Local winds are winds that are generated by local temperature and pressure differences, such as sea breezes and land breezes. These winds are different from the global winds, which are driven by large-scale temperature and pressure differences between the equator and poles.
Table of Contents
What are Local Winds?
A local wind is a type of wind that is influenced by the local geography, temperature, and pressure differences in a particular region. These winds usually occur over a relatively small area and are caused by the interaction of the earth’s surface with the atmosphere.
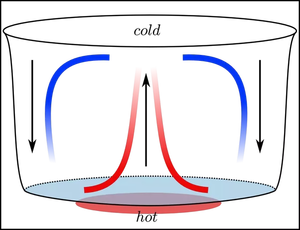
Types of Local Winds
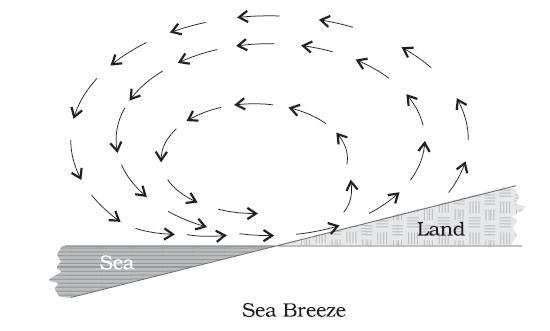
Sea Breezes
Sea breezes are winds that blow from the sea towards the land, driven by the cooling of the sea surface and the heating of the land. During the day, the sun heats the land, causing it to become warmer than the sea. This temperature difference creates a pressure gradient, with the land at a higher pressure than the sea. The sea breeze is created when the air from the sea rushes towards the land, seeking to equalize the pressure difference.
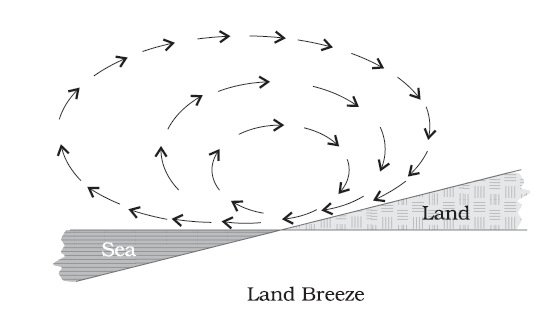
Land Breezes
Land breezes are winds that blow from the land towards the sea, driven by the cooling of the land and the heating of the sea surface. During the night, the land cools faster than the sea, creating a pressure gradient with the land at a lower pressure than the sea. The land breeze is created when the air from the land rushes towards the sea, seeking to equalize the pressure difference.
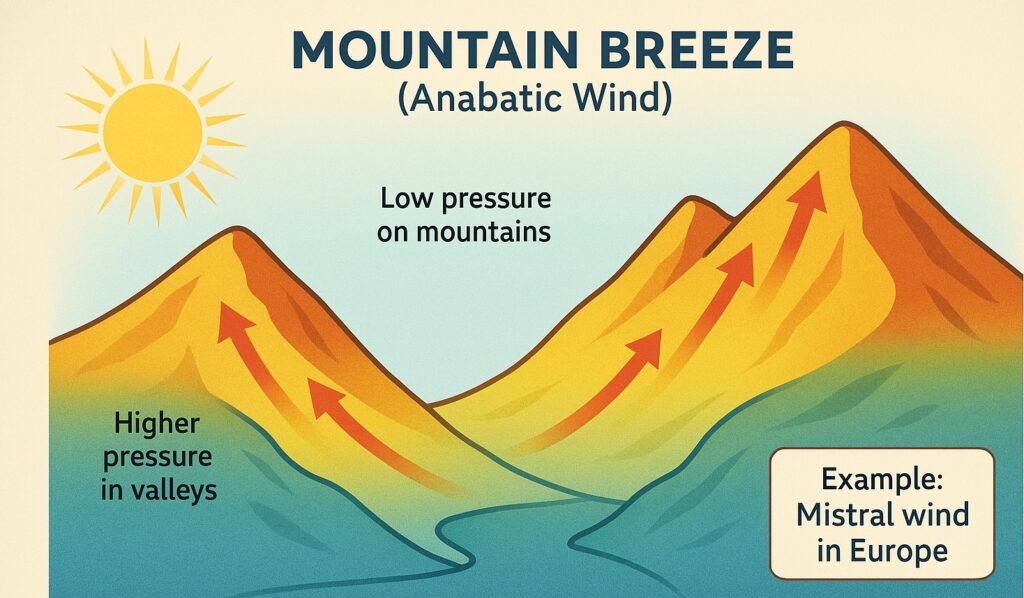
Mountain Breezes
Mountain breezes are winds that blow along the slopes of mountains, driven by temperature differences between the mountains and the adjacent valleys. During the day, the sun heats the mountains, causing them to become warmer than the surrounding valleys. This temperature difference creates a pressure gradient, with the mountains at a lower pressure than the valleys. The mountain breeze is created when the air from the valleys rushes up the slopes of the mountains, seeking to equalize the pressure difference. Mistral wind in Europe is an example of mountain breeze.
