Precipitation is the term used to describe all forms of water that fall from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface. This includes rain, snow, sleet, hail, and other forms of precipitation. Precipitation plays a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle and helps to sustain life on the planet. Understanding the different types and distribution of precipitation is important in predicting and preparing for its potential impacts.
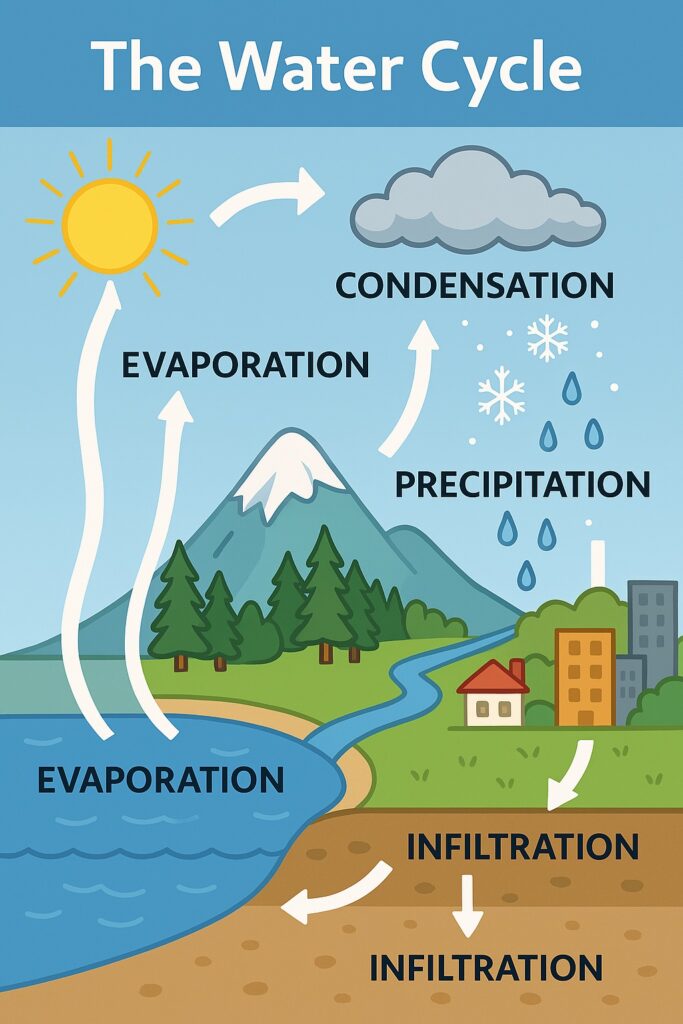
Table of Contents
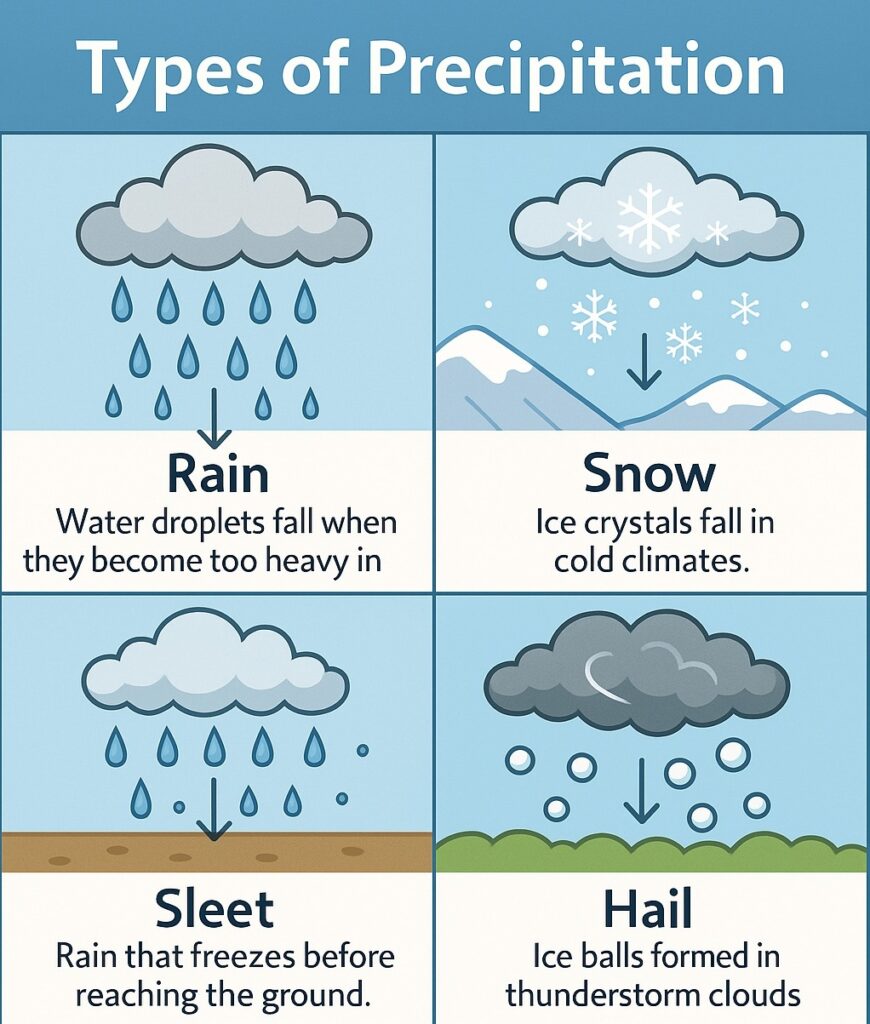
Types of Precipitation
Rain: Rain is the most common form of precipitation, and it occurs when water droplets in the atmosphere combine to form larger droplets that fall from the clouds.
