Westerlies and Easterlies are two prevailing wind patterns that play a critical role in the weather systems of the Earth. These prevailing winds play a crucial role in shaping regional climates, influencing ocean currents, and even impacting historical maritime trade.
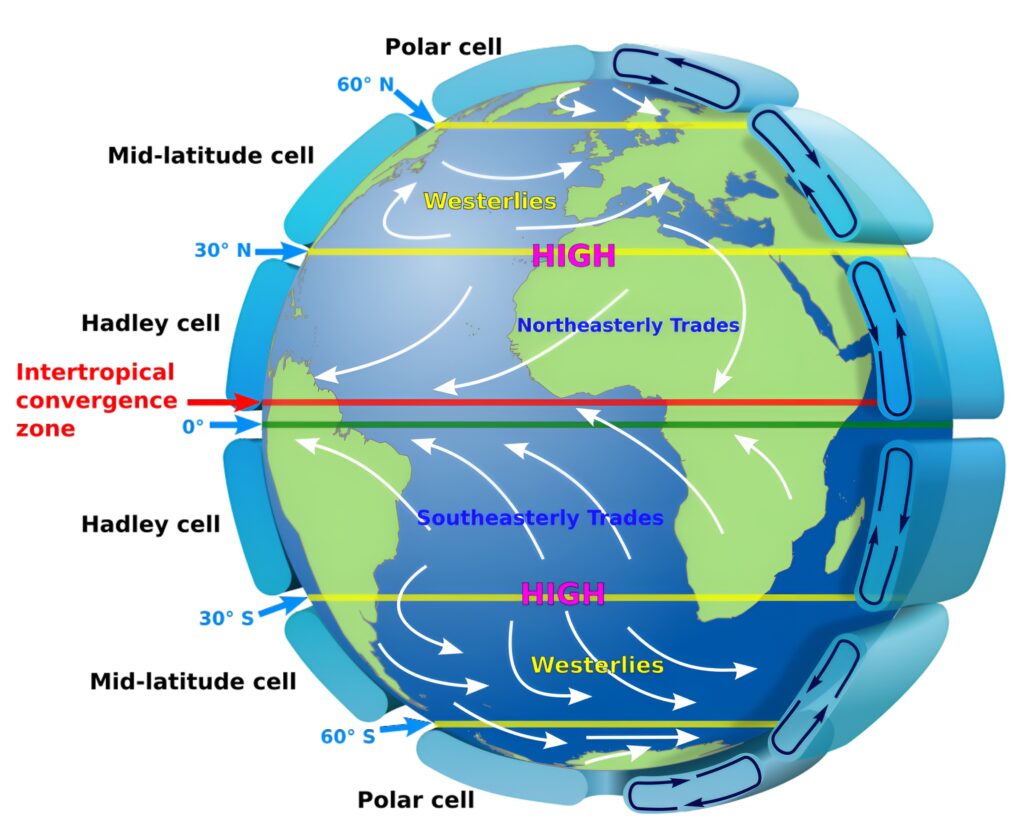
Table of Contents
What are Westerlies?
