The Linkage of Rivers or River Interlinking Project in India is an ambitious plan of connecting major rivers through a network of canals and reservoirs. The objective is to transfer water from surplus river basins to water-deficient regions to ensure uniform water distribution across the country. It is seen as a possible long-term solution to India’s recurring problems of droughts and floods.
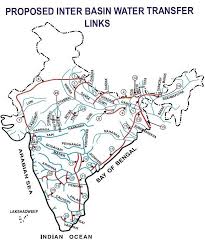
The linkage of rivers in India has been a subject of discussion for several decades and has gained momentum in recent years. The idea is to transfer water from surplus river basins to deficient ones through a network of canals, reservoirs, and pipelines. This would not only address the issue of water scarcity in some regions but also provide a more reliable source of water for agriculture, industry, and households.
Table of Contents
Benefits of River Linkage in India
- Addresses Water Scarcity: The most significant benefit of river linkage in India is that it addresses the issue of water scarcity in some regions. By transferring surplus water from one basin to another, the country can ensure that all regions have access to a reliable source of water, which is essential for agriculture, industry, and households.
- Improved Agricultural Production: Another benefit of river linkage is that it can improve agricultural production by providing a reliable source of water for irrigation. This is particularly important in regions that experience water scarcity, as it can help to increase agricultural yields and boost the economy.
- Flood Control: River linkage can also help to control floods by diverting excess water from flooded areas to other regions. This can reduce the risk of damage to crops, homes, and infrastructure, and help to prevent loss of life.
- Hydropower Generation: River linkage can also provide an additional source of hydropower, as the transfer of water from one basin to another can be used to generate electricity. This can help to meet the growing demand for energy in India and reduce the country’s dependence on fossil fuels.
Challenges of River Linkage in India
- Technical Challenges: One of the biggest challenges of river linkage in India is the technical complexity of the projects. The transfer of water from one basin to another requires the construction of large-scale infrastructure, including canals, reservoirs, and pipelines, which can be expensive and difficult to construct.
- Environmental Concerns: Another challenge of river linkage is the potential environmental impact. The transfer of water from one basin to another can affect the natural flow of rivers, as well as the ecosystem, including the migration patterns of fish and other aquatic species.
- Cost: Another challenge of river linkage is the cost. The construction of large-scale infrastructure projects is expensive, and the cost of river linking projects can be substantial.
- Social and Political Challenges: Finally, river linkage can also face social and political challenges, as it may affect the rights and livelihoods of local communities. In some cases, the transfer of water from one region to another may lead to disputes between states and local communities, which can be difficult to resolve.
Examples of River Linkage Projects in India
- National River Linking Project: The National River Linking Project is one of the largest river linking projects in India. It aims to connect 30 rivers across the country through a network of canals, reservoirs, and pipelines. The project is expected to provide a reliable source of water for agriculture, industry, and households, as well as reduce the risk of floods and increase hydropower generation.
- Ken-Betwa Link Project: The Ken-Betwa Link Project is a river linking project that aims to transfer water from the Ken River in Madhya Pradesh to the Betwa River in Uttar Pradesh. The project will provide a reliable source of water for agriculture and industry in the region and is expected to benefit over 2 million people.
- Godavari-Cauvery Link Project: The Godavari-Cauvery Link Project aims to connect the Godavari River in the south with the Cauvery River in the south. The project will transfer surplus water from the Godavari River to the Cauvery River basin, which will help to address water scarcity in the region and improve agricultural production.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the linkage of rivers in India has the potential to provide a number of benefits, including addressing water scarcity, improving agricultural production, controlling floods, and increasing hydropower generation. However, it also poses a number of challenges, including technical difficulties, environmental concerns, cost, and social and political challenges.
Moving forward, it will be important for the Indian government to carefully consider the potential benefits and challenges of river linkage projects, and to engage with local communities and other stakeholders to ensure that these projects are developed in a responsible and sustainable manner. The success of river linkage projects in India will depend on the ability of the government to balance the needs of different stakeholders, including farmers, industry, and the environment, and to ensure that these projects are developed in a transparent and accountable manner.
Read: Geography Notes