Valley Breezes
Valley breezes are winds that blow up the valleys, driven by temperature differences between the valleys and the adjacent mountains. During the night, the valleys cool faster than the mountains, creating a pressure gradient with the valleys at a lower pressure than the mountains. The valley breeze is created when the air from the mountains rushes down into the valleys, seeking to equalize the pressure difference.
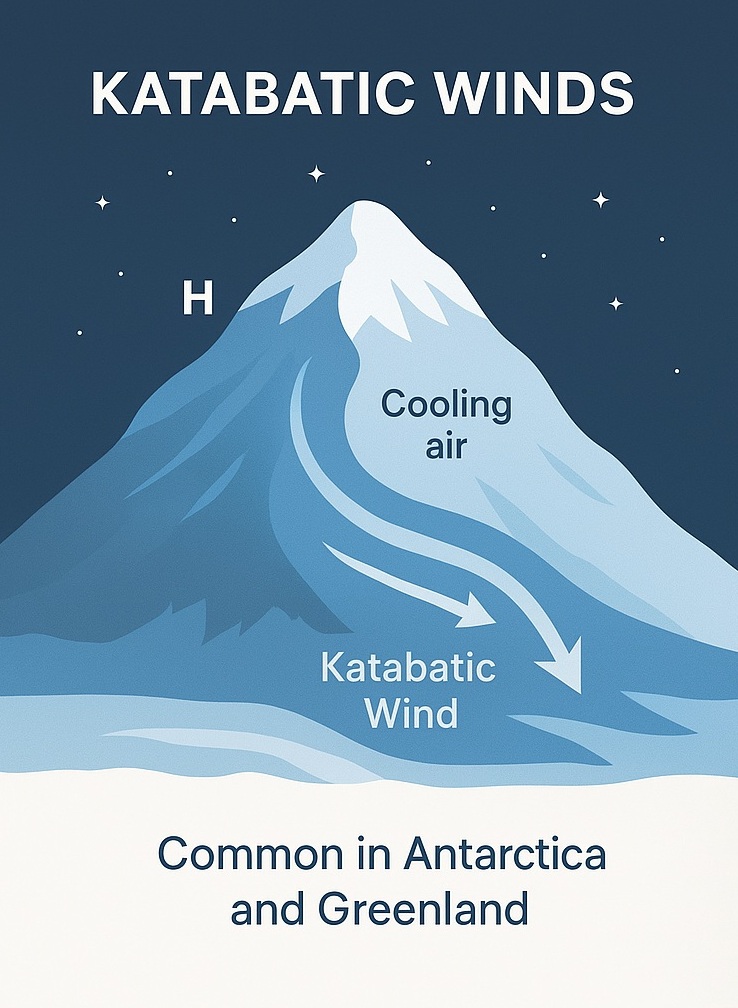
Katabatic Winds
Katabatic winds are winds that occur in polar and mountainous regions. They are caused by the cooling of the air above the slopes, which creates a high-pressure area. The air then flows downhill, creating a katabatic wind.
Katabatic winds can have significant impacts on human activities, such as aviation and transportation, as they can create strong and unpredictable winds.
Adiabatic Winds
Adiabatic wind refers to the change in wind speed and direction that occurs as a result of changes in temperature due to adiabatic processes in the atmosphere. Adiabatic processes are those in which no heat is exchanged between the system and its surroundings, so the temperature change is solely due to changes in pressure and volume.
One example of adiabatic wind is the chinook or foehn wind, which occurs when warm, dry air flows down a mountain slope, compressing and warming up as it descends due to the increase in pressure. This can lead to significant increases in temperature and changes in wind direction and speed in the region below the mountain. Similarly, the “katabatic” wind is another type of adiabatic wind that occurs when cold, dense air flows downhill due to gravity, creating strong, gusty winds that can affect local weather patterns.
Impacts of Local Winds
Agriculture
Local winds play a crucial role in agriculture, helping to distribute heat, moisture, and nutrients to crops. For example, sea breezes can bring cool air and moisture to coastal areas, helping to mitigate the effects of droughts and heatwaves. Land breezes, on the other hand, can bring warm air and moisture from the interior of the land to the coastal regions, helping to increase crop yields and improve soil quality.
Energy Production
Local winds are also important for energy production, particularly wind energy. For example, wind turbines located near the coast can harness the energy of the sea breeze, generating electricity for local communities. Similarly, wind turbines located in mountain and valley regions can harness the energy of the mountain and valley breezes, providing renewable energy to the surrounding communities.
Meteorology
Local winds also play a crucial role in shaping local weather patterns and influencing the distribution of heat and moisture around the planet. For example, sea breezes can help to mitigate the effects of heatwaves in coastal regions, while land breezes can bring warm air and moisture from the interior of the land to the coastal regions, helping to increase humidity and precipitation. Understanding the dynamics of local winds is important in making informed decisions about a wide range of weather-related issues, from air quality and public health to water resource management and disaster response.
Answer: d) Sea breezes. Sea breezes occur during the day along coastal regions and are created due to the temperature difference between the land and the sea.