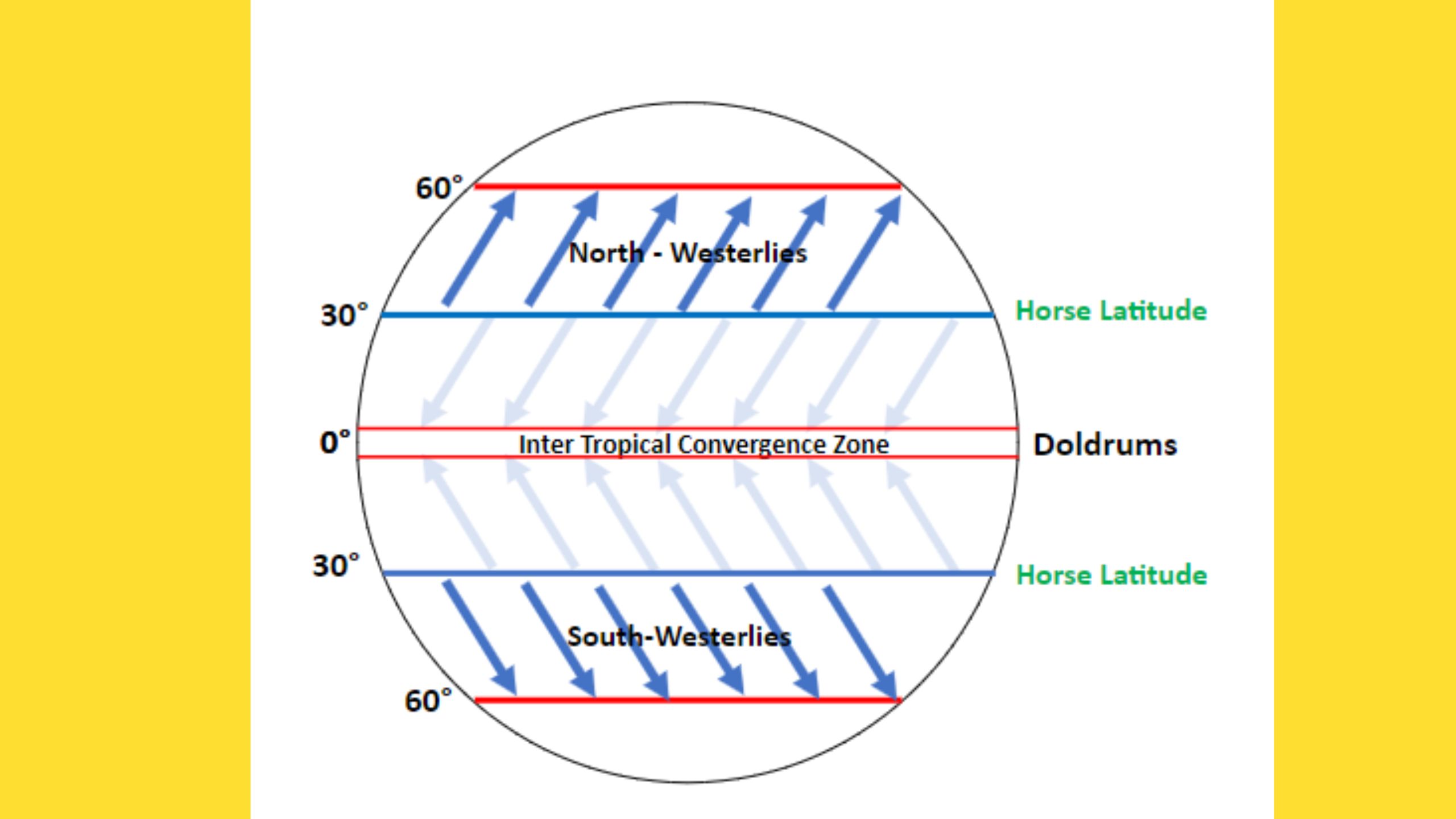
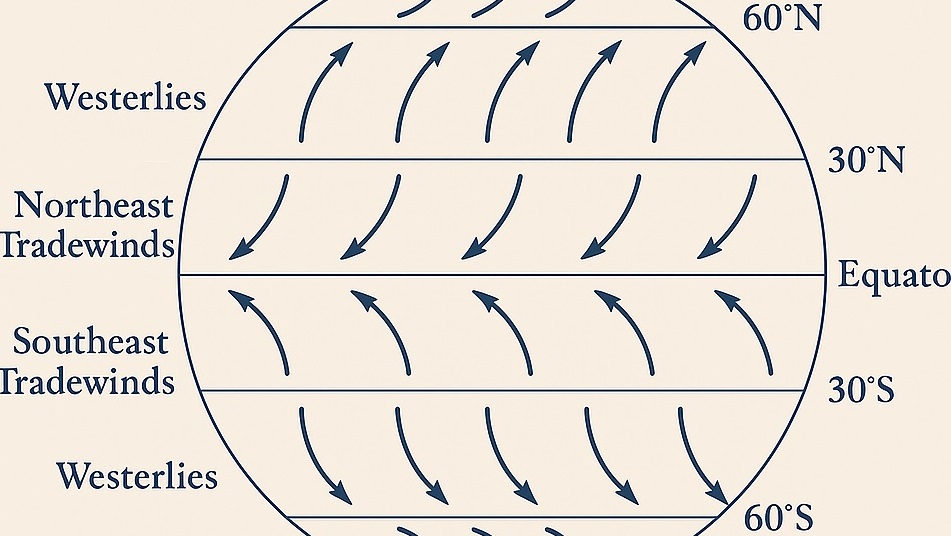
Westerlies refer to a type of prevailing wind that blows from the west towards the east, influenced by the Coriolis effect. These winds are most prominent in the middle latitudes, specifically between 30 and 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres.
