Class 11 Geography NCERT Solutions Chapter 12 World Climate and Climate Change
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following is suitable for Koeppen’s “A” type of climate?
(a) High rainfall in all the months
(b) Mean monthly temperature of the coldest month more than freezing point
(c) Mean monthly temperature of all the months more than 18o C
(d) Average temperature for all the months below 10° C
Ans: (c) Mean monthly temperature of all the months more than 18°C
Explanation: Koeppen’s climate classification system categorizes the “A” type of climate as tropical climates, where the mean monthly temperature of all months is generally above 18°C (64.4°F). This type of climate is typically characterized by high temperatures throughout the year. High rainfall in all the months is not a specific characteristic of the “A” type climate.

(ii) Koeppen’s system of classification of climates can be termed as:
(a) Applied
(b) Systematic
(c) Genetic
(d) Empirical
Answer: (d) Empirical
Explanation: Koeppen’s system of climate classification is based on observed data and empirical relationships between climate parameters. It categorizes climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns, making it an empirical classification system.
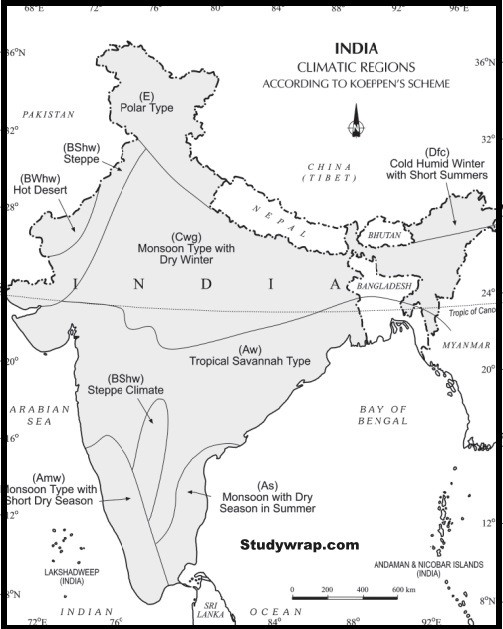
(iii) Most of the Indian Peninsula will be grouped according to Koeppen’s system under:
(a) “Af”
(b) “BSh”
(c) “Cfb”
(d) “Am”
Answer: (d) “Am”
Explanation: According to Koeppen’s climate classification system, most of the Indian Peninsula will be grouped under the category of “Am,” which represents a tropical monsoon climate. This classification is characterized by high temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons, with the majority of the annual precipitation occurring during the monsoon season.
(iv) Which one of the following years is supposed to have recorded the warmest temperature the world over?
(a) 1990
(b) 1998
(c) 1885
(d) 1950
Answer: (b) 1998
Explanation: The year 1998 is often cited as having recorded some of the warmest global temperatures on record. It was a year characterized by significant El Nino conditions, which contributed to elevated global temperatures.
(v) Which one of the following groups of four climates represents humid conditions?
(a) A—B—C—E
(b) A—C—D—E
(c) B—C—D—E
(d) A—C—D—F
Answer: (b) A—C—D—E
Explanation: In Koeppen’s climate classification, the climates that represent humid conditions are A (tropical), C (warm temperate), D (cold temperate), and E (polar climates). This combination collectively represents regions with humid conditions.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Which two climatic variables are used by Koeppen for classification of the climate?
Ans: Koeppen’s classification of climate is primarily based on two climatic variables: temperature and precipitation. These variables help categorize different climate types based on their distinct characteristics.
(ii) How is the “genetic” system of classification different from the “empirical one”?
Ans: The “genetic” system of classification emphasizes the underlying processes and causes that give rise to specific climate types, while the “empirical” system relies on observed data and statistical patterns without necessarily delving into the underlying mechanisms. The genetic approach aims to explain why certain climates occur, while the empirical approach focuses on describing and categorizing climates based on measurable parameters.
(iii) Which types of climates have very low range of temperature?
Ans: Tropical and equatorial climates generally exhibit a very low range of temperature. These regions experience consistently high temperatures throughout the year, with minimal fluctuations between seasons.
(iv) What type of climatic conditions would prevail if the sun spots increase?
Ans: An increase in sunspots is associated with warmer climatic conditions on Earth. Sunspots are linked to variations in solar radiation and can influence the planet’s temperature. An increase in sunspots generally leads to higher solar activity and can contribute to periods of warming.
3. Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Make a comparison of the climatic conditions between the “A” and “B” types of climate.
Ans:
(ii) What type of vegetation would you find in the “C” and “A” type(s) of climate?
Ans: Vegetation in “C” and “A” Type(s) of Climate: In the “C” type climate (Warm Temperate), vegetation includes deciduous forests, mixed forests, and grasslands. This type experiences moderate temperatures with distinct seasons, featuring mild winters and warm summers. “C” climates are found in regions with temperate conditions, such as parts of North America and Europe.
The “A” type climate (Tropical) supports diverse and lush vegetation, including tropical rainforests, tropical seasonal forests, and savannas. Adapted to high temperatures and abundant rainfall, these regions foster rich biodiversity. They are situated near the equator, as seen in the Amazon Basin, Central Africa, and Southeast Asia.
(iii) What do you understand by the term “Greenhouse Gases”? Make a list of
greenhouse gases.
Ans: Understanding “Greenhouse Gases” and List of Greenhouse Gases: Greenhouse gases are atmospheric gases that trap heat from the sun, contributing to the greenhouse effect and warming the Earth’s surface. They play a crucial role in regulating the planet’s temperature. Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Water Vapor (H2O), Ozone (O3), and Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are some greenhouse gases.
CO2 is released primarily through human activities like burning fossil fuels, while CH4 comes from sources such as livestock digestion. N2O is emitted from agriculture, and H2O varies naturally with temperature. O3 exists in the upper atmosphere as protective ozone and at ground level as a pollutant. CFCs, once used in refrigeration and aerosols, were phased out due to ozone depletion concerns. The enhanced greenhouse effect, caused by increased concentrations of these gases, contributes to global warming and climate change.