Snow: Snow occurs when precipitation falls from the clouds as ice crystals, and it is most common in areas with cold climates.
Sleet: Sleet occurs when raindrops freeze in the atmosphere before reaching the ground, forming small balls of ice.
Hail: Hail is formed when precipitation freezes into balls of ice while being lifted and dropped within the thunderstorm clouds.
The Role of Precipitation in the Water Cycle
Precipitation plays a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle, which is the continuous movement of water from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface and back to the atmosphere. Precipitation is one of the main sources of water on the planet, and it is essential for sustaining life.
In addition to its role in the water cycle, precipitation also has a significant impact on the weather patterns in many areas. For example, heavy precipitation can cause flooding, while a lack of precipitation can result in drought conditions.
Seasonal Variations in Precipitation
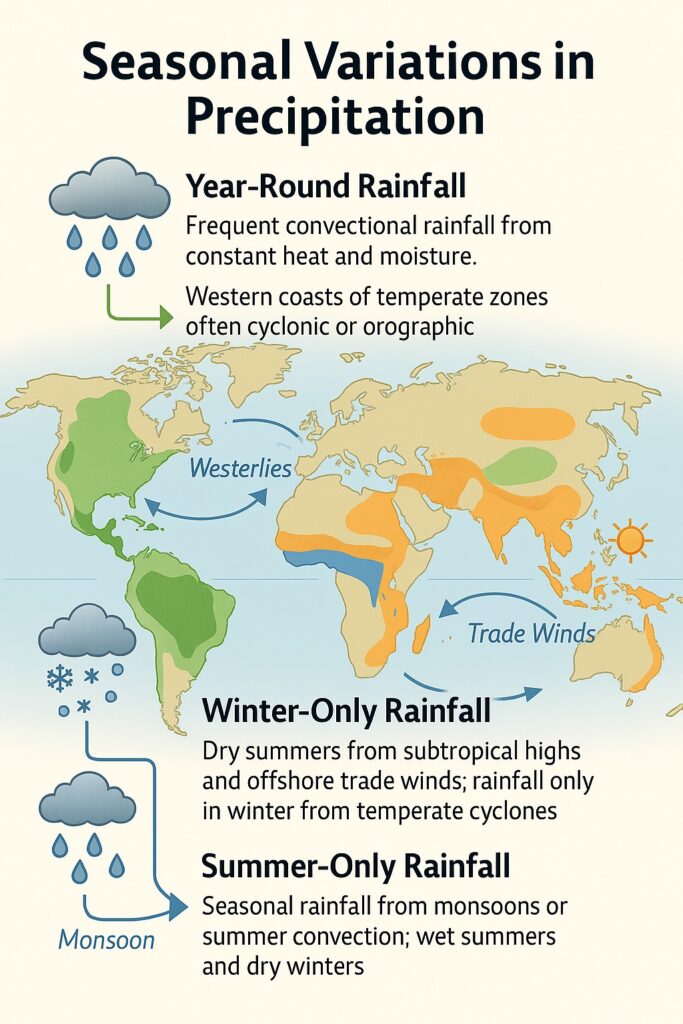
- Year-Round Rainfall
- Equatorial regions get frequent convectional rainfall due to heat and moisture.
- Western coasts of temperate lands get rain from westerlies — often cyclonic or orographic.
- Winter-Only Rainfall
- Seen in Mediterranean-type regions and India’s Coromandel Coast.
- These areas are dry in summer due to sub-tropical highs and offshore trade winds.
- Summer-Only Rainfall
- Most other places (like much of South and Southeast Asia) get rain only in summer, showing clear seasonal variation.
