Evaporation and condensation are two vital processes in the water cycle that have a significant impact on our daily lives. Understanding these processes can help us better manage our water resources, predict weather patterns, and address issues such as drought and climate change.
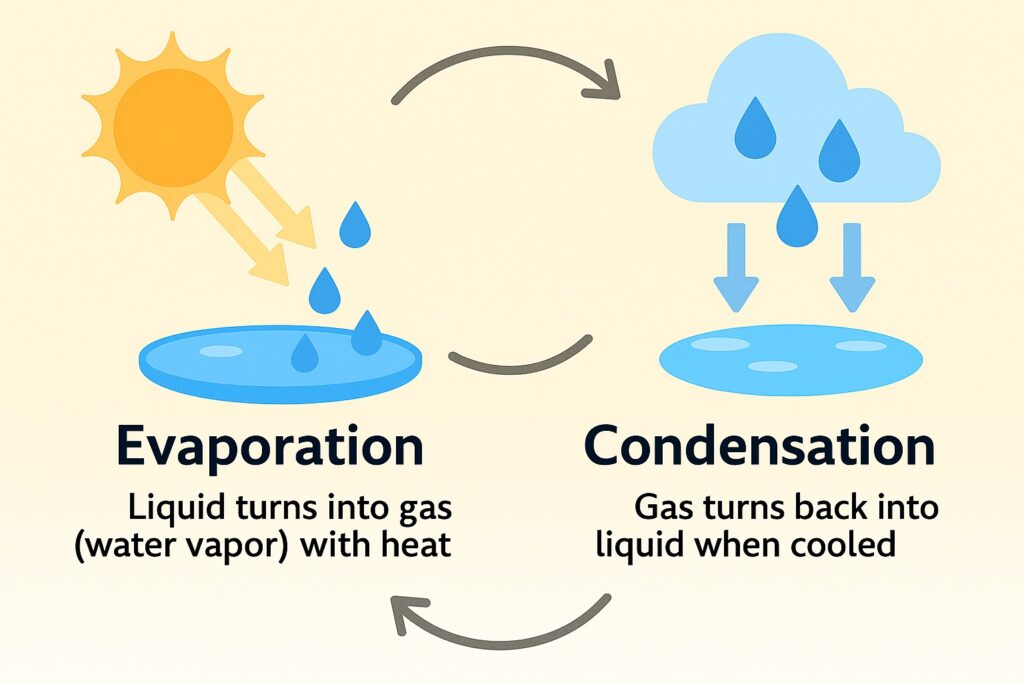
Table of Contents
What is Evaporation?
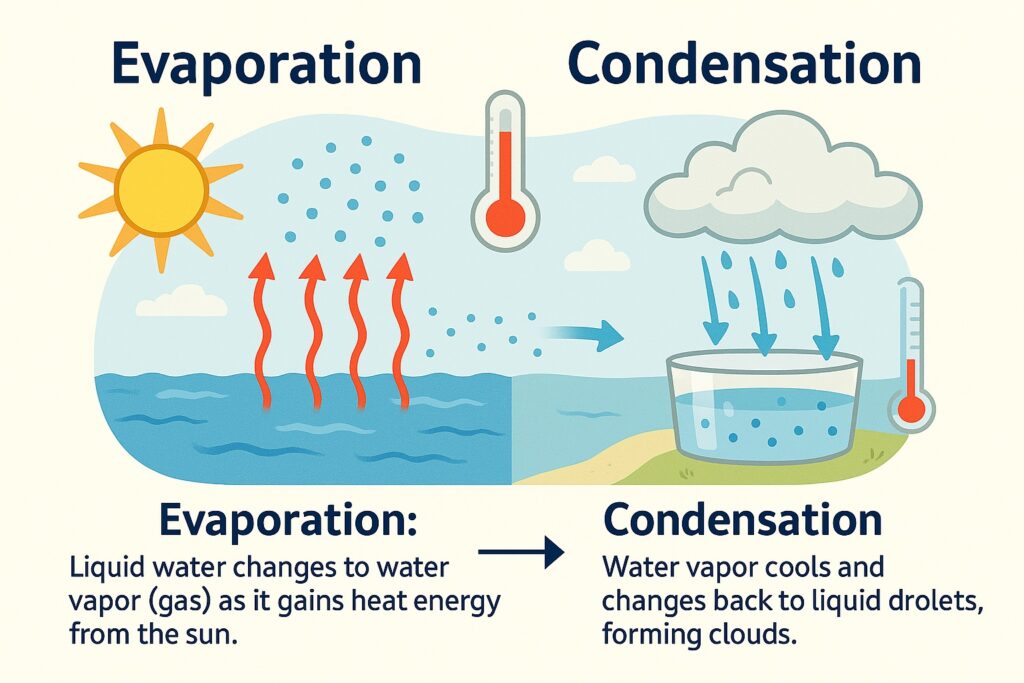
Evaporation is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gaseous state. It occurs when water molecules absorb enough energy from their surroundings to break free from the liquid surface and become water vapor. This energy can come from various sources, including heat from the sun, wind, and warm air.
