Conrad Discontinuity is a boundary that separates the upper and lower continental crust. It is located approximately 10 to 12 kilometers below the Earth’s surface and is characterized by a sudden increase in seismic wave velocity as they pass through it. The increase in velocity is due to the change in the composition of the crustal rocks above and below the discontinuity.
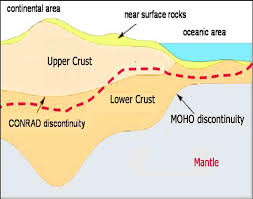
The rocks above the Conrad Discontinuity are typically composed of lighter and less dense granitic rocks, while those below the discontinuity are composed of denser and more mafic rocks such as gabbro and basalt.
Its discovery and study has provided valuable insights into the structure and composition of the Earth’s continental crust. It has also been used in the exploration for natural resources such as oil and gas, as the discontinuity can act as a barrier that traps these resources.
In conclusion, the Conrad Discontinuity is a significant boundary in the Earth’s crust that separates the upper and lower continental crust. Its discovery and study have provided valuable insights into the composition and structure of the Earth’s crust, and continue to inform our understanding of the geological processes that occur within it.
Important Links