The textile industry is one of the largest and oldest industries in India, encompassing cotton, wool, silk, jute, and synthetic fabrics. It contributes significantly to industrial production, employment, and exports. The location of textile industries in India is determined by a combination of natural, economic, and human factors.

Table of Contents
Availability of Raw Materials
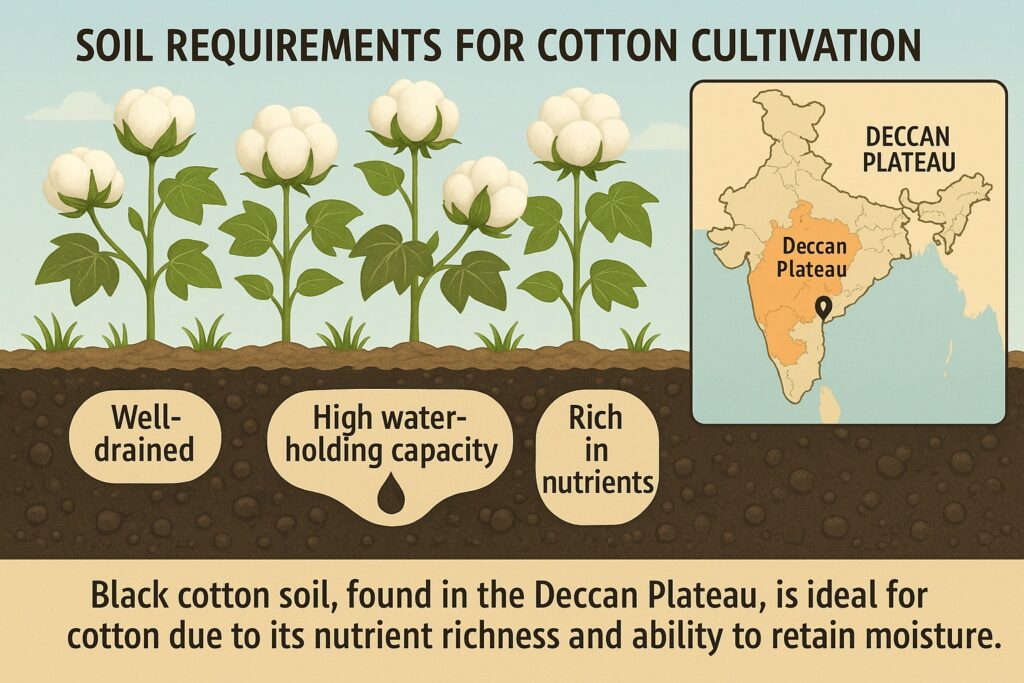
The availability of raw materials such as cotton, silk, jute, wool, and synthetic fibers is a crucial factor in the textile industry. Regions with abundant sources of raw materials are ideal for textile production. In India, the cotton-growing regions in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan, the silk-producing regions of Karnataka, and the jute-growing regions of West Bengal and Bihar are the major sources of raw materials for the textile industry.
Proximity to Markets
Proximity to markets is a critical factor in the textile industry, as textiles are a highly perishable commodity. Regions with easy access to markets are ideal for textile production, as they ensure that the textiles can be transported quickly and efficiently to the markets. The textile-producing regions of Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Chennai are located near major cities and towns, which act as major textile markets in India.
Availability of Skilled Labor
The textile industry requires a significant amount of skilled labor for various tasks such as spinning, weaving, dyeing, and printing. Regions with access to a large pool of skilled labor are ideal for textile production. In India, regions such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu have a long history of textile production and have a large pool of skilled workers.
Transportation Infrastructure
The transportation infrastructure also plays a crucial role in the textile industry. Regions with well-developed transportation networks, such as railways, roads, and ports, are ideal for textile production. The textile-producing regions of Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Surat, Coimbatore, and Tirupur are located near major transportation hubs in India.
Government Policies
The government policies, such as incentives and subsidies, play a key role in the growth and success of the textile industry. The government policies related to taxation, labor laws, and infrastructure development have a significant impact on the textile industry. In India, the government has taken various steps to promote the growth of the textile industry, such as the Textile Upgradation Fund Scheme (TUFS), which provides financial assistance for modernizing the textile industry.
In conclusion, the textile industry in India is influenced by a number of locational factors, including availability of raw materials, proximity to markets, availability of skilled labor, transportation infrastructure, and government policies. Understanding these factors is essential for the success and growth of textile production and trade in India.
Read: Geography Notes