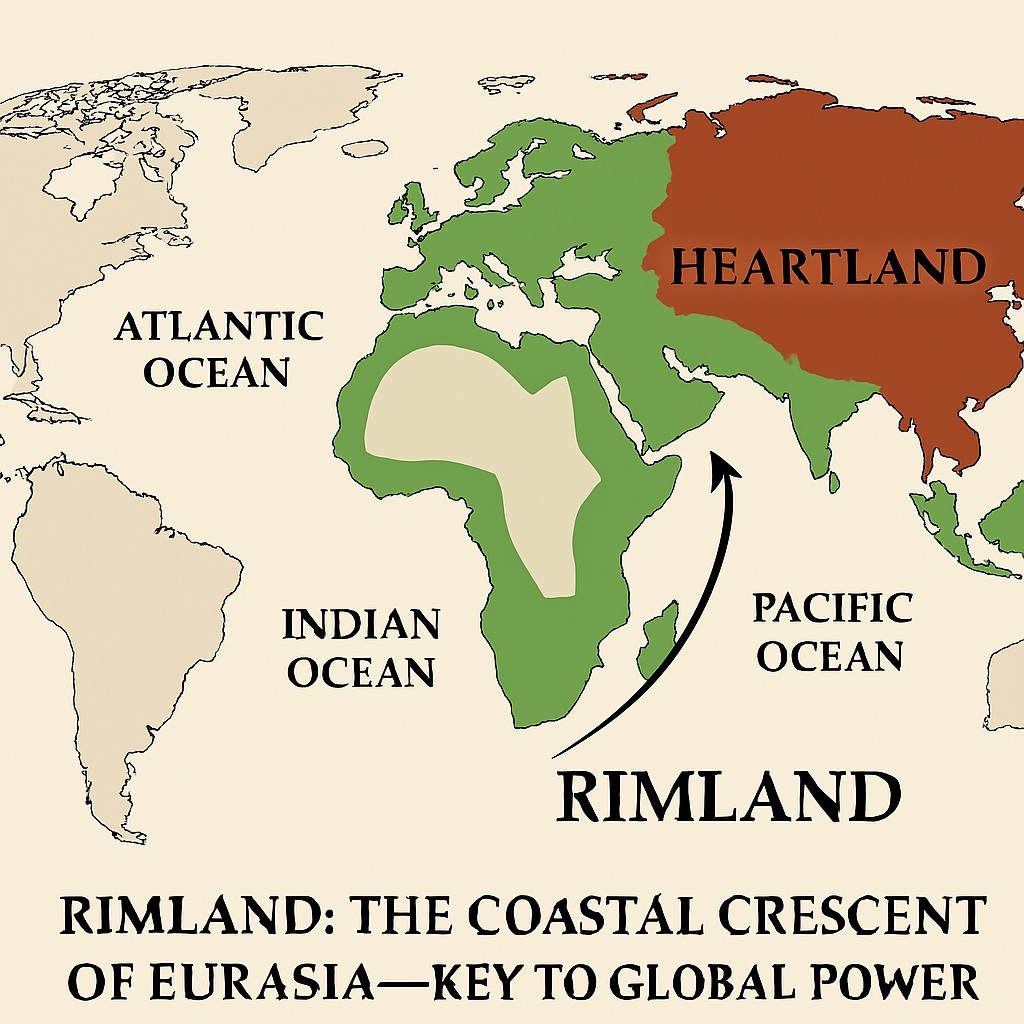
Rimland Theory
According to the theory, the Eurasian Rimland, which includes the coastal areas of Europe and Asia, is a crucial area of geopolitical competition. Spykman argued that control over the Rimland would provide whoever held it with a strategic advantage in controlling the world’s resources and dominating global trade.
Spykman also believed that the Rimland was susceptible to domination by a powerful maritime nation, which he called the “Rimland power.” He argued that the United States had the potential to become the dominant Rimland power, but that it would face competition from other powers, such as the Soviet Union (at the time of Spykman’s writing) and China.
The Skypman Rimland Theory has been influential in the development of American foreign policy, particularly during the Cold War era. The theory was seen as a justification for American intervention in conflicts in the Rimland region, as well as the development of military bases and alliances in the area.
