Areal differentiation is a concept in geography that refers to the spatial variation of geographical phenomena (Human and Physical) across different regions. Its study is a crucial aspect of understanding how different parts of the earth’s surface are unique in terms of their physical and cultural features. This concept was central to traditional geography and was championed by scholars like Richard Hartshorne.
"Areal Differentiation refers to the concept that different areas on the Earth’s surface are unique due to variations in their physical and human characteristics"
Table of Contents
What is Areal Differentiation?
It refers to the process of dividing a given area into smaller units based on their physical, cultural, and socio-economic characteristics. This process enables geographers to study the differences and similarities between regions and to determine how these differences shape the landscape.

Who propounded the concept of areal differentiation?
It was actually first propounded by the American geographer Richard Hartshorne in his book “The Nature of Geography” published in 1939. Hartshorne emphasized the importance of studying the unique characteristics of different regions and their spatial patterns in order to better understand the complex relationships between human and natural systems. He argued that regions should not be viewed simply as collections of individual features, but rather as integrated systems with their own unique structure and function. Hartshorne’s concept of areal differentiation had a significant impact on the development of regional geography as a subfield of geography.
Why is Areal Differentiation Important?
It is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps geographers to understand the complexity of the earth’s surface and the various factors that contribute to the diversity of landscapes. Secondly, it provides a useful tool for regional planning and decision-making by allowing planners and policymakers to understand the unique challenges and opportunities present in each area. Thirdly, it is a useful tool for comparative studies between regions, allowing geographers to identify common trends and patterns and to make meaningful comparisons between areas.
Applications of Areal Differentiation
Areal differentiation has a wide range of applications in geography and other related fields.
Application in Regional Planning
Areal differentiation provides a basis for regional planning by helping planners and policymakers understand the unique challenges and opportunities in each area. This information can be used to make informed decisions about land use, transportation systems, and other critical infrastructure projects. Since different areas have different strengths, weaknesses, and needs, planning must be customized for each region.
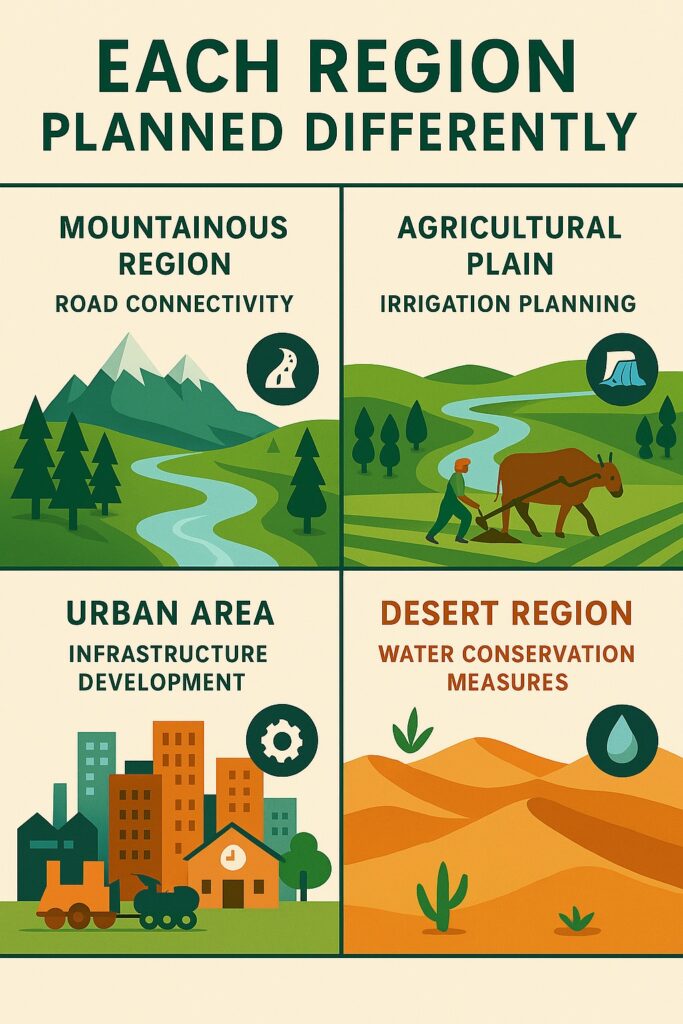
1. Mountainous Region — Road Connectivity
-
Why?: Mountains have difficult terrain, sparse population, and poor accessibility.