Factors That Affect Rainfall
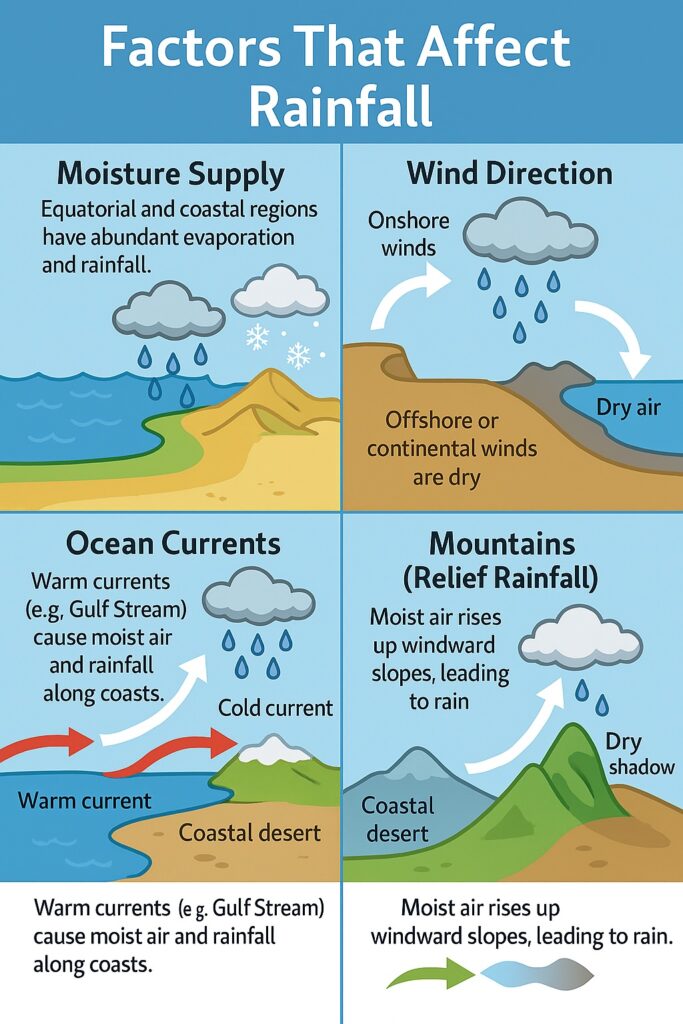
- Moisture Supply
- More water = more evaporation = more rain.
- Equatorial and coastal areas have higher moisture supply.
- Deserts and polar regions have low evaporation and little rain.
- Wind Direction
- Winds from sea to land bring rain.
- Winds from land or higher to lower latitudes tend to be dry.
- Ocean Currents
- Warm currents bring rain;
- Cold currents lead to dry winds and less rain.
- Mountains
- When moist winds hit mountains, they rise, cool, and cause heavy rain.
- The other side (leeward side) gets little or no rain.
Distribution of Rainfall in world
The distribution of rainfall around the world is influenced by a variety of factors, including latitude, topography, and proximity to large bodies of water. Generally speaking, areas near the equator receive the most rainfall, while areas closer to the poles receive less.
- Rainfall is highest near the equator and gets lower as you move toward the poles.
- Coastal areas get more rain than places deep inside continents.
- The east coasts of tropical regions and west coasts of temperate regions receive a lot of rain.
- Windward sides of mountains get heavy rainfall. Leeward sides (rain-shadow areas) are dry.
- Coasts with cold ocean currents are drier than those near warm currents.
- The west sides of tropical lands and polar regions are the driest.
- Tropical easterlies become dry over deserts.
- Polar winds are already cold and dry.
Some of the wettest regions on Earth include the Amazon Rainforest in South America, Central Africa, Southeast Asia, and the islands of the South Pacific. These areas receive high levels of rainfall due to their location near the equator and the presence of tropical rainforests.
In contrast, some of the driest regions on Earth include the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Atacama Desert in South America, and the deserts of Australia. These areas receive very little rainfall due to their location in the subtropics or near the poles, as well as the presence of high pressure systems that inhibit precipitation.
In addition to these broad patterns, rainfall distribution can also be influenced by local factors such as topography, prevailing winds, and ocean currents. For example, mountain ranges can cause orographic rainfall, while coastal regions can experience more rainfall due to the presence of moist ocean air.
Distribution of Rainfall in India
India has a diverse climate due to its large size and varied topography, resulting in a wide range of rainfall patterns across the country. The monsoon season, which lasts from June to September, is the primary source of rainfall for most of India.

The western coast of India, including the states of Maharashtra, Goa, and Kerala, receives some of the highest levels of rainfall in the country due to the influence of the southwest monsoon. The northeastern states of India, including Assam and Meghalaya, also receive heavy rainfall during the monsoon season.
In contrast, the northwestern region of India, including Rajasthan and parts of Gujarat, is relatively dry and experiences very low levels of rainfall throughout the year. The central and southern parts of India, including Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Tamil Nadu, also receive moderate to low levels of rainfall.
Some areas in India experience significant variability in rainfall from year to year. For example, the state of Tamil Nadu in southern India is prone to both droughts and floods due to the erratic behavior of the monsoon.
Overall, India’s rainfall patterns are complex and influenced by a variety of factors, including the monsoon, topography, and ocean currents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precipitation is the term used to describe all forms of water that fall from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, and it plays a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle and in sustaining life on the planet. Understanding the different types and distribution of precipitation is important in predicting and preparing for its potential impacts, and it is essential to be prepared for any potential impacts, such as flooding or drought conditions.