Characteristics of the Westerlies
- Direction: Westerlies blow from the west to the east. They are also known as the “prevailing westerlies.”
- Speed: The speed of the Westerlies varies depending on the season and location. Generally, they are faster in winter than in summer.
- Latitude: Westerlies are most prominent in the middle latitudes, specifically between 30 and 60 degrees latitude.
- Influence on weather: Westerlies influence weather patterns by carrying air masses, which affect temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
Formation of the Westerlies
The Westerlies are formed due to the rotation of the Earth (Coriolis effect) and the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. As warm air rises near the equator, it moves poleward and cools. At around 30° latitude, this air descends and moves back toward the equator as Trade Winds. Meanwhile, some air moves toward the poles and is deflected eastward by the Coriolis force, creating the Westerlies.
These winds are part of the Ferrel Cell, a component of the three-cell model of atmospheric circulation, which includes the Hadley Cell, Ferrel Cell, and Polar Cell.
Factors Affecting Westerlies
The Westerlies are global winds that blow from west to east in the middle latitudes of the Earth’s atmosphere. They are driven by the Earth’s rotation and the differential heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. The following are some of the primary causes of the Westerlies:
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation causes the Westerlies to curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This is known as the Coriolis Effect and is a result of the Earth’s rotation.
- Pressure Gradient Force: The Westerlies are driven by the difference in air pressure between the subtropical high-pressure systems and the polar low-pressure systems. The pressure gradient force causes air to move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, resulting in the Westerlies.
- Temperature Gradient: The Westerlies are also influenced by the temperature gradient between the equator and the poles. As warm air rises near the equator and cold air sinks near the poles, the resulting temperature gradient helps drive the Westerlies.
- Jet Stream: The Westerlies are also influenced by the jet stream, which is a narrow band of strong winds in the upper atmosphere that flows from west to east. The jet stream can influence the direction and strength of the Westerlies.
Overall, the Westerlies are a complex phenomenon that is influenced by many factors, including the Earth’s rotation, air pressure, temperature, and the jet stream.
Effects of the Westerlies
The Westerlies play a significant role in shaping weather patterns across the globe. Some of their effects include:
- Transporting weather systems: Westerlies carry weather systems from west to east, affecting weather patterns in different regions.
- Climate: Westerlies influence climate by transporting air masses that impact temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns.
- Agriculture: Westerlies play a crucial role in agriculture by affecting the distribution of rainfall, which is critical for crop growth.
- Flight paths: Westerlies are also crucial in determining flight paths for commercial airlines.
What are Easterlies?
Easterlies are a type of prevailing wind that blows from the east towards the west. They are most prominent in the low latitudes, specifically between 0 and 30 degrees latitude in both hemispheres. There are two types of Easterlies: Trade Winds and Polar Easterlies.