-
Planning Need: Roads, tunnels, ropeways, and transport infrastructure to connect remote areas and promote tourism, trade, and services.
2. Agricultural Plain — Irrigation Planning
-
Why?: Fertile plains support farming, but productivity depends on water supply.
-
Planning Need: Canals, tube wells, dams, and crop pattern planning to improve agricultural output and food security.
3. Urban Area — Infrastructure Development
-
Why?: Cities face pressure from high population density and rapid urbanization.
-
Planning Need: Housing, transportation, sewage systems, electricity, education, and healthcare infrastructure.
4. Desert Region — Water Conservation Measures
-
Why?: Scarce rainfall and extreme temperatures make life and agriculture difficult.
-
Planning Need: Rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, drip irrigation, and desert-afforestation projects.

Role of Areal Differentiation in Regional Planning
Application in Economic Geography
Areal differentiation is also important in economic geography, as it helps geographers to understand the economic structure of regions and the factors that contribute to economic growth and development.
How Areal Differentiation Supports Economic Geography?
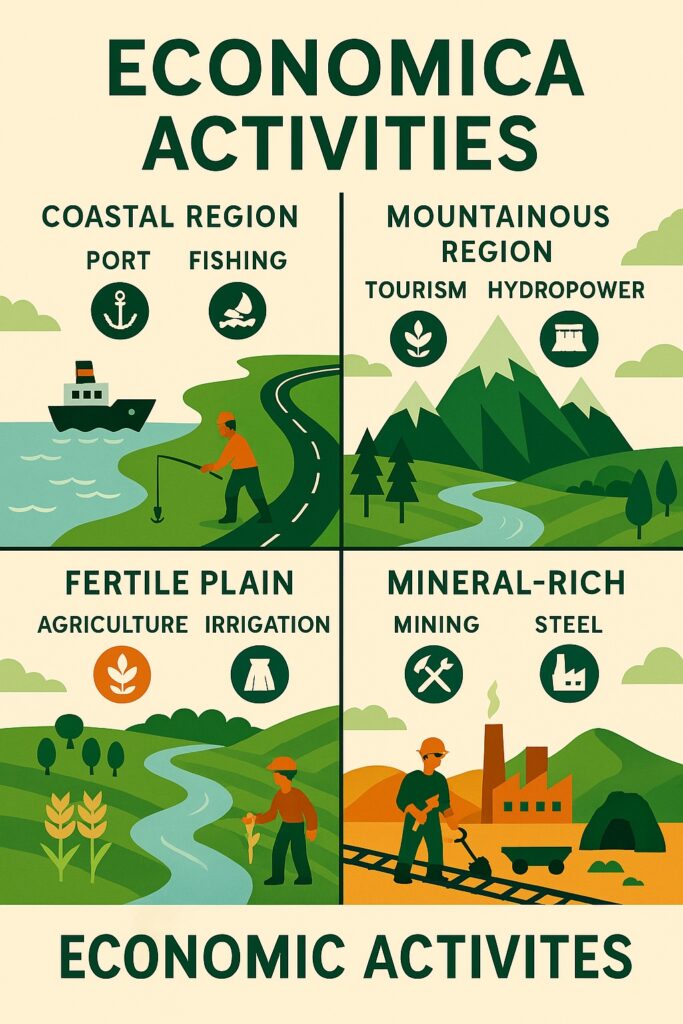
1. Resource Distribution
-
Some areas are rich in minerals (e.g., Jharkhand), while others are fertile for agriculture (e.g., Punjab).
-
Economic activities grow based on local resource availability.
2. Labor and Population Patterns
-
Regions with dense population (like urban centers) support service and manufacturing industries.