Things that affect how fast evaporation happens:
- Temperature
- Humidity of the air
- Wind speed
- Surface area exposed
- Atmospheric pressure
Evaporation takes place in many different environments, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and even in our bodies. In fact, our bodies rely on evaporation to regulate our internal temperature. When we sweat, the moisture on our skin evaporates, cooling us down.
Evaporation also plays a crucial role in the water cycle. As water evaporates from bodies of water, it enters the atmosphere and forms clouds. These clouds eventually release their moisture as precipitation, which falls back to the earth’s surface and replenishes the water supply.
Factors that Influence Evaporation
Several factors can influence the rate of evaporation, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and surface area. As the temperature increases, the rate of evaporation also increases. However, if the air is already saturated with moisture, evaporation will be slower.
Wind speed can also affect the rate of evaporation. When the air is moving faster, it can carry moisture away from the surface, leading to a faster rate of evaporation. Additionally, the surface area of the water can impact the rate of evaporation, with larger surface areas leading to higher rates.
What is Condensation?
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state. It occurs when the water vapor molecules lose energy and slow down enough to come together and form liquid droplets.
Condensation is a common occurrence in our daily lives, often seen on the surface of cold beverages or on bathroom mirrors after a hot shower. In the atmosphere, condensation plays a vital role in cloud formation and precipitation.
As water vapor rises into the atmosphere, it cools down, causing the water vapor molecules to slow down and come together to form clouds. These clouds can eventually release their moisture as precipitation, which falls back to the earth’s surface.
Factors that Influence Condensation
Several factors can influence the rate of condensation, including temperature, humidity, and air pressure. As the temperature decreases, the rate of condensation increases. Additionally, if the air is already saturated with moisture, the rate of condensation will be higher.
Air pressure can also affect the rate of condensation. When the air pressure decreases, the temperature also decreases, leading to a higher rate of condensation. Humidity also plays a crucial role in the rate of condensation, with higher humidity levels leading to higher rates.
Evaporation vs. Condensation
Evaporation and condensation are two opposite processes that work together in the water cycle. While evaporation converts liquid water into water vapor, condensation converts water vapor back into liquid water.
Evaporation and condensation are both influenced by temperature, humidity, and air pressure, but they occur under different circumstances. Evaporation typically occurs at the surface of bodies of water, while condensation occurs in the upper atmosphere.
Both evaporation and condensation play a crucial role in the water cycle, ensuring that water is continuously cycled through the environment. Without these processes, the earth would be unable to sustain life as we know it.
Applications of Evaporation and Condensation
Evaporation and condensation have many practical applications, including in the fields of agriculture, energy production, and weather forecasting.
Additionally, evaporation is used in the production of various products, such as sea salt and essential oils. In the case of sea salt production, seawater is pumped into large shallow pools and allowed to evaporate under the sun, leaving behind salt crystals.
In energy production, evaporation is used in the process of generating electricity. In power plants, steam is produced by boiling water, which is then used to turn turbines and generate electricity.
Condensation is also used in various applications, such as in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. These systems work by compressing and expanding gases, which causes them to cool and release heat. This cooling process leads to the condensation of water vapor, which is then drained away.
Weather forecasting relies heavily on the processes of evaporation and condensation. By studying the patterns of evaporation and condensation, meteorologists can predict weather patterns, including the formation of clouds and the likelihood of precipitation.
Evaporation and Condensation : Differences
| Evaporation | Condensation | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor at the surface of the liquid | The process by which water vapor changes into a liquid or solid |
| Temperature | Occurs at any temperature above the boiling point of the liquid | Occurs at a temperature below the boiling point of the vapor |
| Energy | Evaporation requires heat or energy to change the state of water from a liquid to a gas or vapor | Condensation releases heat or energy when the water vapor changes back to a liquid or solid |
| Humidity | High humidity levels inhibit the rate of evaporation | High humidity levels promote the rate of condensation |
| Occurrence | Occurs naturally in the water cycle and in various human-made processes | Occurs naturally in the atmosphere and in various human-made processes |
| Importance | Plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate and in various practical applications, such as agriculture and energy production | Plays a crucial role in the formation of clouds, weather patterns, and in various practical applications, such as air conditioning and refrigeration |
| Examples | Drying clothes on a clothesline, boiling water, sweat evaporating from skin, and sea salt production | Dew forming on grass in the morning, fog forming in the air, and water droplets forming on a cold drink |
Overall, while evaporation and condensation are opposite processes, they are both crucial in regulating Earth’s climate and have various practical applications. Understanding the differences and similarities between these processes can help us better manage our water resources and address issues related to climate change.
Read: Geography Notes