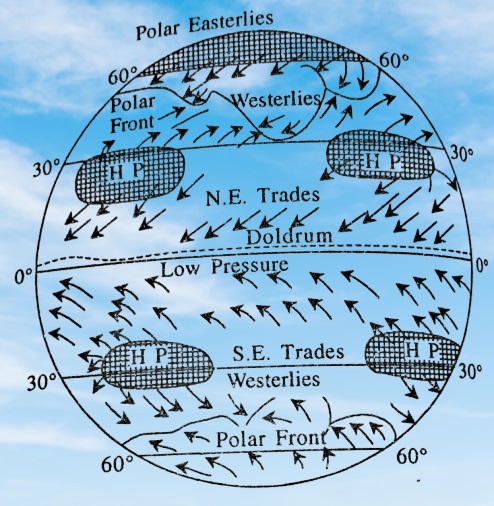

Easterlies (Trade Winds and Polar Easterlies)
Easterlies refer to winds that blow from the east to the west. There are two main types of Easterlies: Tropical easterlies and Polar Easterlies.
Trade Winds (Tropical Easterlies)
-
Found between 30°N and 30°S latitude.
-
These winds blow from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere.
-
Historically, they were used by sailors to navigate across oceans, hence the name “trade winds.”
-
They are steady and strong, helping to drive ocean currents and influencing tropical weather patterns, including the movement of monsoons and cyclones.


Characteristics of the Tropical Easterlies
- Direction: Easterlies blow from the east towards the west.
- Speed: The speed of the Easterlies varies depending on the season and location. They are typically slower than Westerlies.
- Latitude: Easterlies are most prominent in the low latitudes, specifically between 0 and 30 degrees latitude.
- Influence on weather: Easterlies influence weather patterns by carrying air masses, which affect temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
Causes of the Tropical Easterlies
The primary cause of the Easterlies is the Hadley cell circulation. The Hadley cell is a large-scale atmospheric circulation pattern that transports heat and moisture from the equator to the tropics. It consists of rising air near the equator and sinking air near 30 degrees latitude, creating the Easterlies.
Effects of the Tropical Easterlies
The Easterlies also play a significant role in shaping weather patterns across the globe. Some of their effects include:
- Transporting weather systems: Easterlies carry weather systems from east to west, affecting weather patterns in different regions.
- Climate: Easterlies influence climate by transporting air masses that impact temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns.
- Maritime trade: Easterlies have historically played a significant role in facilitating trade routes across the world’s oceans. For example, the trade winds, which are a type of easterly wind, enabled European sailors to reach the Americas from Europe during the Age of Exploration.
- Tropical storms: Easterly winds can contribute to the formation and intensification of tropical storms, such as hurricanes and typhoons. As the easterly winds move from east to west, they carry warm, moist air over the warm ocean waters, creating the ideal conditions for these types of storms to form.
- Drought: In some regions, easterly winds can contribute to drought conditions. For example, in parts of Africa, the easterly winds known as the Harmattan blow dry air over the region, leading to dry and dusty conditions.
- Ocean currents: The easterly winds can also contribute to the formation of ocean currents. As the winds blow across the surface of the ocean, they create surface currents that can affect marine ecosystems and ocean circulation patterns.
Polar Easterlies
-
Located near the poles, between 60° and 90° latitude in both hemispheres.
-
These cold, dry winds blow from the east to the west and are less consistent than trade winds.
-
They are formed when cold air at the poles sinks and moves towards the equator.
Characteristics of Polar Easterlies
- Direction: Flow east to west, opposite to the mid-latitude Westerlies.
- Origin: Develop in polar high-pressure zones (60°–90° latitude).
- Temperature: Extremely cold, due to minimal solar heating.
- Moisture: Generally dry, as cold air holds little water vapor.
- Impact: Help form the polar front, a zone where they meet the warmer Westerlies, leading to storm development.
Geographical Influence of Polar Easterlies
- In the Northern Hemisphere, these winds dominate areas around the Arctic.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, they affect Antarctica, playing a role in extreme cold weather systems.
Differences between Westerlies and Easterlies
Although Westerlies and Easterlies are both prevailing winds that impact weather patterns across the globe, they differ in several ways:
- Direction: Westerlies blow from west to east, while Easterlies blow from east to west.