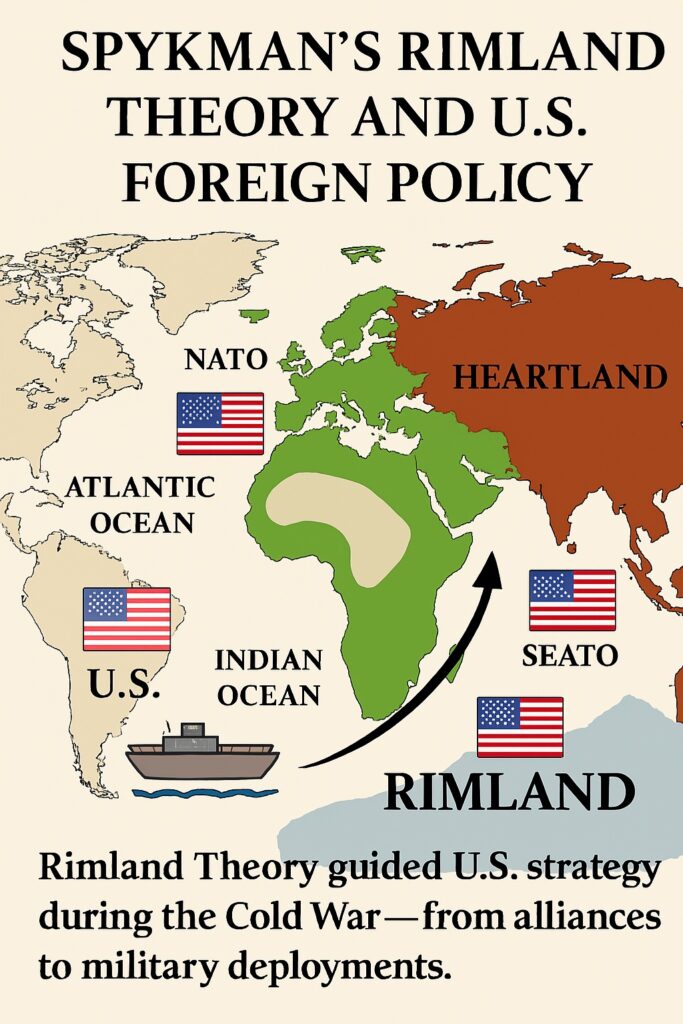
Differences between Heartland and Rimland Theories
While the Heartland theory emphasizes the importance of controlling the landmass of the Eurasian continent, the Rimland theory highlights the significance of controlling the coastal regions surrounding the Heartland. The Heartland theory suggests that control of the Heartland is crucial for global dominance, while the Rimland theory argues that control of the Rimland is equally important in preventing the Heartland from expanding its power.
| Aspect | Heartland Theory | Rimland Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Geopolitical control centered on the “Heartland,” which is the vast interior landmass of Eurasia. | Geopolitical control focused on the “Rimland,” the coastal areas and islands surrounding the Eurasian “Heartland.” |
| Theorist | Sir Halford Mackinder | Nicholas J. Spykman |
| Geographical Emphasis | Emphasizes the importance of the vast, resource-rich, and heavily populated interior landmass. | Emphasizes the significance of the coastal regions, including ports and maritime access. |
| Key Beliefs | Control of the Heartland would lead to dominance over the World Island (Eurasia, Africa, and parts of the Middle East). | Controlling the Rimland would lead to control of the World Island, which would then dominate the world. |
| Importance of Geography | Geographical features, especially the absence of natural barriers in the Heartland, are seen as crucial for expansion. | The presence of seas, oceans, and favorable ports in the Rimland is considered advantageous for projecting power. |
| Potential Threat | The major concern is the rise of a single dominant power in the Heartland, which could challenge the balance of power globally. | The focus is on preventing the domination of the Rimland by a single power, which could threaten global stability. |
| Geopolitical Strategy | Encourages land-based strategies and alliances to control the Heartland and the World Island. | Advocates for maritime strategies and alliances to control the Rimland and the World Island. |
| Key Supporters | Geopolitical analysts and theorists during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including those during the Cold War. | Often associated with analysts and strategists during the Cold War era. |
| Modern Relevance | The theory’s relevance has diminished due to changes in global dynamics, but some elements remain influential in geopolitics. | The Rimland Theory remains relevant in discussions on the importance of maritime power and geopolitical stability. |
Please note that while the Heartland and Rimland theories were influential during their respective times, modern geopolitical dynamics have evolved significantly, and other
Test in Cold War Era
Both the Heartland and Rimland theories were influential in shaping geopolitical thinking, particularly during the Cold War era. The Heartland theory was often cited to justify the need for containment of the Soviet Union, while the Rimland theory was used to support the idea of a strong naval presence to maintain control of the world’s coastlines.
Contemporary Relevance of Heartland and Rimland Theories
Today, these theories continue to be studied and debated as important factors in understanding the balance of power in the world. The Heartland and Rimland theories remain relevant in the contemporary world, particularly as nations continue to compete for influence in various regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Heartland and Rimland theories are two important geopolitical theories that attempt to explain the balance of power in the world. While the Heartland theory emphasizes the importance of controlling the landmass of the Eurasian continent, the Rimland theory highlights the significance of controlling the coastal regions surrounding the Heartland. These theories continue to be studied and debated today as important factors in understanding the balance of power in the world.
Read: Geography Notes