-
Sparsely populated areas (like deserts or mountains) have lower economic density and different needs.
3. Transport and Accessibility
-
Plains and coasts are better connected and attract trade and industries.
-
Remote regions may rely more on subsistence economy or limited commercial activities.
4. Climatic Suitability
-
Tea plantations flourish in Assam due to suitable rainfall and temperature.
-
Dry areas like Rajasthan support pastoralism or solar energy projects.
5. Development Potential
- Each region has comparative advantages.
- Gujarat for industries
- Kerala for tourism and remittances
- Himachal for horticulture and hydropower
Why it Matters for Economic Planning?
-
Balanced Regional Development: Policies can be designed to uplift backward regions based on their local strengths.
-
Avoid Overconcentration: Areal differentiation discourages pushing all industries into a few urban hubs.
-
Sustainability: Planning based on local characteristics ensures that natural and human resources are used wisely.
Application in Political Geography
In political geography, areal differentiation is used to study the distribution of political power and to understand how political boundaries are shaped by physical and cultural factors.

Application in Cultural Geography
Areal differentiation is also important in cultural geography, as it helps geographers to understand the cultural landscape and to study the distribution of different cultural groups.
Criticisms of Areal Differentiation
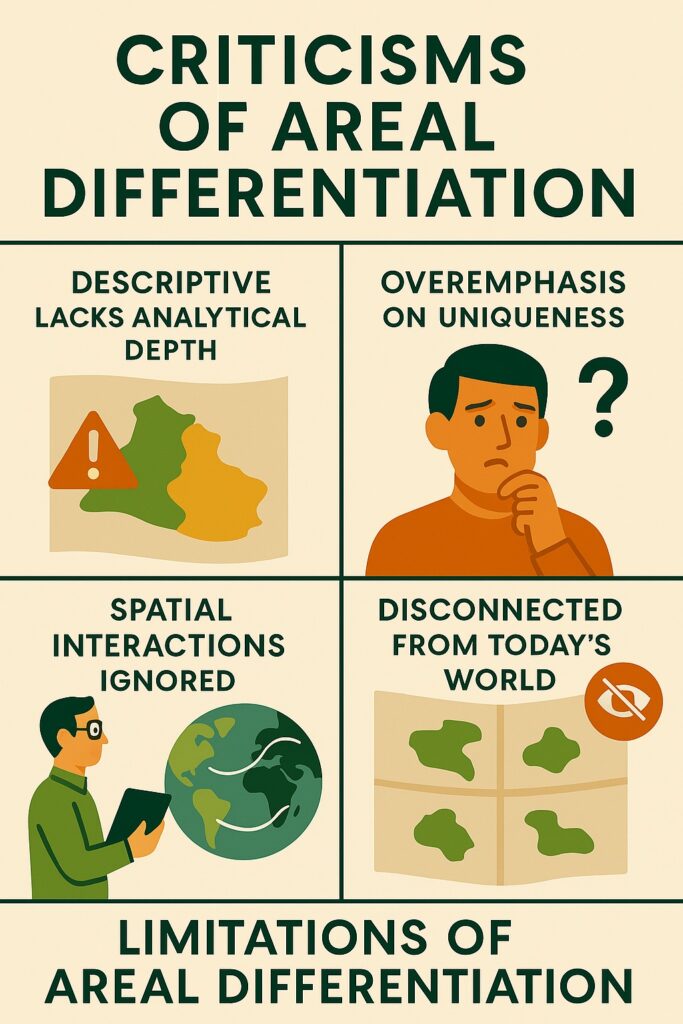
- It has been criticized for its overemphasis on regional differences, which can neglect the ways in which regions are interconnected and interdependent.
- A mathematical model can not be made in this approach.
In conclusion, it is a crucial aspect of geography that enables geographers to understand the complexities of the earth’s surface and the various factors that contribute to the diversity of landscapes. With its wide range of applications, it provides a useful tool for regional planning, economic analysis, political analysis, and cultural analysis.
Read: Geography Notes