- Latitude: Westerlies are most prominent in the middle latitudes, while Easterlies are most prominent in the low latitudes.
- Speed: Westerlies are typically faster than Easterlies, particularly in the winter months.
- Causes: Westerlies are mainly caused by the rotation of the earth, while Easterlies are primarily caused by the Hadley cell circulation.
- Effects: While both types of winds transport weather systems and impact climate, Westerlies play a more significant role in agriculture and flight paths, while Easterlies have a more significant impact on maritime trade, tropical storms, drought, and ocean currents.
| Criteria | Westerlies | Easterlies |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | From west to east | From east to west |
| Latitude | Most prominent in middle latitudes | Most prominent in low latitudes |
| Cause | Earth’s rotation | Hadley cell circulation |
| Speed | Faster, especially in winter months | Slower than Westerlies |
| Effect on Agriculture | Influential and affect agricultural practices | Not significant |
| Impact on Flight Paths | Influential and form jet streams | Limited impact |
| Impact on Maritime Trade | Not significant | Play a significant role in facilitating trade routes and affect ocean currents |
| Effect on Tropical Storms | Not significant | Contribute to the formation and intensification of tropical storms |
| Impact on Drought | Not significant | Can contribute to drought conditions in some regions |
| Contribution to Ocean Currents | Contribute to ocean currents in the Northern Hemisphere | Contribute to ocean currents in the Southern Hemisphere |
Westerlies and Easterlies : Summary
- Westerlies blow from west to east and are most prominent in the middle latitudes, while Easterlies blow from east to west and are most prominent in the low latitudes.
- Westerlies are mainly caused by the rotation of the earth, while Easterlies are primarily caused by the Hadley cell circulation.
- Westerlies are faster than Easterlies, particularly in the winter months.
- Westerlies impact agriculture and flight paths, while Easterlies impact maritime trade, tropical storms, drought, and ocean currents.
- Westerlies play a significant role in the formation of weather systems in the middle latitudes, while Easterlies play a significant role in the formation of tropical storms.
- Westerlies contribute to the formation of ocean currents in the northern hemisphere, while Easterlies contribute to the formation of ocean currents in the southern hemisphere.
- Westerlies can create jet streams, which impact air travel and weather patterns, while Easterlies can contribute to dust storms in some regions.
- Westerlies and Easterlies are interconnected systems that impact climate and weather patterns across the globe.
- Understanding these wind patterns is crucial for various industries and fields, from agriculture and aviation to maritime trade and climate science.
Westerlies and Easterlies : MCQs
Q. Which wind blows from west to east?
A) Westerlies
B) Easterlies
C) Trade winds
D) Monsoons
Answer: A) Westerlies
Explanation: Westerlies blow from west to east, while Easterlies blow from east to west.
Q. What is the primary cause of Westerlies?
A) Hadley cell circulation
B) Polar cell circulation
C) Ferrel cell circulation
D) Earth’s rotation
Answer: D) Earth’s rotation
Explanation: Westerlies are mainly caused by the rotation of the earth, while Easterlies are primarily caused by the Hadley cell circulation.
Q. Which wind pattern is most prominent in the low latitudes?
A) Westerlies
B) Easterlies
C) Polar easterlies
D) Trade winds
Answer: B) Easterlies
Explanation: Easterlies are most prominent in the low latitudes, while Westerlies are most prominent in the middle latitudes.
Q. Which wind is faster, Westerlies or Easterlies?
A) Westerlies
B) Easterlies
C) They are the same speed
D) It depends on the season
Answer: A) Westerlies
Explanation: Westerlies are typically faster than Easterlies, particularly in the winter months.
Q. Which wind contributes to the formation of tropical storms?
A) Westerlies
B) Easterlies
C) Trade winds
D) Monsoons
Answer: B) Easterlies
Explanation: Easterlies can contribute to the formation and intensification of tropical storms, such as hurricanes and typhoons.
Read: Geography Notes